From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/nehalem (client)"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
'''Nehalem''' was the [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[45 nm process]] for desktops and servers as a successor to {{\\|Penryn}}. Nehalem is named after the [[wikipedia:Nehalem River|Nehalem River]]. Nehalem was replaced by the {{\\|Westmere}} microarchitecture in 2010. | '''Nehalem''' was the [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[45 nm process]] for desktops and servers as a successor to {{\\|Penryn}}. Nehalem is named after the [[wikipedia:Nehalem River|Nehalem River]]. Nehalem was replaced by the {{\\|Westmere}} microarchitecture in 2010. | ||
[[File:Nehalem.jpg|right|thumb|300px|Nehalem wafer]] | [[File:Nehalem.jpg|right|thumb|300px|Nehalem wafer]] | ||
| + | |||
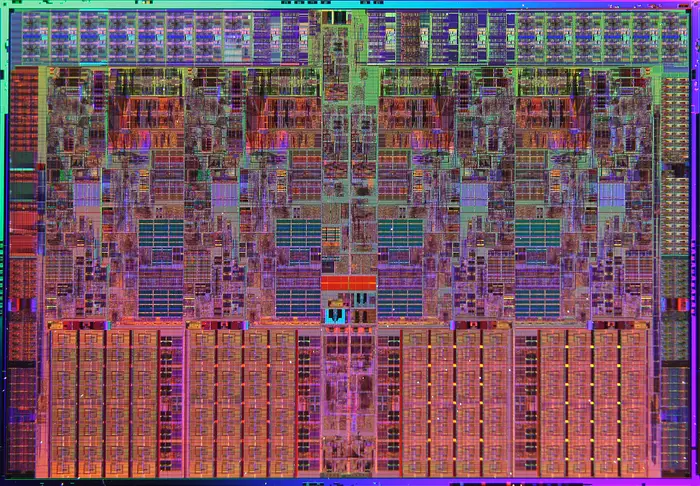
| + | == Die Shot == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Quad-core ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[File:nehalem die shot.png|700px]] | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 30 April 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Nehalem µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | August, 2008 |
| Phase-out | March, 2010 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Succession | |
Nehalem was the microarchitecture for Intel's 45 nm process for desktops and servers as a successor to Penryn. Nehalem is named after the Nehalem River. Nehalem was replaced by the Westmere microarchitecture in 2010.
Die Shot
Quad-core
Facts about "Nehalem - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Nehalem + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | August 2008 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/nehalem (client) + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Nehalem + |
| phase-out | March 2010 + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |