From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/ivy bridge (client)"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
'''Ivy Bridge''' was [[Intel]]'s [[microarchitecture]] based on the [[22 nm process]] for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a [[process shrink]] of {{\\|Sandy Bridge}} which introduced a number enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use [[tri-gate transistor]]s for their commercial products. | '''Ivy Bridge''' was [[Intel]]'s [[microarchitecture]] based on the [[22 nm process]] for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a [[process shrink]] of {{\\|Sandy Bridge}} which introduced a number enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use [[tri-gate transistor]]s for their commercial products. | ||
| + | For desktop and mobile, Ivy Bridge is branded as 3th Generation Intel {{intel|Core}} processors. For single-socket servers, Intel branded it as {{intel|Xeon E3|Xeon E3 v2}}. | ||
== Codenames == | == Codenames == | ||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 21 April 2016
| Edit Values | |
| Ivy Bridge µarch | |
| General Info |
Ivy Bridge was Intel's microarchitecture based on the 22 nm process for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a process shrink of Sandy Bridge which introduced a number enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use tri-gate transistors for their commercial products.
For desktop and mobile, Ivy Bridge is branded as 3th Generation Intel Core processors. For single-socket servers, Intel branded it as Xeon E3 v2.
Codenames
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Architecture
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
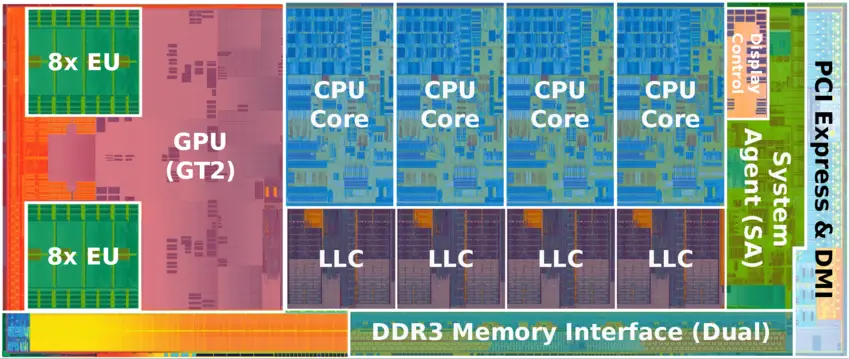
Die
Quad-core Ivy Bridge die:
- 1,480,000,000 transistors
- 160 mm2
- 4 CPU cores
- 1 GPU core
- 2x8xEU (64 ALUs)
- 22 nm process
Cores
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
All Ivy Bridge Chips
| Ivy Bridge Chips | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | IGP | ||||||||||
| Model | µarch | Platform | Core | Launched | SDP | TDP | Freq | Max Mem | Name | Freq | Max Freq |
| 1007U | Ivy Bridge | Ivy Bridge | 20 January 2013 | 17 W 17,000 mW 0.0228 hp 0.017 kW | 1,500 MHz 1.5 GHz 1,500,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i7-3770K | Ivy Bridge | Ivy Bridge-HE-4 | 23 April 2012 | 77 W 77,000 mW 0.103 hp 0.077 kW | 3,500 MHz 3.5 GHz 3,500,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i7-3920XM | Ivy Bridge | Panther Point | Ivy Bridge | 28 April 2012 | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 2,900 MHz 2.9 GHz 2,900,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,300 MHz 1.3 GHz 1,300,000 KHz | |
| i7-3940XM | Ivy Bridge | Panther Point | Ivy Bridge | 30 September 2012 | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 3,000 MHz 3 GHz 3,000,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,350 MHz 1.35 GHz 1,350,000 KHz | |
| i7-4960X | Ivy Bridge | X79 | Ivy Bridge E | 10 September 2013 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 3,600 MHz 3.6 GHz 3,600,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | ||||