(→Block Diagram) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
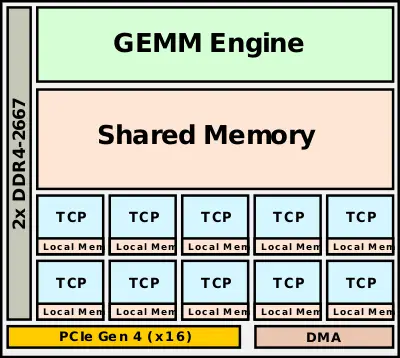
| − | + | Goya is designed as a microarchitecture for the [[acceleration]] of inference. Since the target market is the data center, the [[thermal design point]] for those chips was relatively high - at around 200 W. The design uses a heterogenous approach comprising of a large General Matrix Multiply (GMM) engine, Tensor | |
| + | Processor Cores (TPCs), and a large shared memory pool. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are eight TPCs. Each TPC also incorporates its own local memory but omits caches. Each core is a [[VLIW]] DSP design that has been optimized for AI applications. This includes [[AI]]-specific [[instructions]] and operations. The TPCs are designed for flexibility and can be programmed in plain [[C]]. The TPC supports mixed-prevision operations including 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit SIMD vector operations for both [[integer]] and [[floating-point]]. This was done in order to allow accuracy loss tolerance to be controlled on a per-model design by the programmer. Goya offers both coarse-grained precision control and fine-grained down to the tensor level. | ||
| + | |||
== Scalability == | == Scalability == | ||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
Revision as of 11:18, 28 December 2019
| Edit Values | |
| Goya µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | NPU |
| Designer | Habana |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | 2018 |
| Process | 16 nm |
| PE Configs | 8 |
| Contemporary | |
| Gaudi | |
Goya is a 16-nanometer microarchitecture for inference neural processors designed by Habana Labs.
Process Technology
Goya-based processors are fabricated on TSMC 16-nanometer process.
Architecture
Block Diagram
Overview
Goya is designed as a microarchitecture for the acceleration of inference. Since the target market is the data center, the thermal design point for those chips was relatively high - at around 200 W. The design uses a heterogenous approach comprising of a large General Matrix Multiply (GMM) engine, Tensor Processor Cores (TPCs), and a large shared memory pool.
There are eight TPCs. Each TPC also incorporates its own local memory but omits caches. Each core is a VLIW DSP design that has been optimized for AI applications. This includes AI-specific instructions and operations. The TPCs are designed for flexibility and can be programmed in plain C. The TPC supports mixed-prevision operations including 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit SIMD vector operations for both integer and floating-point. This was done in order to allow accuracy loss tolerance to be controlled on a per-model design by the programmer. Goya offers both coarse-grained precision control and fine-grained down to the tensor level.
Scalability
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
See also
| codename | Goya + |
| designer | Habana + |
| first launched | 2018 + |
| full page name | habana/microarchitectures/goya + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| name | Goya + |
| process | 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) + |
| processing element count | 8 + |