| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The chip is named after the Loihi as a play-on-words - [[wikipedia:Lōʻihi Seamount|Loihi]] is an emerging Hawaiian submarine volcano that is set to surface one day. | The chip is named after the Loihi as a play-on-words - [[wikipedia:Lōʻihi Seamount|Loihi]] is an emerging Hawaiian submarine volcano that is set to surface one day. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | Announced in September 2017, Loihi is predominantly a research chip meaning performance characteristics are not guaranteed. Loihi consists of a asynchronous [[spiking neural network]] (SNN) meaning instead of manipulating signals, the chip sends spikes along activate synapses. Connections are asynchronous and highly timed based. Neuromorphic cores containing many neurons are interlinked and receive spikes from elsewhere in the network. When received spikes accumulate for a certain period of time and reach a set threshold, the core will fire off its own spikes to its connected neurons. Preceding spikes reinforce each other and the neuron connections while spikes that follows will inhibit the connection, declining the connectivity until all activities are halted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === architecture === | ||
| + | The chip itself implements of a fully asynchronous [[many-core]] [[mesh topology|mesh]] of 128 neuromorphic cores. The network supports a wide variety of [[artificial neural network]] such as [[recurrent neural network|RNNs]], [[sparse neural network|SNN]], sparse, hierarchical, and various other topologies where each neuron in the chip is capable of communicating with 1000s of other neurons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are 128 neuromorphic cores, each containing a "learning engine" that can be programmed to adopt to the network parameters during operation such as the spike timings and their impact. This makes the chip more flexible as it allows various paradigms such as supervisor/non-supervisor and reinforcing/reconfigurablity without requiring any particular approach. The choice for higher flexibility is intentional in order to defer various architectural decisions that could be detrimental to research. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The chip was initially tested and simulated using FPGAs. Actual silicon implementations arrived in late November. Loihi is fabricated on Intel's [[14 nm process]] and has a total of 130,000 artificial neurons and 130 million synapses. | ||
| + | |||
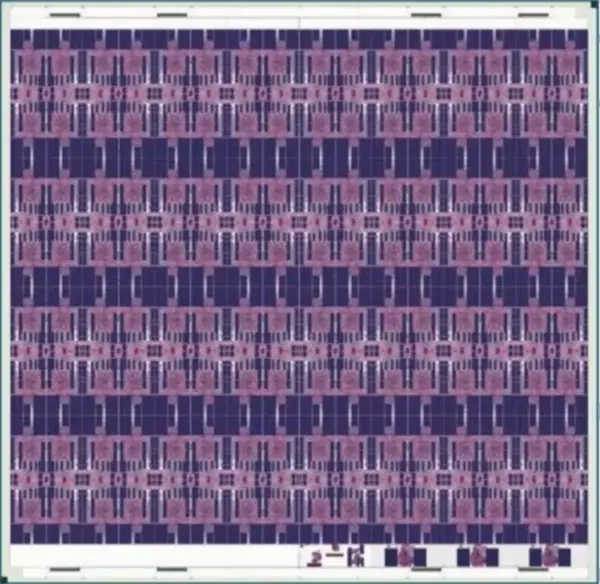
| + | === Floorplan === | ||
| + | * [[14 nm process]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:loihi floorplan.png|600px]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director Emerging Technologies Research, Intel Labs, HPC Developer Conference 2017 ("Leading The Evolution of Compute: Neuromorphic and Quantum Computing"). | * Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director Emerging Technologies Research, Intel Labs, HPC Developer Conference 2017 ("Leading The Evolution of Compute: Neuromorphic and Quantum Computing"). | ||
Revision as of 02:04, 29 November 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Loihi | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Market | Artificial Intelligence |
| Introduction | September 25, 2017 (announced) |
| Shop | Amazon |
| Microarchitecture | |
| Process | 14 nm |
Loihi (pronounced low-ee-hee) is a neuromorphic research test chip designed by Intel Labs that uses a asynchronous spiking neural network (SNN) to implement adaptive self-modifying event-driven fine-grained parallel computations used to implement learning and inference with high efficiency.
The chip is named after the Loihi as a play-on-words - Loihi is an emerging Hawaiian submarine volcano that is set to surface one day.
Overview
Announced in September 2017, Loihi is predominantly a research chip meaning performance characteristics are not guaranteed. Loihi consists of a asynchronous spiking neural network (SNN) meaning instead of manipulating signals, the chip sends spikes along activate synapses. Connections are asynchronous and highly timed based. Neuromorphic cores containing many neurons are interlinked and receive spikes from elsewhere in the network. When received spikes accumulate for a certain period of time and reach a set threshold, the core will fire off its own spikes to its connected neurons. Preceding spikes reinforce each other and the neuron connections while spikes that follows will inhibit the connection, declining the connectivity until all activities are halted.
architecture
The chip itself implements of a fully asynchronous many-core mesh of 128 neuromorphic cores. The network supports a wide variety of artificial neural network such as RNNs, SNN, sparse, hierarchical, and various other topologies where each neuron in the chip is capable of communicating with 1000s of other neurons.
There are 128 neuromorphic cores, each containing a "learning engine" that can be programmed to adopt to the network parameters during operation such as the spike timings and their impact. This makes the chip more flexible as it allows various paradigms such as supervisor/non-supervisor and reinforcing/reconfigurablity without requiring any particular approach. The choice for higher flexibility is intentional in order to defer various architectural decisions that could be detrimental to research.
The chip was initially tested and simulated using FPGAs. Actual silicon implementations arrived in late November. Loihi is fabricated on Intel's 14 nm process and has a total of 130,000 artificial neurons and 130 million synapses.
Floorplan
References
- Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director Emerging Technologies Research, Intel Labs, HPC Developer Conference 2017 ("Leading The Evolution of Compute: Neuromorphic and Quantum Computing").
| back image |  + + |
| core voltage (max) | 1.25 V (12.5 dV, 125 cV, 1,250 mV) + |
| core voltage (min) | 0.5 V (5 dV, 50 cV, 500 mV) + |
| designer | Intel + |
| die area | 60 mm² (0.093 in², 0.6 cm², 60,000,000 µm²) + |
| first announced | September 25, 2017 + |
| first launched | January 2018 + |
| full page name | intel/loihi + |
| instance of | neuromorphic chip + |
| ldate | January 2018 + |
| main image |  + + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| market segment | Artificial Intelligence + |
| max cpu count | 16,384 + |
| name | Loihi + |
| neuron count | 131,072 + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |
| smp max ways | 16,384 + |
| synapse count | 130,000,000 + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| transistor count | 2,070,000,000 + |