From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "amd/microarchitectures/piledriver"
m (Minor mod) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| phase-out = | | phase-out = | ||
| process = 32 nm | | process = 32 nm | ||
| + | |isa=x86-64 | ||
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 30 November 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Piledriver µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | AMD |
| Introduction | May 15, 2012 |
| Process | 32 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
Piledriver was the microarchitecture developed by AMD as a successor to Bulldozer. In 2014, Steamroller superseded Bulldozer.
Architecture
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
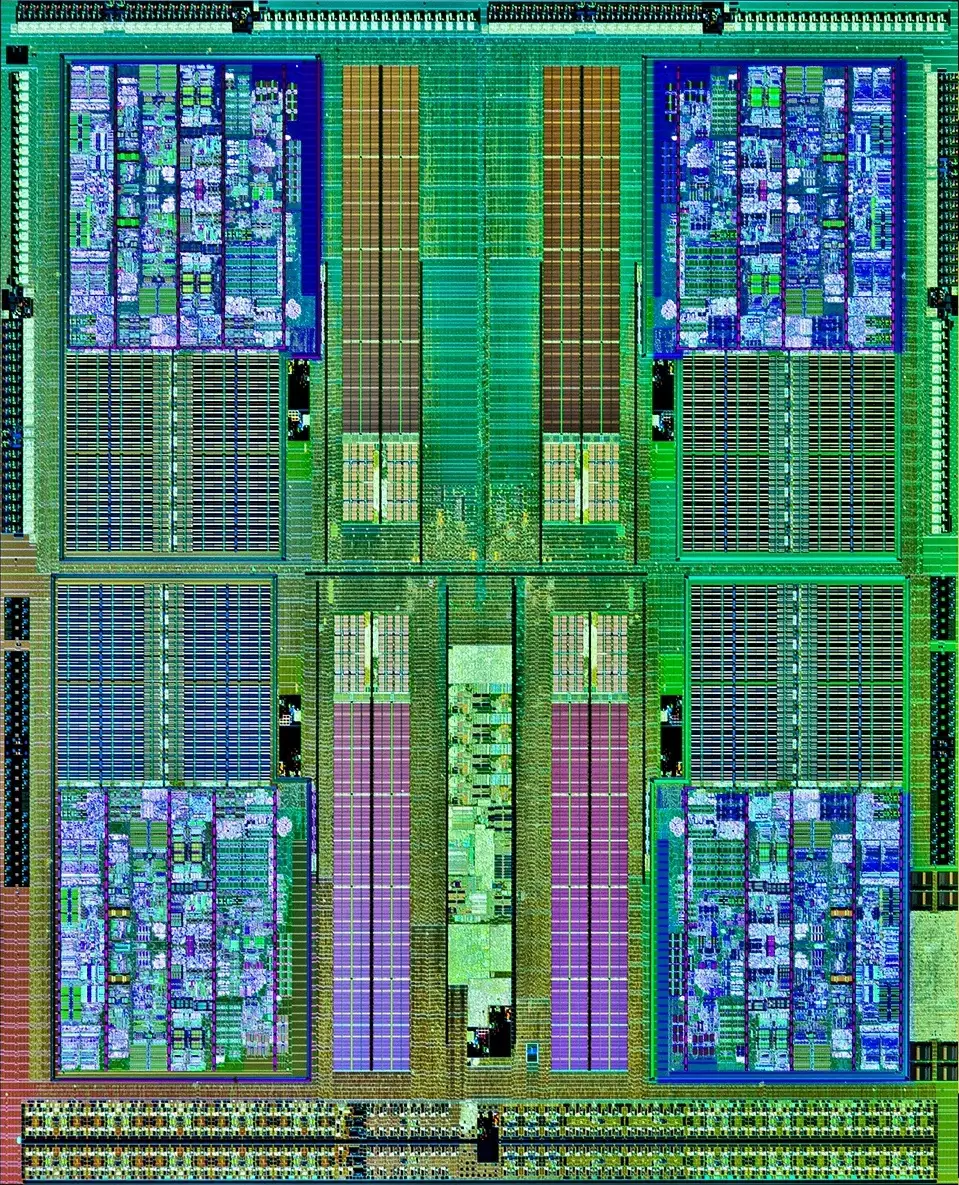
Die Shot
All Piledriver Chips
| Piledriver Chips | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Family | Core | Launched | Power Dissipation | Freq | Max Mem |
| Count: 0 | ||||||
See also
Facts about "Piledriver - Microarchitectures - AMD"
| codename | Piledriver + |
| core count | 2 +, 4 +, 6 +, 8 +, 12 + and 16 + |
| designer | AMD + |
| first launched | May 15, 2012 + |
| full page name | amd/microarchitectures/piledriver + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | AMD + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Piledriver + |
| phase-out | 2014 + |
| process | 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) + |