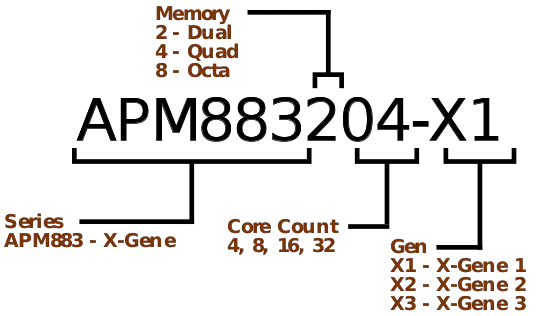(→X-Gene 1) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
| − | | predecessor = | + | | predecessor = PACKETPro |
| − | | predecessor link = | + | | predecessor link = apm/packetpro |
| successor = eMAG | | successor = eMAG | ||
| successor link = ampere computing/emag | | successor link = ampere computing/emag | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | X-Gene was a family of high-performance multi-core ARM microprocessors first announced by [[AppliedMicro]] in 2011. Unlike their traditional product offering, X-Gene directly targeted high-performance data center servers, a market predominantly dominated by [[Intel]] {{intel|Xeon}} processors. AppliedMicro introduced two generations of server processors based on their own custom [[ARM]] microarchitectures - {{apm|Storm|l=arch}} and {{apm|Shadowcat|l=arch}}. Those two generations shipped a total of 25,000 units. In late [[2016]], [[MACOM]] acquired AppliedMicro resulting in the shelving of third-generation X-Gene based on the {{apm| | + | X-Gene was a family of high-performance multi-core ARM microprocessors first announced by [[AppliedMicro]] in 2011. Unlike their traditional product offering, X-Gene directly targeted high-performance data center servers, a market predominantly dominated by [[Intel]] {{intel|Xeon}} processors. AppliedMicro introduced two generations of server processors based on their own custom [[ARM]] microarchitectures - {{apm|Storm|l=arch}} and {{apm|Shadowcat|l=arch}}. Those two generations shipped a total of 25,000 units. In late [[2016]], [[MACOM]] acquired AppliedMicro resulting in the shelving of third-generation X-Gene based on the {{apm|Skylark|l=arch}} microarchitecture. The X-Gene [[intellectual property]] including most of the design team was eventually sold to [[Ampere Computing]] has rebranded the design and improved on it under the {{ampere|eMAG}} brand. |
| + | |||
| + | === Naming Scheme === | ||
| + | :[[File:appliedmicro x-gene naming.svg|550px]] | ||
== Members == | == Members == | ||
| Line 53: | Line 56: | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{comp table start}} | {{comp table start}} | ||
| − | <table class="comptable sortable | + | <table class="comptable sortable tc2 tc3 tc3 tc7"> |
| − | {{comp table header|main| | + | {{comp table header|main|7:List of Storm-based Processors}} |
| − | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Cores|% | + | {{comp table header|main|5:Processor|2:Memory}} |
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|TDP|Cores|%Turbo|L3$|Type|Chans}} | ||
{{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Storm]] | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Storm]] | ||
|?full page name | |?full page name | ||
|?model number | |?model number | ||
|?first launched | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
|?core count | |?core count | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency#GHz | ||
|?l3$ size | |?l3$ size | ||
| − | |? | + | |?supported memory type |
|?max memory channels | |?max memory channels | ||
|format=template | |format=template | ||
|template=proc table 3 | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| − | |userparam= | + | |userparam=9 |
|mainlabel=- | |mainlabel=- | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 80: | ||
=== X-Gene 2 === | === X-Gene 2 === | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{see also|apm/microarchitectures/shadowcat|l1=Shadowcat microarchitecture}} |
| + | Second-generation of X-Gene processors were announced in September 2014 and later launched in early 2015. X-Gene 2 processors are based on the {{apm|Shadowcat|l=arch}} microarchitecture and were fabricated on [[TSMC]]'s [[28 nm process]]. Though those processors were more of a refresh over their predecessor, the new [[process technology]] produced lower-power chips at similar performance. Those processors had up to four memory channels and up to [[eight cores]] operating at up to 2.4 GHz. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Mem:''' up to 4 memory channels, DDR3 @ up to 1866 MT/s | ||
| + | * '''Tech:''' [[ARMv8]] (ARMv8.0-A) | ||
| + | * '''I/O:''' 17 PCIe, SATA/SGMII, 2x SGMII/XFI, 1x RGMII | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc2 tc3 tc4 tc8"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|7:List of Shadowcat-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|5:Processor|2:Memory}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|TDP|Cores|%Turbo|L3$|Type|Chans}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Shadowcat]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory channels | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=9 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Shadowcat]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
=== X-Gene 3 === | === X-Gene 3 === | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{see also|apm/microarchitectures/skylark|l1=Skylark microarchitecture}} |
| + | Third-generation of X-Gene processors were announced in 2016 and started sampling in 2017. X-Gene 3 processors are based on the {{apm|Skylark|l=arch}} microarchitecture and were fabricated on [[TSMC]]'s [[16 nm process]]. AppliedMicro made large changed to the system architecture of the chip and some minor changes to the core. The chip design shifted from incorporating an array of accelerators on-die to offering a large set of I/O (mostly PCIe lanes) so that high-performance [[PCIe]]-based [[accelerators]] could be attached instead. In 2017 AppliedMicro sold the X-Gene assets to [[Ampere Computing]] and consequently discontinued the X-Gene line. X-Gene 3 has re-launched by Ampere under the {{ampere|eMAG}} family. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Mem:''' 8x DDR4 channels, up to 2666 MT/s with ECC; 1 TiB/socket | ||
| + | * '''I/O:''' 42 PCIe Gen 3 lanes | ||
| + | * '''TDP:''' Up to 125 W | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc2 tc3 tc4 tc8"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|7:List of Skylark-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|5:Processor|2:Memory}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|TDP|Cores|%Turbo|L3$|Type|Chans}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Skylark]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory channels | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=9 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by appliedmicro]] [[microarchitecture::Skylark]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| Line 84: | Line 162: | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
| + | * AppliedMicro. (October 30, 2013). ''"[https://www.apm.com/news/appliedmicro-announces-general-availability-of-x-gene-system-development-ki/ AppliedMicro Announces General Availability of X-Gene System Development Kit for ARM 64-Bit Platform]"''. | ||
| + | * AppliedMicro. (March 08, 2017). ''"[https://www.apm.com/news/macom-announces-sampling-of-x-gene-3-server-on-a-chip-solution/ MACOM Announces Sampling of X-Gene® 3 Server-on-a-Chip® Solution]"''. | ||
* David Schor. (February 5, 2018). "''[https://fuse.wikichip.org/news/776/x-gene-3-gets-a-second-chance-at-ampere-with-a-new-32-core-16nm-arm-processor/ X-Gene 3 gets a second chance at Ampere with a new 32-core 16nm ARM processor]''". | * David Schor. (February 5, 2018). "''[https://fuse.wikichip.org/news/776/x-gene-3-gets-a-second-chance-at-ampere-with-a-new-32-core-16nm-arm-processor/ X-Gene 3 gets a second chance at Ampere with a new 32-core 16nm ARM processor]''". | ||
Latest revision as of 01:25, 26 January 2021
| X-Gene | |

| |
| Developer | AppliedMicro |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Type | Microprocessors |
| Introduction | October 28, 2011 (announced) 2012 (launch) |
| ISA | ARM |
| µarch | Storm, Shadowcat, Skylark |
| Word size | 64 bit 8 octets
16 nibbles |
| Process | 40 nm 0.04 μm , 28 nm4.0e-5 mm 0.028 μm , 16 nm2.8e-5 mm 0.016 μm
1.6e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 2.4 GHz-3.3 GHz |
| Succession | |
| ← | → |
| PACKETPro | eMAG |
X-Gene was a family of 64-bit ARM server microprocessors designed and introduced by AppliedMicro.
Contents
Overview[edit]
X-Gene was a family of high-performance multi-core ARM microprocessors first announced by AppliedMicro in 2011. Unlike their traditional product offering, X-Gene directly targeted high-performance data center servers, a market predominantly dominated by Intel Xeon processors. AppliedMicro introduced two generations of server processors based on their own custom ARM microarchitectures - Storm and Shadowcat. Those two generations shipped a total of 25,000 units. In late 2016, MACOM acquired AppliedMicro resulting in the shelving of third-generation X-Gene based on the Skylark microarchitecture. The X-Gene intellectual property including most of the design team was eventually sold to Ampere Computing has rebranded the design and improved on it under the eMAG brand.
Naming Scheme[edit]
Members[edit]
X-Gene 1[edit]
- See also: Storm microarchitecture
First-generation of X-Gene processors were announced in October 2011 and later launched in late 2012. X-Gene 1 processors are based on the Storm microarchitecture and were fabricated on TSMC's 40 nm process. Those processors had up to four memory channels and up to eight cores operating at up to 2.4 GHz.
- Mem: up to 4 memory channels, DDR3 @ up to 1866 MT/s
- Tech: ARMv8 (ARMv8.0-A)
- I/O: 17 PCIe, SATA/SGMII, 2x SGMII/XFI, 1x RGMII
| List of Storm-based Processors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Memory | ||||||
| Model | Launched | TDP | Cores | Turbo | L3$ | Type | Chans |
| APM883204-X1 | 2012 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 4 | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | DDR3-1866 | 4 |
| APM883208-X1 | 2012 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 8 | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | DDR3-1866 | 2 |
| APM883408-X1 | 2012 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 8 | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | DDR3-1866 | 4 |
| Count: 3 | |||||||
X-Gene 2[edit]
- See also: Shadowcat microarchitecture
Second-generation of X-Gene processors were announced in September 2014 and later launched in early 2015. X-Gene 2 processors are based on the Shadowcat microarchitecture and were fabricated on TSMC's 28 nm process. Though those processors were more of a refresh over their predecessor, the new process technology produced lower-power chips at similar performance. Those processors had up to four memory channels and up to eight cores operating at up to 2.4 GHz.
- Mem: up to 4 memory channels, DDR3 @ up to 1866 MT/s
- Tech: ARMv8 (ARMv8.0-A)
- I/O: 17 PCIe, SATA/SGMII, 2x SGMII/XFI, 1x RGMII
| List of Shadowcat-based Processors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Memory | ||||||
| Model | Launched | TDP | Cores | Turbo | L3$ | Type | Chans |
| APM883208-X2 | March 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 8 | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | DDR3-1866 | 2 |
| APM883408-X2 | March 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 8 | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | DDR3-1866 | 4 |
| Count: 2 | |||||||
X-Gene 3[edit]
- See also: Skylark microarchitecture
Third-generation of X-Gene processors were announced in 2016 and started sampling in 2017. X-Gene 3 processors are based on the Skylark microarchitecture and were fabricated on TSMC's 16 nm process. AppliedMicro made large changed to the system architecture of the chip and some minor changes to the core. The chip design shifted from incorporating an array of accelerators on-die to offering a large set of I/O (mostly PCIe lanes) so that high-performance PCIe-based accelerators could be attached instead. In 2017 AppliedMicro sold the X-Gene assets to Ampere Computing and consequently discontinued the X-Gene line. X-Gene 3 has re-launched by Ampere under the eMAG family.
- Mem: 8x DDR4 channels, up to 2666 MT/s with ECC; 1 TiB/socket
- I/O: 42 PCIe Gen 3 lanes
- TDP: Up to 125 W
| List of Skylark-based Processors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Memory | ||||||
| Model | Launched | TDP | Cores | Turbo | L3$ | Type | Chans |
| APM883832-X3 | 125 W 125,000 mW 0.168 hp 0.125 kW | 32 | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 32 MiB 32,768 KiB 33,554,432 B 0.0313 GiB | DDR4-2666 DDR4-2400 | 8 | |
| Count: 1 | |||||||
See also[edit]
Bibliography[edit]
- AppliedMicro. (October 30, 2013). "AppliedMicro Announces General Availability of X-Gene System Development Kit for ARM 64-Bit Platform".
- AppliedMicro. (March 08, 2017). "MACOM Announces Sampling of X-Gene® 3 Server-on-a-Chip® Solution".
- David Schor. (February 5, 2018). "X-Gene 3 gets a second chance at Ampere with a new 32-core 16nm ARM processor".
| designer | AppliedMicro + |
| first announced | October 28, 2011 + |
| first launched | 2012 + |
| full page name | apm/x-gene + |
| instance of | microprocessor family + |
| instruction set architecture | ARM + |
| main designer | AppliedMicro + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture | Storm +, Shadowcat + and Skylark + |
| name | X-Gene + |
| process | 40 nm (0.04 μm, 4.0e-5 mm) +, 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) + and 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |