(Created page with "{{princeton title|Piton}} '''Piton''' is a {{arch|64}} many-core microprocessor developed by Princeton's Parallel Computing Group and announced in August of 2016. The...") |
(Update name of OpenPiton page) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{princeton title|Piton}} | {{princeton title|Piton}} | ||
| − | '''Piton''' is a {{arch|64}} [[many-core microprocessor]] developed by [[Princeton]]'s Parallel Computing Group and announced in August of 2016. The [[massively parallel processor array|MPPA]] chip contains 25 modified [[OpenSPARC T1]] cores (an implementation of {{sparc|V9|SPARC V9}}). | + | {{chip |
| + | | name = Piton | ||
| + | | no image = | ||
| + | | image = Princeton piton.png | ||
| + | | image size = | ||
| + | | caption = Piton face | ||
| + | | designer = Princeton | ||
| + | | manufacturer = IBM | ||
| + | | model number = | ||
| + | | part number = | ||
| + | | market = Server | ||
| + | | first announced = August 23, 2016 | ||
| + | | first launched = | ||
| + | | last order = | ||
| + | | last shipment = | ||
| + | |||
| + | | family = | ||
| + | | series = | ||
| + | | locked = | ||
| + | | frequency = 1000 MHz | ||
| + | | bus type = | ||
| + | | bus speed = 350 MHz | ||
| + | | bus rate = 2,800 MT/s | ||
| + | | clock multiplier = 2.85 | ||
| + | | cpuid = | ||
| + | | cpuid 2 = | ||
| + | |||
| + | | microarch = | ||
| + | | platform = | ||
| + | | chipset = | ||
| + | | core name = | ||
| + | | core family = | ||
| + | | core model = | ||
| + | | core stepping = | ||
| + | | process = 32 nm | ||
| + | | transistors = 460,000,000 | ||
| + | | technology = CMOS | ||
| + | | die area = 36 mm² | ||
| + | | die width = 6 mm | ||
| + | | die length = 6 mm | ||
| + | | word size = 64 bit | ||
| + | | core count = 25 | ||
| + | | thread count = 50 | ||
| + | | max cpus = 20,000 | ||
| + | | max memory = | ||
| + | | max memory addr = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | | power = | ||
| + | | v core = 0.9 V | ||
| + | | v core tolerance = | ||
| + | | v io = | ||
| + | | v io tolerance = | ||
| + | | sdp = | ||
| + | | tdp = | ||
| + | | ctdp down = | ||
| + | | ctdp down frequency = | ||
| + | | ctdp up = | ||
| + | | ctdp up frequency = | ||
| + | | temp min = | ||
| + | | temp max = | ||
| + | | tjunc min = | ||
| + | | tjunc max = | ||
| + | | tcase min = | ||
| + | | tcase max = | ||
| + | | tstorage min = | ||
| + | | tstorage max = | ||
| + | |||
| + | | packaging = Yes | ||
| + | | package 0 = QFP-208 | ||
| + | | package 0 type = QFP | ||
| + | | package 0 pins = 208 | ||
| + | | package 0 pitch = 0.5 mm | ||
| + | | package 0 width = 30.60 mm | ||
| + | | package 0 length = 30.60 mm | ||
| + | | package 0 height = 3.75 mm | ||
| + | | socket 0 = QFP-208 | ||
| + | | socket 0 type = QFP | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Piton''' is a {{arch|64}} [[many-core microprocessor]] developed by [[Princeton]]'s Parallel Computing Group and announced in August of 2016. The [[massively parallel processor array|MPPA]] chip contains 25 modified [[OpenSPARC T1]] cores (an implementation of {{sparc|V9|SPARC V9}}). The chip, which was manufactured on [[IBM]]'s [[32 nm|32 nm SOI process]], operates at 1 GHz. The chip was presented in August 2016 at the [[Hot Chips]] 28. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Architecture == | ||
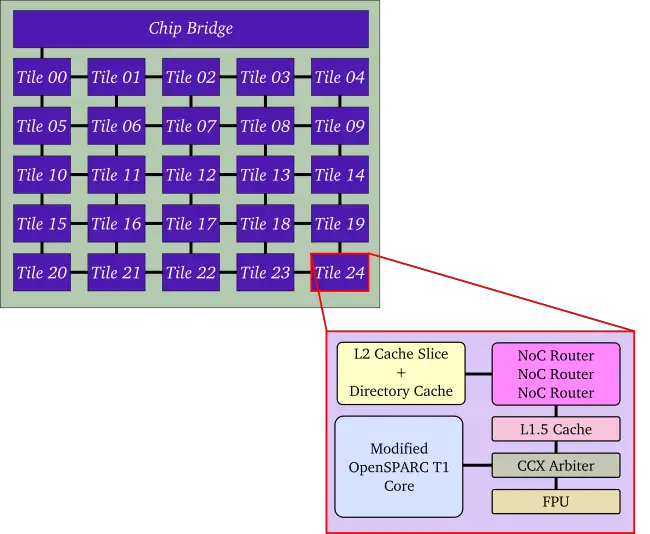
| + | The chip is designed as a [[massively parallel processor array]], with 25 cores ("tiles") arranged as a 2D grid of 5 by 5. Each core is a modified [[OpenSPARC T1]] which implements {{sparc|V9|SPARC V9}} capable of booting a standard [[operating system|OS]]. Piton implements a 64-bit [[network on chip]] (NoC) interconnect made of 3 physical networks operating with a 1 cycle/hop latency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:piton layout.svg|650px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Tiles === | ||
| + | Piton is made of an array of tiles in a grid of 5x5. Each tile is composed of a modified [[OpenSPARC T1]] core (+L1$), an L1.5 cache, L2 cache, a [[floating-point unit]] (FPU), a CPU Cache-Crossbar (CCX) arbiter, and three [[network on chip]] (NoC) routers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Cache ==== | ||
| + | Pitons uses a distributed write-back [[L2$]] model that implements a directory-based [[MESI protocol]] - adhering to OpenSPARC's total store order (TSO) model. Each tile contains 64 KB slice of the L2 cache and an attached cache directory. The L2 cache is inclusive of both the L1.5$ and the L1$. Note that the L1.5 is called as such because the [[OpenSPARC T1]] core already implements an 8 KB [[L1d$]] and 16 KB [[L1i$]] which are tightly coupled with the pipeline and was thus only modified to work in a scaleable multi-core environment. The L1.5$ acts as a middleman between the OpenSPARC T1's crossbar protocol and the Piton's NoC. It relays requests and replies to and from the core through CCX. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{cache info | ||
| + | |l1i cache= | ||
| + | |l1i break= | ||
| + | |l1i desc= | ||
| + | |l1i extra= | ||
| + | |l1d cache=200 KiB | ||
| + | |l1d break=25x8 KiB | ||
| + | |l1d desc=4-way set associative | ||
| + | |l1d extra=(write-back, per tile) | ||
| + | |l2 cache=1.5 MiB | ||
| + | |l2 break=25x64 KiB | ||
| + | |l2 desc=4-way set associative | ||
| + | |l2 extra=(per tile) | ||
| + | |l3 cache= | ||
| + | |l3 break= | ||
| + | |l3 desc=16-way set associative | ||
| + | |l3 extra= | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Network On-chip (NoC) == | ||
| + | Piton implements 3 physical [[networks on chip]] (NoC) that provide all the communication between the [[#tiles|tiles]], deliver I/O and memory traffic, and pass inter-core [[interrupt]]s. Piton implements 3 physical neworks - each consisting of two 64-bit uni-directional links (one in each direction). Packets routing implements [[dimension-order routing]]. Each packet reserves 29 bits for core address, allowing a theoretical network size of 500 million cores. The three NoCs have descending priorities - i.e. NoC3 has the highest priority, followed by NoC2, followed by NoC1 with the lowest priority. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Documents == | ||
| + | * Jonathan Balkind, Michael McKeown, Yaosheng Fu, Tri Nguyen, Yanqi Zhou, Alexey Lavrov, Mohammad Shahrad, Adi Fuchs, Samuel Payne, Xiaohua Liang, Matthew Matl, David Wentzlaff. [https://parallel.princeton.edu/papers/openpiton-asplos16.pdf OpenPiton: An open source manycore research framework]. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems 2016 Mar 25 (pp. 217-232). ACM. | ||
| + | * Michael McKeown, Yaosheng Fu, Tri Nguyen, Yanqi Zhou, Jonathan Balkind, Alexey Lavrov, Mohammad Shahrad, Samuel Payne, and David Wentzlaf. [http://parallel.princeton.edu/piton/piton_hotchips28_talk.pdf Piton: A 25-core Academic Manycore Research Processor] | ||
| + | * OpenPiton [http://parallel.princeton.edu/openpiton/docs/micro_arch.pdf OpenPiton Microarchitecture Specification]. Hot Chips 28. August 23, 2016. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == External links == | ||
| + | * [http://parallel.princeton.edu/piton/ Piton] | ||
| + | * [http://www.openpiton.org Open Piton] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{DEFAULTSORT: Piton}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:41, 5 July 2018
| Edit Values | |
| Piton | |
 | |
| Piton face | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Princeton |
| Manufacturer | IBM |
| Market | Server |
| Introduction | August 23, 2016 (announced) |
| General Specs | |
| Frequency | 1000 MHz |
| Bus speed | 350 MHz |
| Bus rate | 2,800 MT/s |
| Clock multiplier | 2.85 |
| Microarchitecture | |
| Process | 32 nm |
| Transistors | 460,000,000 |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Die | 36 mm² 6 mm × 6 mm |
| Word Size | 64 bit |
| Cores | 25 |
| Threads | 50 |
| Multiprocessing | |
| Max SMP | 20,000-Way (Multiprocessor) |
| Electrical | |
| Vcore | 0.9 V |
Piton is a 64-bit many-core microprocessor developed by Princeton's Parallel Computing Group and announced in August of 2016. The MPPA chip contains 25 modified OpenSPARC T1 cores (an implementation of SPARC V9). The chip, which was manufactured on IBM's 32 nm SOI process, operates at 1 GHz. The chip was presented in August 2016 at the Hot Chips 28.
Architecture[edit]
The chip is designed as a massively parallel processor array, with 25 cores ("tiles") arranged as a 2D grid of 5 by 5. Each core is a modified OpenSPARC T1 which implements SPARC V9 capable of booting a standard OS. Piton implements a 64-bit network on chip (NoC) interconnect made of 3 physical networks operating with a 1 cycle/hop latency.
Tiles[edit]
Piton is made of an array of tiles in a grid of 5x5. Each tile is composed of a modified OpenSPARC T1 core (+L1$), an L1.5 cache, L2 cache, a floating-point unit (FPU), a CPU Cache-Crossbar (CCX) arbiter, and three network on chip (NoC) routers.
Cache[edit]
Pitons uses a distributed write-back L2$ model that implements a directory-based MESI protocol - adhering to OpenSPARC's total store order (TSO) model. Each tile contains 64 KB slice of the L2 cache and an attached cache directory. The L2 cache is inclusive of both the L1.5$ and the L1$. Note that the L1.5 is called as such because the OpenSPARC T1 core already implements an 8 KB L1d$ and 16 KB L1i$ which are tightly coupled with the pipeline and was thus only modified to work in a scaleable multi-core environment. The L1.5$ acts as a middleman between the OpenSPARC T1's crossbar protocol and the Piton's NoC. It relays requests and replies to and from the core through CCX.
| Cache Info [Edit Values] | ||
| L1D$ | 200 KiB 204,800 B 0.195 MiB |
25x8 KiB 4-way set associative (write-back, per tile) |
| L2$ | 1.5 MiB 1,536 KiB 1,572,864 B 0.00146 GiB |
25x64 KiB 4-way set associative (per tile) |
Network On-chip (NoC)[edit]
Piton implements 3 physical networks on chip (NoC) that provide all the communication between the tiles, deliver I/O and memory traffic, and pass inter-core interrupts. Piton implements 3 physical neworks - each consisting of two 64-bit uni-directional links (one in each direction). Packets routing implements dimension-order routing. Each packet reserves 29 bits for core address, allowing a theoretical network size of 500 million cores. The three NoCs have descending priorities - i.e. NoC3 has the highest priority, followed by NoC2, followed by NoC1 with the lowest priority.
Documents[edit]
- Jonathan Balkind, Michael McKeown, Yaosheng Fu, Tri Nguyen, Yanqi Zhou, Alexey Lavrov, Mohammad Shahrad, Adi Fuchs, Samuel Payne, Xiaohua Liang, Matthew Matl, David Wentzlaff. OpenPiton: An open source manycore research framework. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems 2016 Mar 25 (pp. 217-232). ACM.
- Michael McKeown, Yaosheng Fu, Tri Nguyen, Yanqi Zhou, Jonathan Balkind, Alexey Lavrov, Mohammad Shahrad, Samuel Payne, and David Wentzlaf. Piton: A 25-core Academic Manycore Research Processor
- OpenPiton OpenPiton Microarchitecture Specification. Hot Chips 28. August 23, 2016.
External links[edit]
| base frequency | 1,000 MHz (1 GHz, 1,000,000 kHz) + |
| bus rate | 2,800 MT/s (2.8 GT/s, 2,800,000 kT/s) + |
| bus speed | 350 MHz (0.35 GHz, 350,000 kHz) + |
| clock multiplier | 2.85 + |
| core count | 25 + |
| core voltage | 0.9 V (9 dV, 90 cV, 900 mV) + |
| designer | Princeton + |
| die area | 36 mm² (0.0558 in², 0.36 cm², 36,000,000 µm²) + |
| die length | 6 mm (0.6 cm, 0.236 in, 6,000 µm) + |
| die width | 6 mm (0.6 cm, 0.236 in, 6,000 µm) + |
| first announced | August 23, 2016 + |
| full page name | princeton/piton + |
| instance of | microprocessor + |
| l1d$ description | 4-way set associative + |
| l1d$ size | 200 KiB (204,800 B, 0.195 MiB) + |
| l2$ description | 4-way set associative + |
| l2$ size | 1.5 MiB (1,536 KiB, 1,572,864 B, 0.00146 GiB) + |
| ldate | August 23, 2016 + |
| main image |  + + |
| main image caption | Piton face + |
| manufacturer | IBM + |
| market segment | Server + |
| max cpu count | 20,000 + |
| name | Piton + |
| process | 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) + |
| smp max ways | 20,000 + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| thread count | 50 + |
| transistor count | 460,000,000 + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |