m (→StorageBuilder) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| first launched = 2003 | | first launched = 2003 | ||
| production start = 2003 | | production start = 2003 | ||
| − | | production end = | + | | production end = 2006 |
| microarch = | | microarch = | ||
| word = 16 bit | | word = 16 bit | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| package = | | package = | ||
| socket = | | socket = | ||
| + | |||
| + | | succession = Yes | ||
| + | | predecessor = | ||
| + | | predecessor link = | ||
| + | | successor = Arrix | ||
| + | | successor link = mathstar/arrix | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Builder''' was a family of [[FPOA]]s introduced by [[MathStar]] in 2003. This family the earliest attempt at designing an FPOA and was discontinued shortly after due to some technical issues. | + | '''Builder''' was a family of [[FPOA]]s introduced by [[MathStar]] in 2003. This family the earliest attempt at designing an FPOA and was discontinued shortly after due to some technical issues. The Builder family was phased out entirely by 2006. |
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 33: | ||
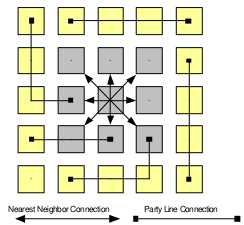
The Builder family was the MathStar's initial attempt at a [[field-programmable object array]]. Each chip contains 100s of silicon objects laid out in a grid, broken down to arrays of five objects each. Instructions are loaded to each of the objects at power-up. | The Builder family was the MathStar's initial attempt at a [[field-programmable object array]]. Each chip contains 100s of silicon objects laid out in a grid, broken down to arrays of five objects each. Instructions are loaded to each of the objects at power-up. | ||
| − | |||
Inter-Object communication was done primarily by passing data to the nearest neighbor through a unidirectional synchronous interconnect. Communication is configured dynamically and on-demand. Each object had the facilities needed for clock synchronization, [[built-in self-test]], etc... | Inter-Object communication was done primarily by passing data to the nearest neighbor through a unidirectional synchronous interconnect. Communication is configured dynamically and on-demand. Each object had the facilities needed for clock synchronization, [[built-in self-test]], etc... | ||
=== Object === | === Object === | ||
| − | There are five different types of components: [[Arithmetic Logic Unit]] (ALU), [[Content Addressable Memory]] (CAM), [[Cyclic Redundancy Check]] (CRC), [[Multiply Accumulator]] (MAC), and [[Register File]] (RF). The control program guides the overall program execution and the datapath setup. Datapath is {{arch|16 | + | [[File:mathstar layout.png|right]] |
| + | There are five different types of components: [[Arithmetic Logic Unit]] (ALU), [[Content Addressable Memory]] (CAM), [[Cyclic Redundancy Check]] (CRC), [[Multiply Accumulator]] (MAC), and [[Register File]] (RF). The control program guides the overall program execution and the datapath setup. Datapath is {{arch|16}} but may be combined with adjacent objects to [[bit-slice microprocessor|form larger datapaths]] of desired size. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Type: | ||
| + | * [[arithmetic logic unit|ALU]] | ||
| + | ** {{arch|16}} add/sub/shift/rotate/AND/OR/XOR | ||
| + | ** circuitry for cascading status bits for making larger word | ||
| + | * [[truth function]] | ||
| + | ** 4x 4:1 [[lookup table]]s | ||
| + | * [[multiply accumulator|MAC]] | ||
| + | ** 16x16 single clock cycle [[multiplier]] | ||
| + | ** 40-bit [[accumulator]] | ||
| + | * [[register file|RF]] | ||
| + | ** 320 Bytes | ||
| + | ** Configurable 20 or 40-bit data | ||
| + | ** Two modes: | ||
| + | *** Dual-ported RAM, single-cycle access | ||
| + | *** Single-cycle FIFO | ||
| + | * [[crc unit|CRC]] | ||
| + | ** 16x 20-bit patterns | ||
| + | ** 20-bit result | ||
| + | ** output feedback | ||
| + | * Internal Block [[RAM]] | ||
| + | ** 1024x76b (9KB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Members == | ||
| + | The amount and types of the individual objects were chosen based on the applications the were meant to run on the chip. MathStar divided the product line into BridgeBuilder, FilterBuilder, StorageBuilder, SecurityBuilder and SwitchBuilder. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === BridgeBuilder === | ||
| + | The BridgeBuilder series was designed for high-speed networking applications handling 10Gbps or more as well as bus bridging applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | ! Model !! Objects !! Parallel I/O Inter. !! Serial I/O Trans. !! GPIO !! 36-bit Memory Cntr | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13C20}} || 200 || 0-1 || 0-4 || 50-200 || 0-2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13C40}} || 400 || 0-2 || 0-16 || 50-200 || 0-2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13C80}} || 800 || 0-2 || 0-16 || 50-200 || 2-4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13C120}} || 1200 || 0-3 || 16 || 50-200 || 4 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === FilterBuilder === | ||
| + | The FilterBuilder series was designed for filter applications (high performance [[fast Fourier transform|FFTs]] and [[finite impulse response|FIRs]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | ! Model !! Objects !! Parallel I/O Inter. !! GPIO !! 36-bit Memory Cntr | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13D156}} || 156 || 0-1 || 50-200 || 0-2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{\|SOA13D40}} || 400 || 0-2 || 50-200 || 0-2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === StorageBuilder === | ||
| + | The FilterBuilder series was aimed to be combined with MathStar's network [[offload engine]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === SecurityBuilder === | ||
| + | The SecurityBuilder series was designed for various security applications with libraries that implement custom versions of security protocols at up to 10Gbps throughput. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === SwitchBuilder === | ||
| + | The SwitchBuilder series was designed for high-performance switching/networking applications such as for PCI-Express, Fibre Channel, Ethernet, RapidIO and others. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Documents == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Datasheet / Brief === | ||
| + | * [[:File:mathstar fpoa architecture.pdf|MathStar FPOA Architecture]], 2003 | ||
| + | * [[:File:mathstar builder product family.pdf|MathStar Builder Family]], 2003 | ||
| + | * [[:File:mathstar bridgebuilder.pdf|MathStar BridgeBuilder Series]], 2003 | ||
| + | * [[:File:mathstar filterbuilder series.pdf|MathStar FilterBuilder Series]], 2005 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Software === | ||
| + | * [[:File:mathstar tools overview.pdf|MathStar Tools Overview]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Application Notes === | ||
| + | * [[:File:8K AppNote.pdf|8K Point FFT Implementation]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:1024 AppNote.pdf|1024 Point FFT Implementation]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:polyphase fft.pdf|64 8-Tap PolyPhase FFT Implementation]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:RAID 6 Q Encode.pdf|RAID 6 Q Encoder Implementation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[field-programmable object array]] | ||
| + | * Ambric's {{ambric|Am2000}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:23, 19 November 2017
| Builder | |
| Developer | MathStar |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Type | Programmable logic device |
| Introduction | 2002 (announced) 2003 (launch) |
| Production | 2003-2006 |
| Word size | 16 bit 2 octets
4 nibbles |
| Process | 130 nm 0.13 μm
1.3e-4 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 100 MHz-1,000 MHz |
| Succession | |
| → | |
| Arrix | |
Builder was a family of FPOAs introduced by MathStar in 2003. This family the earliest attempt at designing an FPOA and was discontinued shortly after due to some technical issues. The Builder family was phased out entirely by 2006.
Contents
Architecture[edit]
- Main article: field-programmable object array
The Builder family was the MathStar's initial attempt at a field-programmable object array. Each chip contains 100s of silicon objects laid out in a grid, broken down to arrays of five objects each. Instructions are loaded to each of the objects at power-up.
Inter-Object communication was done primarily by passing data to the nearest neighbor through a unidirectional synchronous interconnect. Communication is configured dynamically and on-demand. Each object had the facilities needed for clock synchronization, built-in self-test, etc...
Object[edit]
There are five different types of components: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Content Addressable Memory (CAM), Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC), Multiply Accumulator (MAC), and Register File (RF). The control program guides the overall program execution and the datapath setup. Datapath is 16-bit but may be combined with adjacent objects to form larger datapaths of desired size.
Type:
- ALU
- 16-bit add/sub/shift/rotate/AND/OR/XOR
- circuitry for cascading status bits for making larger word
- truth function
- 4x 4:1 lookup tables
- MAC
- 16x16 single clock cycle multiplier
- 40-bit accumulator
- RF
- 320 Bytes
- Configurable 20 or 40-bit data
- Two modes:
- Dual-ported RAM, single-cycle access
- Single-cycle FIFO
- CRC
- 16x 20-bit patterns
- 20-bit result
- output feedback
- Internal Block RAM
- 1024x76b (9KB)
Members[edit]
The amount and types of the individual objects were chosen based on the applications the were meant to run on the chip. MathStar divided the product line into BridgeBuilder, FilterBuilder, StorageBuilder, SecurityBuilder and SwitchBuilder.
BridgeBuilder[edit]
The BridgeBuilder series was designed for high-speed networking applications handling 10Gbps or more as well as bus bridging applications.
| Model | Objects | Parallel I/O Inter. | Serial I/O Trans. | GPIO | 36-bit Memory Cntr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOA13C20 | 200 | 0-1 | 0-4 | 50-200 | 0-2 |
| SOA13C40 | 400 | 0-2 | 0-16 | 50-200 | 0-2 |
| SOA13C80 | 800 | 0-2 | 0-16 | 50-200 | 2-4 |
| SOA13C120 | 1200 | 0-3 | 16 | 50-200 | 4 |
FilterBuilder[edit]
The FilterBuilder series was designed for filter applications (high performance FFTs and FIRs).
| Model | Objects | Parallel I/O Inter. | GPIO | 36-bit Memory Cntr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOA13D156 | 156 | 0-1 | 50-200 | 0-2 |
| SOA13D40 | 400 | 0-2 | 50-200 | 0-2 |
StorageBuilder[edit]
The FilterBuilder series was aimed to be combined with MathStar's network offload engine.
SecurityBuilder[edit]
The SecurityBuilder series was designed for various security applications with libraries that implement custom versions of security protocols at up to 10Gbps throughput.
SwitchBuilder[edit]
The SwitchBuilder series was designed for high-performance switching/networking applications such as for PCI-Express, Fibre Channel, Ethernet, RapidIO and others.
Documents[edit]
Datasheet / Brief[edit]
- MathStar FPOA Architecture, 2003
- MathStar Builder Family, 2003
- MathStar BridgeBuilder Series, 2003
- MathStar FilterBuilder Series, 2005
Software[edit]
Application Notes[edit]
- 8K Point FFT Implementation
- 1024 Point FFT Implementation
- 64 8-Tap PolyPhase FFT Implementation
- RAID 6 Q Encoder Implementation
See also[edit]
- field-programmable object array
- Ambric's Am2000
| designer | MathStar + |
| first announced | 2002 + |
| first launched | 2003 + |
| full page name | mathstar/builder + |
| instance of | integrated circuit family + |
| main designer | MathStar + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| name | Builder + |
| process | 130 nm (0.13 μm, 1.3e-4 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 16 bit (2 octets, 4 nibbles) + |