From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/nehalem (client)"
(Created page with "{{intel title|Nehalem|arch}} {{microarchitecture | name = Nehalem | manufacturer = Intel | introduction = August, 2008 | phase-out = March, 2010 | p...") |
(Corrected Nehalem-EX die size.) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{intel title|Nehalem|arch}} | {{intel title|Nehalem|arch}} | ||
{{microarchitecture | {{microarchitecture | ||
| + | | atype = CPU | ||
| name = Nehalem | | name = Nehalem | ||
| + | | designer = Intel | ||
| manufacturer = Intel | | manufacturer = Intel | ||
| introduction = August, 2008 | | introduction = August, 2008 | ||
| phase-out = March, 2010 | | phase-out = March, 2010 | ||
| process = 45 nm | | process = 45 nm | ||
| − | + | |isa=x86-64 | |
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
| predecessor = Penryn | | predecessor = Penryn | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Nehalem''' was the [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[45 nm process]] for desktops and servers as a successor to {{\\|Penryn}}. Nehalem is named after the [[wikipedia:Nehalem River|Nehalem River]]. Nehalem was replaced by the {{\\|Westmere}} microarchitecture in 2010. | '''Nehalem''' was the [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[45 nm process]] for desktops and servers as a successor to {{\\|Penryn}}. Nehalem is named after the [[wikipedia:Nehalem River|Nehalem River]]. Nehalem was replaced by the {{\\|Westmere}} microarchitecture in 2010. | ||
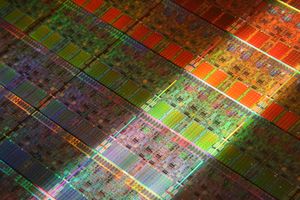
| + | [[File:Nehalem.jpg|right|thumb|300px|Nehalem wafer]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="float: right;" | ||
| + | ! colspan="2" | 45 nm Manufacturing Fabs | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Fab !! Location | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | D1D || Hillsboro, Oregon | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fab 32 || Chandler, Arizona | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fab 28 || Kiryat Gat, Israel | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Penryn-based [[microprocessors]] were manufactured on a [[45 nm process]]. Intel's 45 nm process is the is the first high-volume manufacturing process to introduce High-k + metal gate transistors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Scaling: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! !! Core !! Nehalem !! Δ !! rowspan="7" | [[File:intel 45nm gate.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || [[65 nm]] || [[45 nm]] || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Metal Layers || 8 || 9 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gate Pitch || 220 nm || 180 nm || 0.82x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Interconnect Pitch || 210 nm || 160 nm || 0.76x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SRAM bit cell (HD) || 0.570 µm² || 0.346 um² || 0.61x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SRAM bit cell (LP) || 0.680 µm² || 0.382 um² || 0.56x | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
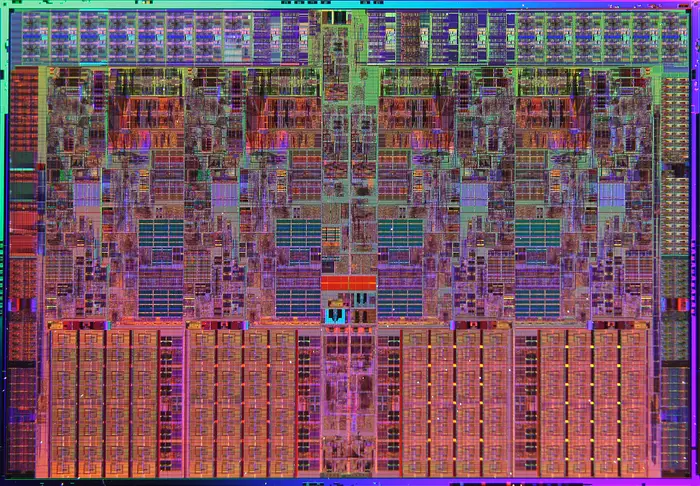
| + | == Die Shot == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bloomfield=== | ||
| + | * 263 mm² | ||
| + | * 731,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | * [[45 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 4 cores | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[File:nehalem die shot.png|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
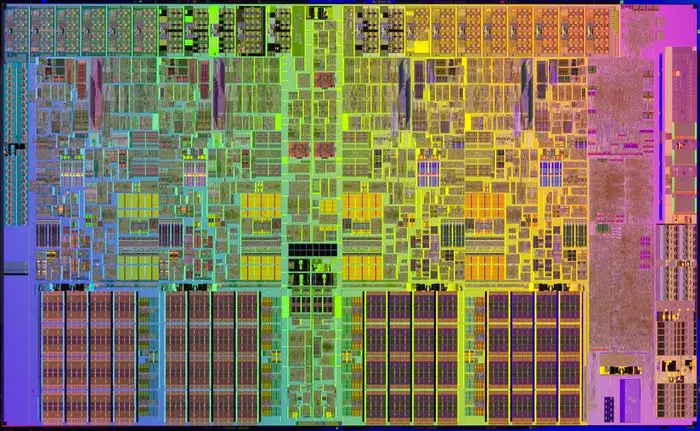
| + | ===Lynnfield=== | ||
| + | * 296 mm² | ||
| + | * 774,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | * [[45 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 4 cores | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[File:intel nehalem lynfield die shot.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
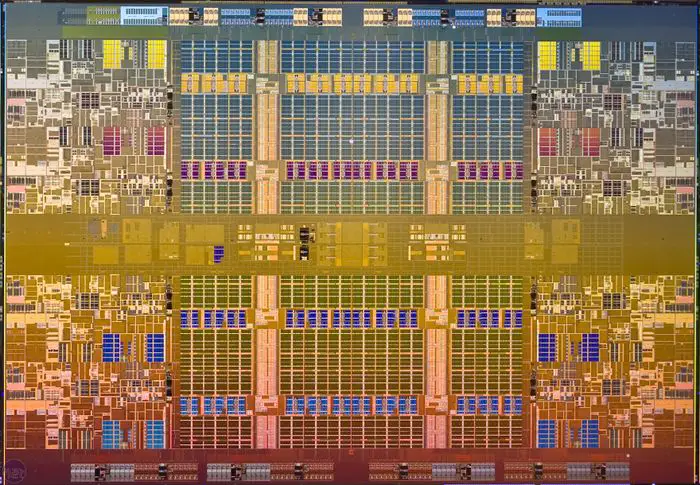
| + | ===Nehalem-EX=== | ||
| + | * 684 mm² | ||
| + | * 2.300,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | * [[45 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 8 cores | ||
| + | |||
| + | : [[File:intel Nehalem-EX die shot.jpeg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == All Nehalem Chips == | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc6 tc7 tc20 tc21 tc22 tc23 tc24 tc25"> | ||
| + | <tr class="comptable-header"><th> </th><th colspan="20">List of Nehalem Processors</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr class="comptable-header"><th> </th><th colspan="9">Main processor</th><th colspan="2">{{intel|Turbo Boost}}</th><th>Mem</th><th colspan="3">IGP</th><th colspan="4">Major Feature Diff</th></tr> | ||
| + | {{comp table header 1|cols=Launched, Price, Family, Core Name, Cores, Threads, %L2$, %L3$, TDP, %Frequency, {{intel|TBT 1.0}}, Max Mem, GPU, %Frequency, Turbo, {{x86|AES}}, vPro, VT-d, VT-x}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[instance of::microprocessor]] [[microarchitecture:: Nehalem]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?release price | ||
| + | |?microprocessor family | ||
| + | |?core name | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?thread count | ||
| + | |?l2$ size | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GiB | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu base frequency | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu max frequency | ||
| + | |?has x86 advanced encryption standard instruction set extension | ||
| + | |?has_intel_vpro_technology | ||
| + | |?has intel vt-d technology | ||
| + | |?has intel vt-x technology | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |searchlabel= | ||
| + | |sort=microprocessor family, model number | ||
| + | |order=asc,asc | ||
| + | |userparam=21:18 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | |limit=200 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:44, 26 December 2023
| Edit Values | |
| Nehalem µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | August, 2008 |
| Phase-out | March, 2010 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
Nehalem was the microarchitecture for Intel's 45 nm process for desktops and servers as a successor to Penryn. Nehalem is named after the Nehalem River. Nehalem was replaced by the Westmere microarchitecture in 2010.
Contents
Process Technology[edit]
| 45 nm Manufacturing Fabs | |
|---|---|
| Fab | Location |
| D1D | Hillsboro, Oregon |
| Fab 32 | Chandler, Arizona |
| Fab 28 | Kiryat Gat, Israel |
Penryn-based microprocessors were manufactured on a 45 nm process. Intel's 45 nm process is the is the first high-volume manufacturing process to introduce High-k + metal gate transistors.
Scaling:
| Core | Nehalem | Δ | 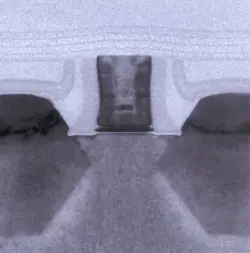
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 nm | 45 nm | |||
| Metal Layers | 8 | 9 | ||
| Gate Pitch | 220 nm | 180 nm | 0.82x | |
| Interconnect Pitch | 210 nm | 160 nm | 0.76x | |
| SRAM bit cell (HD) | 0.570 µm² | 0.346 um² | 0.61x | |
| SRAM bit cell (LP) | 0.680 µm² | 0.382 um² | 0.56x |
Die Shot[edit]
Bloomfield[edit]
- 263 mm²
- 731,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 4 cores
Lynnfield[edit]
- 296 mm²
- 774,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 4 cores
Nehalem-EX[edit]
- 684 mm²
- 2.300,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 8 cores
All Nehalem Chips[edit]
| List of Nehalem Processors | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | Turbo Boost | Mem | IGP | Major Feature Diff | ||||||||||||||||
| Model | Launched | Price | Family | Core Name | Cores | Threads | L2$ | L3$ | TDP | Frequency | TBT 1.0 | Max Mem | GPU | Frequency | Turbo | AES | vPro | VT-d | VT-x | |
| i7-720QM | 23 September 2009 | $ 364.00 € 327.60 £ 294.84 ¥ 37,612.12 | Core i7 | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 1.6 GHz 1,599.99 MHz 1,599,990 kHz | 2.8 GHz 2,799.99 MHz 2,799,990 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-740QM | 22 June 2010 | $ 378.00 € 340.20 £ 306.18 ¥ 39,058.74 | Core i7 | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 1.733 GHz 1,733.33 MHz 1,733,330 kHz | 2.933 GHz 2,933.33 MHz 2,933,330 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-820QM | 23 September 2009 | $ 546.00 € 491.40 £ 442.26 ¥ 56,418.18 | Core i7 | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 1.733 GHz 1,733.33 MHz 1,733,330 kHz | 3.067 GHz 3,066.66 MHz 3,066,660 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-840QM | 22 June 2010 | $ 568.00 € 511.20 £ 460.08 ¥ 58,691.44 | Core i7 | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 1.867 GHz 1,866.66 MHz 1,866,660 kHz | 3.2 GHz 3,199.99 MHz 3,199,990 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-920XM | 23 September 2009 | $ 1,054.00 € 948.60 £ 853.74 ¥ 108,909.82 | Core i7EE | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 2 GHz 1,999.99 MHz 1,999,990 kHz | 3.2 GHz 3,199.99 MHz 3,199,990 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-940XM | 22 June 2010 | $ 1,096.00 € 986.40 £ 887.76 ¥ 113,249.68 | Core i7EE | Clarksfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 2.133 GHz 2,133.33 MHz 2,133,330 kHz | 3.333 GHz 3,333.33 MHz 3,333,330 kHz | 8 GiB 8,192 MiB 8,388,608 KiB 8,589,934,592 B 0.00781 TiB | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| i7-965 | 17 November 2008 | Core i7EE | Bloomfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 3.467 GHz 3,467 MHz 3,467,000 kHz | 24 GiB 24,576 MiB 25,165,824 KiB 25,769,803,776 B 0.0234 TiB | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | |||||
| i7-975 | 2 June 2009 | Core i7EE | Bloomfield | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 3.333 GHz 3,333 MHz 3,333,000 kHz | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 24 GiB 24,576 MiB 25,165,824 KiB 25,769,803,776 B 0.0234 TiB | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | |||||