| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{annapurna title|AWS Graviton4}} | {{annapurna title|AWS Graviton4}} | ||
| − | {{chip}} | + | {{chip |
| − | '''AWS Graviton4''' ('''Alpine ALC14C00''') is a [[hexanonaconta-core]] [[ARMv9]] multiprocessor designed by [[Amazon]] ([[Annapurna Labs]]) for Amazon's own infrastructure. Graviton4 is a [[5 nm]](?) 7-chiplet design SoC based on the Arm [[CMN-700 mesh interconnect]] and [[Neoverse V2]] core microarchitecture. This chip | + | |name=AWS Graviton4 |
| + | |image=graviton4.png | ||
| + | |caption=Graviton4 Package Front | ||
| + | |designer=Annapurna Labs | ||
| + | |manufacturer=TSMC | ||
| + | |model number=Graviton4 | ||
| + | |part number=ALC14C00 | ||
| + | |market=Server | ||
| + | |first announced=November 28, 2023 | ||
| + | |first launched=November 28, 2023 | ||
| + | |family=Graviton | ||
| + | |isa=ARMv9.0-A | ||
| + | |isa family=ARM | ||
| + | |microarch=Neoverse V2 | ||
| + | |technology=CMOS | ||
| + | |mcp=Yes | ||
| + | |die count=7 | ||
| + | |word size=64 bit | ||
| + | |core count=96 | ||
| + | |thread count=96 | ||
| + | |max cpus=2 | ||
| + | |smp interconnect=CCIX | ||
| + | |smp interconnect links=3 | ||
| + | |predecessor=Graviton3 | ||
| + | |predecessor link=annapurna_labs/graviton/graviton3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
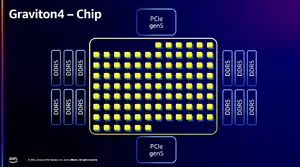
| + | '''AWS Graviton4''' ('''Alpine ALC14C00''') is a [[hexanonaconta-core]] [[ARMv9]] multiprocessor designed by [[Amazon]] ([[Annapurna Labs]]) for Amazon's own infrastructure. Graviton4 is a [[5 nm]](?) 7-chiplet design SoC based on the Arm [[CMN-700 mesh interconnect]] and [[Neoverse V2]] core microarchitecture. This chip supports dodeca-channel DDR5-5600 ECC memory along with 96 lanes of PCIe 5.0. | ||
| − | This 4th-generation server processor was first announced during Amazon's AWS re:Invent 2023 by Adam Selipsky in his keynote. The general rollout for the Graviton4 chip in the AWS data center | + | == Overview == |
| + | This 4th-generation server processor was first announced during Amazon's AWS re:Invent [[2023]] by Adam Selipsky in his keynote. The general rollout for the Graviton4 chip in the AWS data center occurred in early 2024. These processors are offered as part of Amazon's EC2 instances. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Graviton4 features a 7-chiplet design similar to its predecessor, {{\\|Graviton3}}. This chip features 96 cores, 50% more than the prior generation. The core implementation was updated to Arm's {{armh|Neoverse V2}} microarchitecture with 2x256b [[Scalable Vector Extension|SVE]] support, also bringing support up to [[Armv9.0]] ISA for the first time. The chip supports up to 12 channels for DDR5 ECC DIMMs with data rates of up to 5600 MT/s. The Graviton4 tripled the number of PCIe lanes to 96 lanes of PCIe 5.0. | ||
| + | [[File:graviton4 layout.png|thumb|left]] | ||
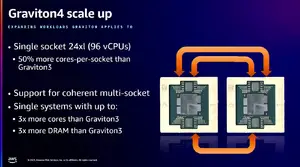
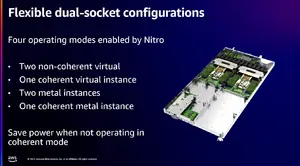
| + | The Graviton4 is the first chip from the Graviton family to feature multiprocessing support. The chip introduced dual-socket support with full coherency for up to 192 vCPUs and DDR5 channels on a single server. The Graviton4 also expanded encryption support to the new multi-socket coherency links as well as to the Nitro cards interfaces. The full platform can be configured to run in a number of modes that can potentially offer additional power saving: two non-coherent virtual systems, one coherent virtual system, two metal systems, or one metal system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{clear|left}}[[File:graviton4 sockets.png|thumb|right]] [[File:graviton4 server.png|thumb|right]] [[File:graviton4 held.png|thumb|right]] | ||
| + | === Packaging === | ||
| + | The Graviton4 features a 7-chiplet architecture similar in design to the Graviton3. The compute SoC die sits in the middle with 4 DDR memory controller dies and 2 PCIe controller dies. Each DDR memory controller features support for 3 memory channels - two dies to the east and two dies to the west for a total of 6 memory channels on each side. There are two PCIe controller dies - one to the north and one to the south of the chip. The four DDR memory controller dies are interconnected with the SoC via embedded silicon bridges in the package.Unlike the {{\\|Graviton3}}, the two PCIe controller dies are not abutting the compute SoC die and are no longer controller via an embedded bridge in the package. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cache == | ||
| + | {{main|arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse v2#Memory_Hierarchy|l1=Neoverse V2 § Cache}} | ||
| + | {{cache size | ||
| + | |l1 cache=12 MiB | ||
| + | |l1i cache=6 MiB | ||
| + | |l1i break=96x64 KiB | ||
| + | |l1d cache=6 MiB | ||
| + | |l1d break=96x64 KiB | ||
| + | |l2 cache=192 MiB | ||
| + | |l2 break=96x2 MiB | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Memory controller == | ||
| + | {{memory controller | ||
| + | |type=DDR5-5600 | ||
| + | |ecc=Yes | ||
| + | |controllers=4 | ||
| + | |channels=12 | ||
| + | |max bandwidth=537.6 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth schan=44.8 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth dchan=89.6 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth qchan=179.2 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth ochan=358.4 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth 10chan=448.0 GB/s | ||
| + | |bandwidth 12chan=537.6 GB/s | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Expansions == | ||
| + | {{expansions | ||
| + | | pcie revision = 5.0 | ||
| + | | pcie lanes = 96 | ||
| + | | pcie config = x16 | ||
| + | | pcie config 2 = x8 | ||
| + | | pcie config 3 = x4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 12 December 2023
| Edit Values | |
| AWS Graviton4 | |
 | |
| Graviton4 Package Front | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Annapurna Labs |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Model Number | Graviton4 |
| Part Number | ALC14C00 |
| Market | Server |
| Introduction | November 28, 2023 (announced) November 28, 2023 (launched) |
| General Specs | |
| Family | Graviton |
| Microarchitecture | |
| ISA | ARMv9.0-A (ARM) |
| Microarchitecture | Neoverse V2 |
| Technology | CMOS |
| MCP | Yes (7 dies) |
| Word Size | 64 bit |
| Cores | 96 |
| Threads | 96 |
| Multiprocessing | |
| Max SMP | 2-Way (Multiprocessor) |
| Interconnect | CCIX |
| Interconnect Links | 3 |
| Succession | |
AWS Graviton4 (Alpine ALC14C00) is a hexanonaconta-core ARMv9 multiprocessor designed by Amazon (Annapurna Labs) for Amazon's own infrastructure. Graviton4 is a 5 nm(?) 7-chiplet design SoC based on the Arm CMN-700 mesh interconnect and Neoverse V2 core microarchitecture. This chip supports dodeca-channel DDR5-5600 ECC memory along with 96 lanes of PCIe 5.0.
Overview[edit]
This 4th-generation server processor was first announced during Amazon's AWS re:Invent 2023 by Adam Selipsky in his keynote. The general rollout for the Graviton4 chip in the AWS data center occurred in early 2024. These processors are offered as part of Amazon's EC2 instances.
Graviton4 features a 7-chiplet design similar to its predecessor, Graviton3. This chip features 96 cores, 50% more than the prior generation. The core implementation was updated to Arm's Neoverse V2 microarchitecture with 2x256b SVE support, also bringing support up to Armv9.0 ISA for the first time. The chip supports up to 12 channels for DDR5 ECC DIMMs with data rates of up to 5600 MT/s. The Graviton4 tripled the number of PCIe lanes to 96 lanes of PCIe 5.0.
The Graviton4 is the first chip from the Graviton family to feature multiprocessing support. The chip introduced dual-socket support with full coherency for up to 192 vCPUs and DDR5 channels on a single server. The Graviton4 also expanded encryption support to the new multi-socket coherency links as well as to the Nitro cards interfaces. The full platform can be configured to run in a number of modes that can potentially offer additional power saving: two non-coherent virtual systems, one coherent virtual system, two metal systems, or one metal system.
Packaging[edit]
The Graviton4 features a 7-chiplet architecture similar in design to the Graviton3. The compute SoC die sits in the middle with 4 DDR memory controller dies and 2 PCIe controller dies. Each DDR memory controller features support for 3 memory channels - two dies to the east and two dies to the west for a total of 6 memory channels on each side. There are two PCIe controller dies - one to the north and one to the south of the chip. The four DDR memory controller dies are interconnected with the SoC via embedded silicon bridges in the package.Unlike the Graviton3, the two PCIe controller dies are not abutting the compute SoC die and are no longer controller via an embedded bridge in the package.
Cache[edit]
- Main article: Neoverse V2 § Cache
|
Cache Organization
Cache is a hardware component containing a relatively small and extremely fast memory designed to speed up the performance of a CPU by preparing ahead of time the data it needs to read from a relatively slower medium such as main memory. The organization and amount of cache can have a large impact on the performance, power consumption, die size, and consequently cost of the IC. Cache is specified by its size, number of sets, associativity, block size, sub-block size, and fetch and write-back policies. Note: All units are in kibibytes and mebibytes. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Memory controller[edit]
|
Integrated Memory Controller
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Expansions[edit]
|
Expansion Options
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| full page name | annapurna labs/graviton/graviton4 + |
| instance of | microprocessor + |
| ldate | 1900 + |