From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/atom/z500"
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
== Features == | == Features == | ||
| − | {{x86 features}} | + | {{x86 features |
| + | |real=Yes | ||
| + | |protected=Yes | ||
| + | |smm=Yes | ||
| + | |fpu=Yes | ||
| + | |x8616=Yes | ||
| + | |x8632=Yes | ||
| + | |x8664=No | ||
| + | |nx=Yes | ||
| + | |mmx=Yes | ||
| + | |emmx=Yes | ||
| + | |sse=Yes | ||
| + | |sse2=Yes | ||
| + | |sse3=Yes | ||
| + | |ssse3=Yes | ||
| + | |sse41=No | ||
| + | |sse42=No | ||
| + | |sse4a=No | ||
| + | |avx=No | ||
| + | |avx2=No | ||
| + | |avx512=No | ||
| + | |abm=No | ||
| + | |tbm=No | ||
| + | |bmi1=No | ||
| + | |bmi2=No | ||
| + | |fma3=No | ||
| + | |fma4=No | ||
| + | |aes=No | ||
| + | |rdrand=No | ||
| + | |sha=No | ||
| + | |xop=No | ||
| + | |adx=No | ||
| + | |clmul=No | ||
| + | |f16c=No | ||
| + | |tbt1=No | ||
| + | |tbt2=No | ||
| + | |tbmt3=No | ||
| + | |bpt=No | ||
| + | |eist=Yes | ||
| + | |sst=No | ||
| + | |flex=No | ||
| + | |fastmem=No | ||
| + | |isrt=No | ||
| + | |sba=No | ||
| + | |mwt=No | ||
| + | |sipp=No | ||
| + | |att=No | ||
| + | |ipt=No | ||
| + | |tsx=No | ||
| + | |txt=No | ||
| + | |ht=No | ||
| + | |vpro=No | ||
| + | |vtx=No | ||
| + | |vtd=No | ||
| + | |ept=No | ||
| + | |mpx=No | ||
| + | |sgx=No | ||
| + | |securekey=No | ||
| + | |osguard=No | ||
| + | |3dnow=No | ||
| + | |e3dnow=No | ||
| + | |smartmp=No | ||
| + | |powernow=No | ||
| + | |amdvi=No | ||
| + | |amdv=No | ||
| + | |rvi=No | ||
| + | |smt=No | ||
| + | |sensemi=No | ||
| + | |xfr=No | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Die Shot == | == Die Shot == | ||
Revision as of 20:23, 1 April 2017
Template:mpu Z500 is an ultra-low power 32-bit x86 microprocessor introduced by Intel in early 2008 specifically for Mobile Internet Devices (MID). The Z500, which is based on the Bonnell microarchitecture (Silverthorne core), is manufactured on a 45 nm process. This processor operates at 800 MHz with a TDP of just 650 mW and an average power of 160 mW. The MPU features a legacy 400 MT/s front-side bus capable of communicating with the Poulsbo chipset in both low-power CMOS mode as well as normal GTL mode (which also works with other chipsets).
Cache
- Main article: Bonnell § Cache
|
Cache Organization
Cache is a hardware component containing a relatively small and extremely fast memory designed to speed up the performance of a CPU by preparing ahead of time the data it needs to read from a relatively slower medium such as main memory. The organization and amount of cache can have a large impact on the performance, power consumption, die size, and consequently cost of the IC. Cache is specified by its size, number of sets, associativity, block size, sub-block size, and fetch and write-back policies. Note: All units are in kibibytes and mebibytes. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Memory controller
This processor has no integrated memory controller.
Graphics
This processor has no integrated graphics.
Features
[Edit/Modify Supported Features]
|
Supported x86 Extensions & Processor Features
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
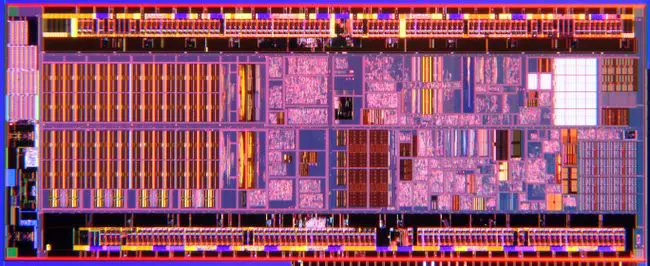
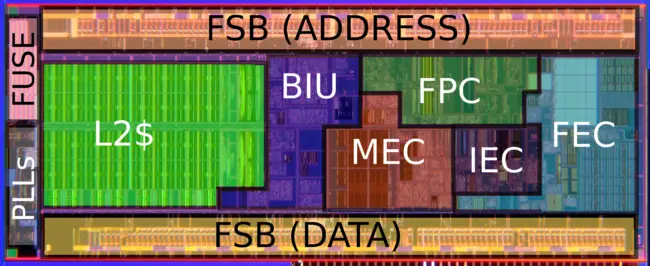
Die Shot
- See also: Bonnell § Silverthorne Die
- 45 nm process
- 9 metal layers
- 47,212,207 transistors
- 3.1 mm x 7.8 mm
- 24.18 mm² die size
Facts about "Atom Z500 - Intel"
| has feature | Enhanced SpeedStep Technology + |
| has intel enhanced speedstep technology | true + |
| l1$ size | 56 KiB (57,344 B, 0.0547 MiB) + |
| l1d$ description | 6-way set associative + |
| l1d$ size | 24 KiB (24,576 B, 0.0234 MiB) + |
| l1i$ description | 8-way set associative + |
| l1i$ size | 32 KiB (32,768 B, 0.0313 MiB) + |
| l2$ description | 8-way set associative + |
| l2$ size | 0.5 MiB (512 KiB, 524,288 B, 4.882812e-4 GiB) + |