(→Architecture) |
(→New Power Management) |
||
| Line 196: | Line 196: | ||
Intel introduced '''{{intel|Speed Shift}}''' with Skylake, a new methodology for quickly alternating core frequencies in response to power loads. Intel introduced a new unit called PCU (Package Control Unit) which is effectively a full fledged microcontroller (containing power management logic and firmware) that collects and tracks many internal SoC statistics as well as external power telemetry (e.g. Psys and iMon). PCU is also capable of interfacing with the OS, [[BIOS]], and {{intel|Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework|DPTF}}. Speed Shift improves the performance of frequency shifting by off-loading the control from the [[operating system]] to the PCU. | Intel introduced '''{{intel|Speed Shift}}''' with Skylake, a new methodology for quickly alternating core frequencies in response to power loads. Intel introduced a new unit called PCU (Package Control Unit) which is effectively a full fledged microcontroller (containing power management logic and firmware) that collects and tracks many internal SoC statistics as well as external power telemetry (e.g. Psys and iMon). PCU is also capable of interfacing with the OS, [[BIOS]], and {{intel|Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework|DPTF}}. Speed Shift improves the performance of frequency shifting by off-loading the control from the [[operating system]] to the PCU. | ||
| − | Speed Shift effectively eliminates the need for the OS to manages the P-states - though it does have the final (unless special exceptions occur such as thermal throttling). Intel calls this "autonomous P-state", allowing Speed Shift to kick in in a matter of just ~1 millisecond (whereas the operating system-based p-states control can be as slow as 30 ms) | + | Speed Shift effectively eliminates the need for the OS to manages the P-states - though it does have the final (unless special exceptions occur such as thermal throttling). Intel calls this "autonomous P-state", allowing Speed Shift to kick in in a matter of just ~1 millisecond (whereas the operating system-based p-states control can be as slow as 30 ms). Speed Shift effectively reduces hitting peak frequency in around ~30 ms from over 100 ms (OS-based implementation as before). |
===== Power of System (Psys) ===== | ===== Power of System (Psys) ===== | ||
Revision as of 00:20, 9 September 2016
| Edit Values | |
| Skylake µarch | |
| General Info |
Skylake (SKL) is Intel's microarchitecture using 14 nm process for mainstream desktops, servers, and mobiles. Skylake became the successor to the short-lived Broadwell which experienced severe delays.
For desktop and mobile, Skylake is branded as 6th Generation Intel Core processors. For server class processors, Intel branded it as Xeon E3 v5, Xeon E5 v5, and Xeon E7 v5.
Contents
Codenames
| Core | Abbrev | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Skylake Y | SKL-Y | 2-in-1s detachable, tablets, and computer sticks |
| Skylake U | SKL-U | Light notebooks, portable All-in-Ones (AiOs), Minis, and conference room |
| Skylake H | SKL-H | Ultimate mobile performance, mobile workstations |
| Skylake S | SKL-S | Desktop performance to value, AiOs, and minis |
| Skylake X | SKL-X | High-end desktops & enthusiasts market |
| Skylake W | SKL-W | Workstations |
Technology
- Main article: Broadwell § Technology
Skylake uses the same 14 nm process used for the Broadwell microarchitecture.
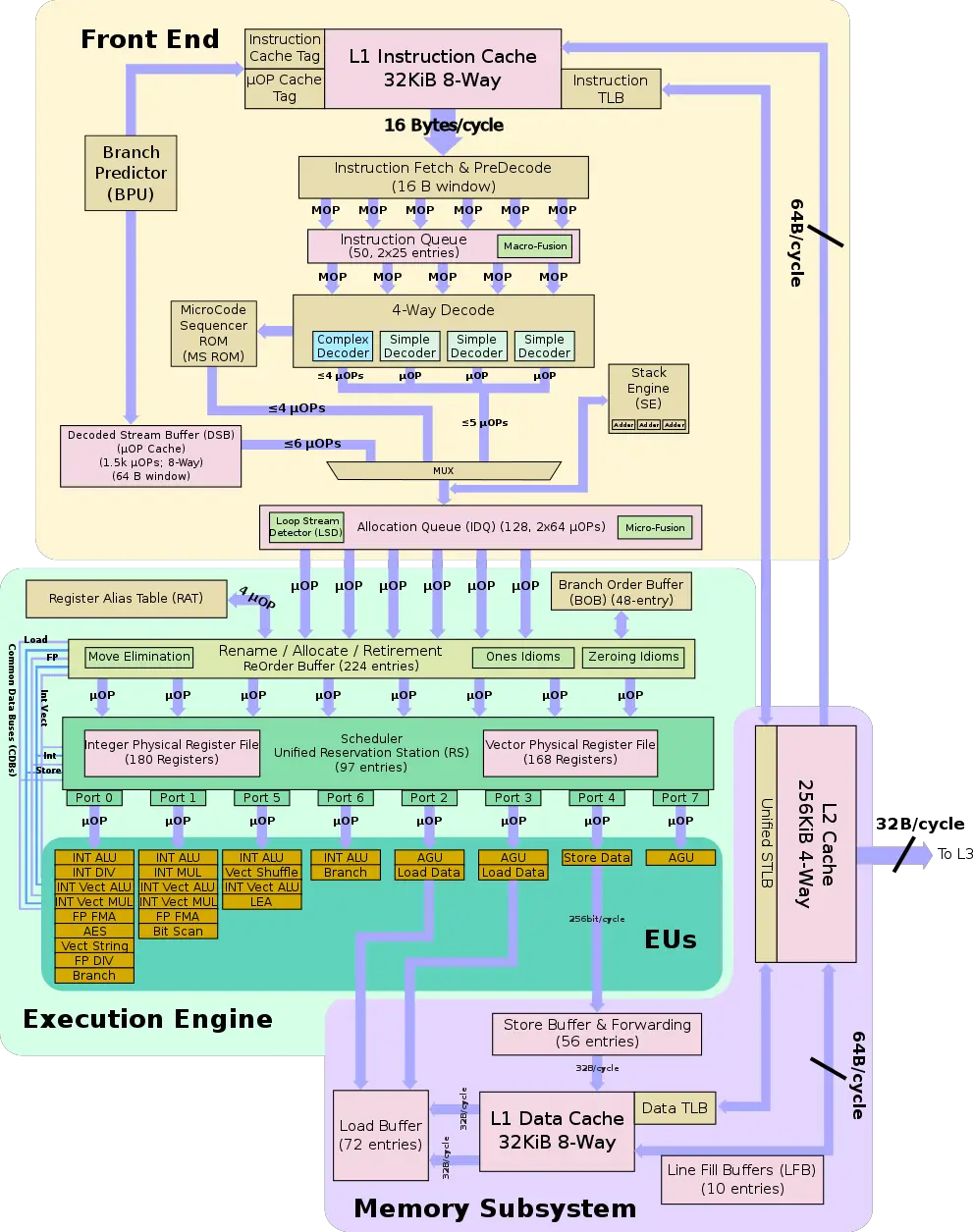
Architecture
Overall Skylake builds upon Intel's previous microarchitecture, Broadwell, but includes a more beefed up front end, more optimized execution engine, and numerous number of smaller enhancements. Intel designed Skylake to encompass a wide range of devices and applications with a large emphasis on mobile with models ranging from as low as 4.5 W to as high as 100 W.
Key changes from Broadwell
- Bus/Interface to Chipset
- DMI 3.0 (from 2.0)
- Skylake S and Skylake H cores, connected by 4-lane DMI 3.0
- Skylake Y and Skylake U cores have chipset in the same package (simplified OPIO)
- Increases speed from 5.0 GT/s to 8.0 GT/s (~3.93GB/s up from 2GB/s)
- Limits motherboard trace design to 7 inches max from (down from 8) from the CPU to chipset
- DMI 3.0 (from 2.0)
- Front End
- Larger legacy pipeline delivery (5 µOPs, up from 4)
- Larger IDQ delivery (6 µOPs, up from 4)
- 2.28x larger allocation queue (64/thread, up from 28/thread)
- Improved branch prediction unit
- Execution Engine
- Larger re-order buffer (224 entries, up from 192)
- Larger scheduler (97 entries, up from 64)
- Larger Integer Register File (180 entries, up from 160)
- Larger store buffer (56 entries, up from 42)
- Memory
- L2$ was changed from 8-way to 4-way set associative
- TLBs
- ITLB
- 4KB page translations was changed from 4-way to 8-way associative
- STLB
- 4KB+2M page translations was changed from 6-way to 12-way associative
- ITLB
- Electrical
- The fully integrated voltage regulator (FIVR) is moved back to the motherboard
- Originally intended to be a cost-cutting measure by moving the FIVR on-die as well as making it more efficient, the move resulted in unintentionally making the FIVR the limiting factor when it came to overclocking.
- The fully integrated voltage regulator (FIVR) is moved back to the motherboard
Graphics
- Skylake retires VGA support, multi-monitor support for up to 3 displays via HDMI 1.4, DP 1.2, and eDP 1.3 interfaces.
- Direct X 12
- OpenCL 2.0
- OpenGL 4.4
- Up to 24 EUs GT2 (same as Haswell); 48 EUs for GT3, and up to 72 EUs on Iris Pro Graphics
- 1,152 GFLOPS
IGP Execution Units GT eDRAM Series (Y/U/H/S) HD Graphics 12 2+1 - Y HD Graphics 510 12 2+2 - U/S HD Graphics 515 24 2+2 - Y HD Graphics 520 24 4+2
2+2- U HD Graphics 530 24 4+2
2+2- H/S HD Graphics P530 24 4+2 - H Iris Graphics 540 48 2+3e 64 MB U Iris Graphics 550 48 2+3e 64 MB U Iris Pro Graphics 580 72 4+4e 128 MB H
New GPU Features
- Adaptive scalable texture compression (ASTC)
- 16x multi-sample anti-aliasing (MSAA)
- Post depth test coverage mask
- Floating point atomics (min/max/cmpexch)
- Min/max texture filtering
- Multi-plane overlays
New instructions
- Main article: See §Added_instructions for the complete list
Skylake introduced a number of new instructions:
-
SGX- Software Guard Extensions -
MPX-Memory Protection Extensions -
AVX-512- Advanced Vector Extensions 512 (Only on high-end Xeon models (SKX))
New Power Management
Intel introduced Speed Shift with Skylake, a new methodology for quickly alternating core frequencies in response to power loads. Intel introduced a new unit called PCU (Package Control Unit) which is effectively a full fledged microcontroller (containing power management logic and firmware) that collects and tracks many internal SoC statistics as well as external power telemetry (e.g. Psys and iMon). PCU is also capable of interfacing with the OS, BIOS, and DPTF. Speed Shift improves the performance of frequency shifting by off-loading the control from the operating system to the PCU.
Speed Shift effectively eliminates the need for the OS to manages the P-states - though it does have the final (unless special exceptions occur such as thermal throttling). Intel calls this "autonomous P-state", allowing Speed Shift to kick in in a matter of just ~1 millisecond (whereas the operating system-based p-states control can be as slow as 30 ms). Speed Shift effectively reduces hitting peak frequency in around ~30 ms from over 100 ms (OS-based implementation as before).
Power of System (Psys)
Psys (Power of System) is a way for the PCU to monitor the performance and the total platform power provided to the chip. The chip uses a number of autonomous algorithms (one for "Low Range" and one for "High Range"). The Low Range algorithm frequency is lowered to conserve energy. Algorithm is capable of overriding the low P state - a state calculated ever millisecond based on the active workload and system characteristics. The High Range algorithm deals with elevating frequency for the benefit of increase performance (at the cost of increase energy/inefficiency). The exact ratio of ΔPower/ΔPerformance ≤ αPreference can be finely controlled via the OS and user preferences.
Block Diagram
Memory Hierarchy
Other than a few organizational changes (e.g. L2$ went from 8-way to 4-way set associative), the overall memory structure is identical to Broadwell/Haswell.
- Cache
- L1I Cache:
- 32 KB 8-way set associative
- 64 B line size
- Write-back policy
- shared by the two threads, per core
- 32 KB 8-way set associative
- L1D Cache:
- 32 KB 8-way set associative
- 64 B line size
- shared by the two threads, per core
- 4 cycles for fastest load-to-use
- 64 Bytes/cycle load bandwidth
- 32 Bytes/cycle store bandwidth
- Write-back policy
- L2 Cache:
- unified, 256 KB 4-way set associative
- 12 cycles for fastest load-to-use
- 64B/cycle bandwidth to L1$
- Write-back policy
- L3 Cache:
- Up to 2 MB
- Per core
- Up to 16-way set associative
- Write-back policy
- L4 Cache:
- 128 MB
- Per package
- Only on the Iris Pro GPUs
- L1I Cache:
Skylake TLB consists of dedicated level one TLB for instruction cache and another one for data cache. Additionally there is a unified second level TLB.
- TLBs:
- ITLB
- 4KB page translations:
- 128 entries; 8-way set associative
- dynamic partition; divided between the two threads
- 2MB/4MB page translations:
- 8 entries; fully associative
- Duplicated for each thread
- 4KB page translations:
- DTLB
- 4KB page translations:
- 64 entries; 4-way set associative
- fixed partition; divided between the two threads
- 2MB/4MB page translations:
- 32 entries; 4-way set associative
- fixed partition
- 1G page translations:
- 4 entries; 4-way set associative
- fixed partition
- 4KB page translations:
- STLB
- 4KB+2M page translations:
- 1536 entries; 12-way set associative
- fixed partition
- 1G page translations:
- 16 entries; 4-way set associative
- fixed partition
- 4KB+2M page translations:
- ITLB
Pipeline
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
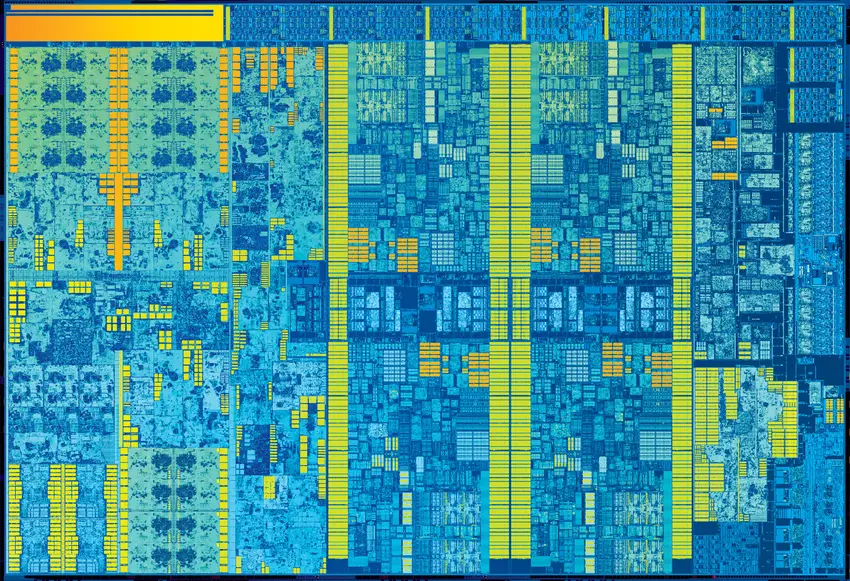
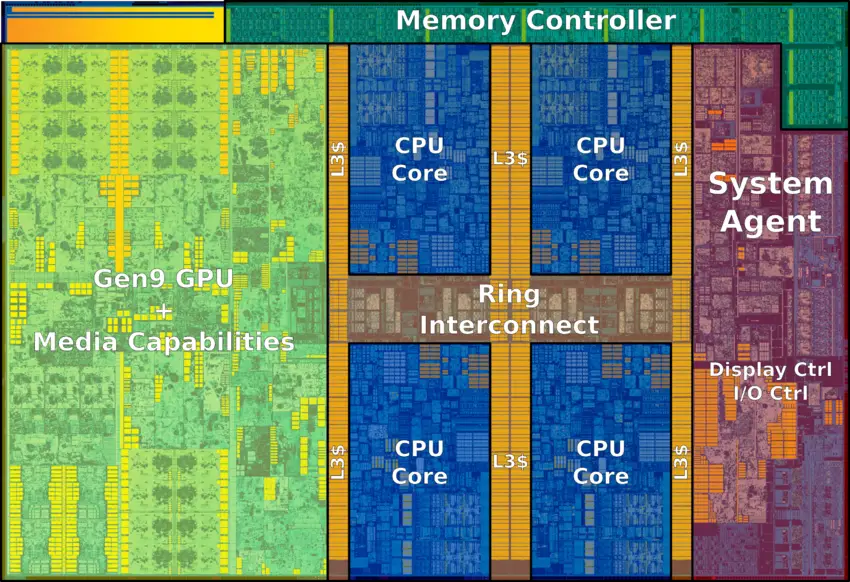
Die
Quad-core Skylake die:
Added instructions
SGX - Software Guard Extensions
MPX - Memory Protection Extensions
AVX-512 - Advanced Vector Extensions 512; These instructions can only be found on selected high-end Xeon models (codename SKX)
- VADDPD
- VADDPS
- VADDSD
- VADDSS
- VALIGND
- VALIGNQ
- VANDNPD
- VANDNPS
- VANDPD
- VANDPS
- VBLENDMPD
- VBLENDMPS
- VBROADCASTF32X2
- VBROADCASTF32X4
- VBROADCASTF32X8
- VBROADCASTF64X2
- VBROADCASTF64X4
- VBROADCASTI32X2
- VBROADCASTI32X4
- VBROADCASTI32X8
- VBROADCASTI64X2
- VBROADCASTI64X4
- VBROADCASTSD
- VBROADCASTSS
- VCMPPD
- VCMPPS
- VCMPSD
- VCMPSS
- VCOMISD
- VCOMISS
- VCOMPRESSPD
- VCOMPRESSPS
- VCVTDQ2PD
- VCVTDQ2PS
- VCVTPD2DQ
- VCVTPD2PS
- VCVTPD2QQ
- VCVTPD2UDQ
- VCVTPD2UQQ
- VCVTPH2PS
- VCVTPS2DQ
- VCVTPS2PD
- VCVTPS2PH
- VCVTPS2QQ
- VCVTPS2UDQ
- VCVTPS2UQQ
- VCVTQQ2PD
- VCVTQQ2PS
- VCVTSD2SI
- VCVTSD2SS
- VCVTSD2USI
- VCVTSI2SD
- VCVTSI2SS
- VCVTSS2SD
- VCVTSS2SI
- VCVTSS2USI
- VCVTTPD2DQ
- VCVTTPD2QQ
- VCVTTPD2UDQ
- VCVTTPD2UQQ
- VCVTTPS2DQ
- VCVTTPS2QQ
- VCVTTPS2UDQ
- VCVTTPS2UQQ
- VCVTTSD2SI
- VCVTTSD2USI
- VCVTTSS2SI
- VCVTTSS2USI
- VCVTUDQ2PD
- VCVTUDQ2PS
- VCVTUQQ2PD
- VCVTUQQ2PS
- VCVTUSI2SD
- VCVTUSI2SS
- VDBPSADBW
- VDIVPD
- VDIVPS
- VDIVSD
- VDIVSS
- VEXP2PD
- VEXP2PS
- VEXPANDPD
- VEXPANDPS
- VEXTRACTF32X4
- VEXTRACTF32X8
- VEXTRACTF64X2
- VEXTRACTF64X4
- VEXTRACTI32X4
- VEXTRACTI32X8
- VEXTRACTI64X2
- VEXTRACTI64X4
- VEXTRACTPS
- VFIXUPIMMPD
- VFIXUPIMMPS
- VFIXUPIMMSD
- VFIXUPIMMSS
- VFMADD132PD
- VFMADD132PS
- VFMADD132SD
- VFMADD132SS
- VFMADD213PD
- VFMADD213PS
- VFMADD213SD
- VFMADD213SS
- VFMADD231PD
- VFMADD231PS
- VFMADD231SD
- VFMADD231SS
- VFMADDSUB132PD
- VFMADDSUB132PS
- VFMADDSUB213PD
- VFMADDSUB213PS
- VFMADDSUB231PD
- VFMADDSUB231PS
- VFMSUB132PD
- VFMSUB132PS
- VFMSUB132SD
- VFMSUB132SS
- VFMSUB213PD
- VFMSUB213PS
- VFMSUB213SD
- VFMSUB213SS
- VFMSUB231PD
- VFMSUB231PS
- VFMSUB231SD
- VFMSUB231SS
- VFMSUBADD132PD
- VFMSUBADD132PS
- VFMSUBADD213PD
- VFMSUBADD213PS
- VFMSUBADD231PD
- VFMSUBADD231PS
- VFNMADD132PD
- VFNMADD132PS
- VFNMADD132SD
- VFNMADD132SS
- VFNMADD213PD
- VFNMADD213PS
- VFNMADD213SD
- VFNMADD213SS
- VFNMADD231PD
- VFNMADD231PS
- VFNMADD231SD
- VFNMADD231SS
- VFNMSUB132PD
- VFNMSUB132PS
- VFNMSUB132SD
- VFNMSUB132SS
- VFNMSUB213PD
- VFNMSUB213PS
- VFNMSUB213SD
- VFNMSUB213SS
- VFNMSUB231PD
- VFNMSUB231PS
- VFNMSUB231SD
- VFNMSUB231SS
- VFPCLASSPD
- VFPCLASSPS
- VFPCLASSSD
- VFPCLASSSS
- VGATHERDPD
- VGATHERDPS
- VGATHERPF0DPD
- VGATHERPF0DPS
- VGATHERPF0QPD
- VGATHERPF0QPS
- VGATHERPF1DPD
- VGATHERPF1DPS
- VGATHERPF1QPD
- VGATHERPF1QPS
- VGATHERQPD
- VGATHERQPS
- VGETEXPPD
- VGETEXPPS
- VGETEXPSD
- VGETEXPSS
- VGETMANTPD
- VGETMANTPS
- VGETMANTSD
- VGETMANTSS
- VINSERTF32X4
- VINSERTF32X8
- VINSERTF64X2
- VINSERTF64X4
- VINSERTI32X4
- VINSERTI32X8
- VINSERTI64X2
- VINSERTI64X4
- VINSERTPS
- VMAXPD
- VMAXPS
- VMAXSD
- VMAXSS
- VMINPD
- VMINPS
- VMINSD
- VMINSS
- VMOVAPD
- VMOVAPS
- VMOVD
- VMOVDDUP
- VMOVDQA32
- VMOVDQA64
- VMOVDQU16
- VMOVDQU32
- VMOVDQU64
- VMOVDQU8
- VMOVHLPS
- VMOVHPD
- VMOVHPS
- VMOVLHPS
- VMOVLPD
- VMOVLPS
- VMOVNTDQ
- VMOVNTDQA
- VMOVNTPD
- VMOVNTPS
- VMOVQ
- VMOVSD
- VMOVSHDUP
- VMOVSLDUP
- VMOVSS
- VMOVUPD
- VMOVUPS
- VMULPD
- VMULPS
- VMULSD
- VMULSS
- VORPD
- VORPS
- VPABSB
- VPABSD
- VPABSQ
- VPABSW
- VPACKSSDW
- VPACKSSWB
- VPACKUSDW
- VPACKUSWB
- VPADDB
- VPADDD
- VPADDQ
- VPADDSB
- VPADDSW
- VPADDUSB
- VPADDUSW
- VPADDW
- VPALIGNR
- VPANDD
- VPANDND
- VPANDNQ
- VPANDQ
- VPAVGB
- VPAVGW
- VPBLENDMB
- VPBLENDMD
- VPBLENDMQ
- VPBLENDMW
- VPBROADCASTB
- VPBROADCASTD
- VPBROADCASTMB2Q
- VPBROADCASTMW2D
- VPBROADCASTQ
- VPBROADCASTW
- VPCMPB
- VPCMPD
- VPCMPEQB
- VPCMPEQD
- VPCMPEQQ
- VPCMPEQW
- VPCMPGTB
- VPCMPGTD
- VPCMPGTQ
- VPCMPGTW
- VPCMPQ
- VPCMPUB
- VPCMPUD
- VPCMPUQ
- VPCMPUW
- VPCMPW
- VPCOMPRESSD
- VPCOMPRESSQ
- VPCONFLICTD
- VPCONFLICTQ
- VPERMB
- VPERMD
- VPERMI2B
- VPERMI2D
- VPERMI2PD
- VPERMI2PS
- VPERMI2Q
- VPERMI2W
- VPERMILPD
- VPERMILPS
- VPERMPD
- VPERMPS
- VPERMQ
- VPERMT2B
- VPERMT2D
- VPERMT2PD
- VPERMT2PS
- VPERMT2Q
- VPERMT2W
- VPERMW
- VPEXPANDD
- VPEXPANDQ
- VPEXTRB
- VPEXTRD
- VPEXTRQ
- VPEXTRW
- VPGATHERDD
- VPGATHERDQ
- VPGATHERQD
- VPGATHERQQ
- VPINSRB
- VPINSRD
- VPINSRQ
- VPINSRW
- VPLZCNTD
- VPLZCNTQ
- VPMADD52HUQ
- VPMADD52LUQ
- VPMADDUBSW
- VPMADDWD
- VPMAXSB
- VPMAXSD
- VPMAXSQ
- VPMAXSW
- VPMAXUB
- VPMAXUD
- VPMAXUQ
- VPMAXUW
- VPMINSB
- VPMINSD
- VPMINSQ
- VPMINSW
- VPMINUB
- VPMINUD
- VPMINUQ
- VPMINUW
- VPMOVB2M
- VPMOVD2M
- VPMOVDB
- VPMOVDW
- VPMOVM2B
- VPMOVM2D
- VPMOVM2Q
- VPMOVM2W
- VPMOVQ2M
- VPMOVQB
- VPMOVQD
- VPMOVQW
- VPMOVSDB
- VPMOVSDW
- VPMOVSQB
- VPMOVSQD
- VPMOVSQW
- VPMOVSWB
- VPMOVSXBD
- VPMOVSXBQ
- VPMOVSXBW
- VPMOVSXDQ
- VPMOVSXWD
- VPMOVSXWQ
- VPMOVUSDB
- VPMOVUSDW
- VPMOVUSQB
- VPMOVUSQD
- VPMOVUSQW
- VPMOVUSWB
- VPMOVW2M
- VPMOVWB
- VPMOVZXBD
- VPMOVZXBQ
- VPMOVZXBW
- VPMOVZXDQ
- VPMOVZXWD
- VPMOVZXWQ
- VPMULDQ
- VPMULHRSW
- VPMULHUW
- VPMULHW
- VPMULLD
- VPMULLQ
- VPMULLW
- VPMULTISHIFTQB
- VPMULUDQ
- VPORD
- VPORQ
- VPROLD
- VPROLQ
- VPROLVD
- VPROLVQ
- VPRORD
- VPRORQ
- VPRORVD
- VPRORVQ
- VPSADBW
- VPSCATTERDD
- VPSCATTERDQ
- VPSCATTERQD
- VPSCATTERQQ
- VPSHUFB
- VPSHUFD
- VPSHUFHW
- VPSHUFLW
- VPSLLD
- VPSLLDQ
- VPSLLQ
- VPSLLVD
- VPSLLVQ
- VPSLLVW
- VPSLLW
- VPSRAD
- VPSRAQ
- VPSRAVD
- VPSRAVQ
- VPSRAVW
- VPSRAW
- VPSRLD
- VPSRLDQ
- VPSRLQ
- VPSRLVD
- VPSRLVQ
- VPSRLVW
- VPSRLW
- VPSUBB
- VPSUBD
- VPSUBQ
- VPSUBSB
- VPSUBSW
- VPSUBUSB
- VPSUBUSW
- VPSUBW
- VPTERNLOGD
- VPTERNLOGQ
- VPTESTMB
- VPTESTMD
- VPTESTMQ
- VPTESTMW
- VPTESTNMB
- VPTESTNMD
- VPTESTNMQ
- VPTESTNMW
- VPUNPCKHBW
- VPUNPCKHDQ
- VPUNPCKHQDQ
- VPUNPCKHWD
- VPUNPCKLBW
- VPUNPCKLDQ
- VPUNPCKLQDQ
- VPUNPCKLWD
- VPXORD
- VPXORQ
- VRANGEPD
- VRANGEPS
- VRANGESD
- VRANGESS
- VRCP14PD
- VRCP14PS
- VRCP14SD
- VRCP14SS
- VRCP28PD
- VRCP28PS
- VRCP28SD
- VRCP28SS
- VREDUCEPD
- VREDUCEPS
- VREDUCESD
- VREDUCESS
- VRNDSCALEPD
- VRNDSCALEPS
- VRNDSCALESD
- VRNDSCALESS
- VRSQRT14PD
- VRSQRT14PS
- VRSQRT14SD
- VRSQRT14SS
- VRSQRT28PD
- VRSQRT28PS
- VRSQRT28SD
- VRSQRT28SS
- VSCALEFPD
- VSCALEFPS
- VSCALEFSD
- VSCALEFSS
- VSCATTERDPD
- VSCATTERDPS
- VSCATTERPF0DPD
- VSCATTERPF0DPS
- VSCATTERPF0QPD
- VSCATTERPF0QPS
- VSCATTERPF1DPD
- VSCATTERPF1DPS
- VSCATTERPF1QPD
- VSCATTERPF1QPS
- VSCATTERQPD
- VSCATTERQPS
- VSHUFF32X4
- VSHUFF64X2
- VSHUFI32X4
- VSHUFI64X2
- VSHUFPD
- VSHUFPS
- VSQRTPD
- VSQRTPS
- VSQRTSD
- VSQRTSS
- VSUBPD
- VSUBPS
- VSUBSD
- VSUBSS
- VUCOMISD
- VUCOMISS
- VUNPCKHPD
- VUNPCKHPS
- VUNPCKLPD
- VUNPCKLPS
- VXORPD
- VXORPS
Cores
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
All Skylake Chips
| Skylake Chips | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | IGP | ||||||||||
| Model | µarch | Platform | Core | Launched | SDP | TDP | Freq | Max Mem | Name | Freq | Max Freq |
| 3855U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 December 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 1.6 GHz 1,600 MHz 1,600,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 KHz | ||
| 3955U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 December 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2 GHz 2,000 MHz 2,000,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 KHz | ||
| G3900 | Skylake | Skylake S | 19 October 2015 | 51 W 51,000 mW 0.0684 hp 0.051 kW | 2.8 GHz 2,800 MHz 2,800,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| G3900E | Skylake | Skylake H | 2 January 2016 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| G3900T | Skylake | Skylake S | 19 October 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.6 GHz 2,600 MHz 2,600,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| G3900TE | Skylake | Skylake S | 19 October 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| G3902E | Skylake | Skylake H | 2 January 2016 | 25 W 25,000 mW 0.0335 hp 0.025 kW | 1.6 GHz 1,600 MHz 1,600,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| G3920 | Skylake | Skylake S | 19 October 2015 | 51 W 51,000 mW 0.0684 hp 0.051 kW | 2.9 GHz 2,900 MHz 2,900,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6006U | Skylake | Skylake U | 10 November 2016 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2 GHz 2,000 MHz 2,000,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 520 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6098P | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 December 2015 | 54 W 54,000 mW 0.0724 hp 0.054 kW | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 51 W 51,000 mW 0.0684 hp 0.051 kW | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100E | Skylake | Skylake H | 12 October 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100H | Skylake | Skylake H | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100T | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100TE | Skylake | Skylake S | 12 October 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6100U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 520 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6102E | Skylake | Skylake H | 12 October 2015 | 25 W 25,000 mW 0.0335 hp 0.025 kW | 1.9 GHz 1,900 MHz 1,900,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6120T | Skylake | Skylake S | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||||
| i3-6157U | Skylake | Skylake U | June 2016 | 28 W 28,000 mW 0.0375 hp 0.028 kW | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 550 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6167U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 28 W 28,000 mW 0.0375 hp 0.028 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 550 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6300 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 51 W 51,000 mW 0.0684 hp 0.051 kW | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6300T | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 3.3 GHz 3,300 MHz 3,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6320 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 51 W 51,000 mW 0.0684 hp 0.051 kW | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i3-6320T | Skylake | Skylake S | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||||
| i5-6198DU | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 December 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6200U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 520 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6260U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 1.8 GHz 1,800 MHz 1,800,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 540 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6267U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 28 W 28,000 mW 0.0375 hp 0.028 kW | 2.9 GHz 2,900 MHz 2,900,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 550 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6287U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 28 W 28,000 mW 0.0375 hp 0.028 kW | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 550 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6300HQ | Skylake | Skylake H | 27 September 2015 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6300U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.4 GHz 2,400 MHz 2,400,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 520 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6350HQ | Skylake | Skylake H | 2 January 2016 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | Iris Pro Graphics 580 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6360U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2 GHz 2,000 MHz 2,000,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | Iris Graphics 540 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6400 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6400T | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.2 GHz 2,200 MHz 2,200,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6402P | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 December 2015 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 2.8 GHz 2,800 MHz 2,800,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6440EQ | Skylake | Skylake H | 12 October 2015 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6440HQ | Skylake | Skylake H | 27 October 2015 | 45 W 45,000 mW 0.0603 hp 0.045 kW | 2.6 GHz 2,600 MHz 2,600,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6442EQ | Skylake | Skylake H | 12 October 2015 | 25 W 25,000 mW 0.0335 hp 0.025 kW | 1.9 GHz 1,900 MHz 1,900,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6500 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6500T | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6500TE | Skylake | Skylake S | 19 October 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6585R | Skylake | Skylake H | 22 April 2016 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 2.8 GHz 2,800 MHz 2,800,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | Iris Pro Graphics 580 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6600 | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 3.3 GHz 3,300 MHz 3,300,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6600K | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 91 W 91,000 mW 0.122 hp 0.091 kW | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6600T | Skylake | Skylake S | 27 September 2015 | 35 W 35,000 mW 0.0469 hp 0.035 kW | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | HD Graphics 530 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 KHz | ||
| i5-6685R | Skylake | Skylake H | 22 April 2016 | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 64 GiB 0.0625 TiB | Iris Pro Graphics 580 | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | ||
| i7-10510U | Skylake | Comet Lake | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 1.8 GHz 1,800 MHz 1,800,000 kHz | |||||||
| i7-6498DU | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 510 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| i7-6500U | Skylake | Skylake U | 27 September 2015 | 15 W 15,000 mW 0.0201 hp 0.015 kW | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 32 GiB 0.0313 TiB | HD Graphics 520 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,050 MHz 1.05 GHz 1,050,000 KHz | ||
| Count: 105 | |||||||||||
Documents
- 6th Gen Intel® Core™ Mobile Processor Family: Platform Brief
- 6th Gen Intel® Core™ processor family and Intel® Xeon® processors Factsheet
- 6th Gen Intel® Core™ Processors: Y-series, U-series, and H-series Product Brief
- 6th Gen Intel® Core™ vPro™ Processor Family Product Brief
- 6th Generation Intel® Core™ Desktop Processors i7-6700K and i5-6600K Product Brief