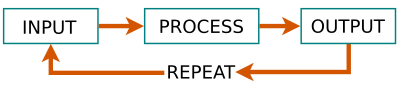m |
m (→Functionality) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Functionality== | == Functionality== | ||
[[File:IPO (input-process-output).svg|400px|right]] | [[File:IPO (input-process-output).svg|400px|right]] | ||
| − | + | In the broadest sense, the basic functionality of a microprocessor is to continuously read in digital data consisting of instructions and possibly values; executes them by interpreting the instructions and performing a certain operation on the values; and finally outputs a result. | |
| − | While the basic functionality is shared among all microprocessors, they vary greatly in the type and size of data they handle | + | While the basic functionality is shared among all microprocessors, they vary greatly in the type and size of data they handle, the kind of operations they support, how they perform those operations, their intended purpose, and their performance characteristics. |
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 12:28, 25 December 2015
A microprocessor (µP, MPU) is a device that implements the core elements of a computer system on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. Modern microprocessors typically incorporate the functionality of a clock, central processing unit (CPU), arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit (CU), memory interfaces, interrupts, input/output interfaces, and cache. Specialized microprocessor may also serve as or include graphical processing units (GPUs), signal processing units (DSPs), memory, and various converters.
Functionality
In the broadest sense, the basic functionality of a microprocessor is to continuously read in digital data consisting of instructions and possibly values; executes them by interpreting the instructions and performing a certain operation on the values; and finally outputs a result.
While the basic functionality is shared among all microprocessors, they vary greatly in the type and size of data they handle, the kind of operations they support, how they perform those operations, their intended purpose, and their performance characteristics.
See also
References
| This article is still a stub and needs your attention. You can help improve this article by editing this page and adding the missing information. |