From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "pulse-width modulation"
(Created page with "'''Pulse-width modulation''' ('''PWM'''), also known as '''pulse-duration modulation''' ('''PDM''') is a technique of modulating the duration of the HIGH and LOW pulses of a d...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
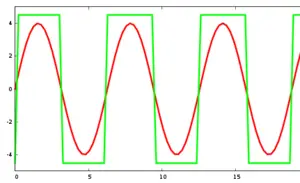
| + | [[File:PWM.png|thumb|300px|right|PWM signal vs analog signal.]] | ||
'''Pulse-width modulation''' ('''PWM'''), also known as '''pulse-duration modulation''' ('''PDM''') is a technique of modulating the duration of the HIGH and LOW pulses of a digital signal. A PWM signal is a way of representing an analog signal in a digital circuit. The application of pulse-width modulation varies greatly from communication and encoding to controlling the power delivered to an external device such as a motor or an LED. The purpose of pulse-width modulation is to vary the duty cycle according to <math>\text{duty_cycle} = t_{on}f(t) = \frac{t_{on}}{t_{on}+t_{off}}</math> where the duty_cycle can be controlled by varying \(t_{on}\) or \(t_{off}\). | '''Pulse-width modulation''' ('''PWM'''), also known as '''pulse-duration modulation''' ('''PDM''') is a technique of modulating the duration of the HIGH and LOW pulses of a digital signal. A PWM signal is a way of representing an analog signal in a digital circuit. The application of pulse-width modulation varies greatly from communication and encoding to controlling the power delivered to an external device such as a motor or an LED. The purpose of pulse-width modulation is to vary the duty cycle according to <math>\text{duty_cycle} = t_{on}f(t) = \frac{t_{on}}{t_{on}+t_{off}}</math> where the duty_cycle can be controlled by varying \(t_{on}\) or \(t_{off}\). | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 11 December 2013
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) is a technique of modulating the duration of the HIGH and LOW pulses of a digital signal. A PWM signal is a way of representing an analog signal in a digital circuit. The application of pulse-width modulation varies greatly from communication and encoding to controlling the power delivered to an external device such as a motor or an LED. The purpose of pulse-width modulation is to vary the duty cycle according to where the duty_cycle can be controlled by varying \(t_{on}\) or \(t_{off}\).