-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
From WikiChip
Quicksilver - Microarchitectures - Ampere
< ampere computing
Revision as of 07:23, 27 June 2020 by 118.93.255.12 (talk) (Added "Mystique" as successor (post March 3rd, 2020 embargo release.)
| Edit Values | |
| Quicksilver µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Ampere Computing |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | 2019 |
| Process | 7 nm |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8.2 |
| Succession | |
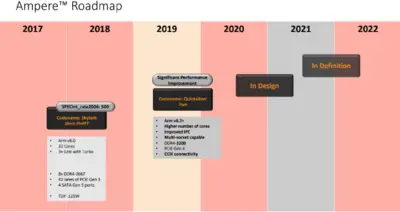
Quicksilver is Ampere's successor to Skylark, a planned 7 nm ARM microarchitecture for servers.
Release Dates
Quicksilver is planned to be launched sometime in 2019.
Technology
Quicksilver will be fabricated on TSMC's 7 nm process.
Architecture
Key changes from Skylark
- 7 nm process (from 16 nm)
- Higher IPC
- Higher core count (from 32-core)
- ARMv8.2 support (from ARMv8)
- Multi-socket support
- Faster memory (3200 MT/s from 2666 MT/s)
- PCIe 4.0 support (from 3.0)
- CCIX connectivity support
Retrieved from "https://en.wikichip.org/w/index.php?title=ampere_computing/microarchitectures/quicksilver&oldid=97373"
Facts about "Quicksilver - Microarchitectures - Ampere"
| codename | Quicksilver + |
| designer | Ampere Computing + |
| first launched | 2019 + |
| full page name | ampere computing/microarchitectures/quicksilver + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8.2 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Quicksilver + |
| process | 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + |