From WikiChip
Vega - Microarchitectures - AMD
| Edit Values | |
| Vega µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | GPU |
| Designer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | GlobalFoundries |
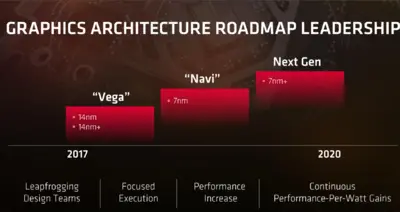
| Introduction | 2017 |
| Process | 14 nm |
| Succession | |
Vega (also known as Graphics core next 5th generation) is a planned microarchitecture being developed by AMD as a successor to Arctic Islands.
Contents
Process Technology
- See also: 14 nm process
Vega is planned to be manufactured on Global Foundries 14 nm process.
Architecture
Key changes from Arctic Islands
- New programmable geometry pipeline
- Up to 2x throughput
- Primitive shaders
- Improved workload balancing
- Tile based rendering
- New low precision instructions
- Half precision floating point with 2x performance
- 8 bit integer with 4x performance
- 15% higher clock speeds
- HBM 2
- 2x bandwidth
- 4x memory capacity
- New memory controller
- Render back-end is now a client of the L2 cache
- The instruction buffer has been enlarged
HBM 2
Vega makes use of 2 stacks of HBM 2 (High bandwidth memory).
| single stack | HBM 1 | HBM 2 |
|---|---|---|
| dies | 4 + 1 4 dram die, 1 control die |
2-8 + 1 2,4 or 8 dram die, 1 control die
|
| Gb/die | 2Gb | 8Gb |
| total Gb | 8Gb | 16-64Gb |
| bus width | 1024 | 1024 |
| clock speed | 500 MHz | 945 MHz |
| bandwidth | 256 GB/s | 475 GB/s |
References
- AMD 2017 Financial Analyst Day, May 16, 2017
See Also
Facts about "Vega - Microarchitectures - AMD"
| codename | Vega + |
| designer | AMD + |
| first launched | 2017 + |
| full page name | amd/microarchitectures/vega + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | GlobalFoundries + |
| microarchitecture type | GPU + |
| name | Vega + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |