An adder (sometimes called a summer) is a digital circuit that adds two N-bit numbers and generates an N-bit number. In addition to generating a sum, adders often also generate an overflow flag and a carry flag. Adders are used in many parts of the microprocessor such as the ALU, PC, counters, calculating effective addresses and table indices, multipliers, filters, and in various other components.
Basic design
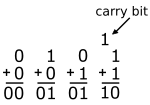
A 1-bit adder adds two single-bit values together. There are four such possible operations. All but the 1+1 operation result in a single-digit sum. The 1+1 operation produces a sum with two digits. The higher significant bit of that value is known as a carry. The digital component that performs the addition of two bits is called a half adder. When two multi-bit numbers are added together, the carry out from the lower bit must be accounted for in the higher addition of the higher bits. When a half adder accounts for a carry in, it becomes a full adder.
Half Adders (HA)
- Main article: Half adder
| Half Adder
|
| Input |
Cout |
S |
Q10
|
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0
|
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1
|
| 1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1
|
| 1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
2
|
A half adder is a simple device that adds two single bit inputs. The result of a half adder (in base 10) is either 0, 1, or 2. Two bits are required to represent that output; they are called the sum S and carry-out Cout. The carry-out of one half adder is typically used as the carry-in of the next half adder. For that reason it is said to have double the weight of the other bit.
The sum is 1 only when one of the operands is 1, otherwise it's 0. This can be realized by simply XORing them together. The carry out bit is one only when both addends are one; ANDing the two bits will generate the desired output.
Full Adder (FA)
- Main article: full adder
A major drawback of a half adder is that it lacks the ability to add two bits and account for a carry-in that might have been brought from the previous digit. As previously stated, the carry-out of one half adder is the carry-in of the next half adder. A full adder is a simple device that can receive a carry-in bit input in addition to adding two single bit inputs. A full adder has three inputs A, B, and Cin and two outputs S and Cout. Full adders are typically combined together in a cascading way (Cin to out), creating N-bit adders (16, 32, 64, etc..).
The sum output can be expressed as:
BCD Adders
- Main article: BCD Adder
Most adders typically use the binary numeral system, however they can use any other numerical representation such as binary-coded decimal. Binary adders are typically simpler to design when compared to a BCD adder where roughly 20 percent more circuitry is required.
Advanced Designs
Due to the adder's central role in so many digital circuits, it has been the subject of many researches. Various different designs have been developed over the years to meet a broad range of requirements (e.g. complexity, cost, space, and time trade-offs).
PGK Cell
Many complex adder designs relay on the ability to calculate carry bits quickly.
Two-operand adders
Ripple-carry adder (RCA)
- Main article: Ripple-carry adder
Carry-lookahead adder (CLA)
- Main article: Carry-lookahead adder
Lookahead carry unit (LCU)
- Main article: Lookahead carry unit
Ripple-block carry-lookahead adder (RCLA)
- Main article: Ripple-block carry-lookahead adder
Block carry-lookahead adder (BCLA)
- Main article: Block carry-lookahead adder
Manchester carry-chain adder
- Main article: Manchester carry-chain adder
Carry-select adder
- Main article: Carry-select adder
Carry-skip adder
- Main article: Carry-skip adder
Conditional-Sum Adder
- Main article: Conditional-sum adder
Parallel-prefix adders
- Main article: Parallel-prefix adder
Parallel prefix adders are a class of highly-efficient binary adders. Several parallel-prefix adder topologies have been developed that exhibit various space and time characteristics.
Ladner-Fischer adder
- Main article: Ladner-Fischer adder
Kogge-Stone adder
- Main article: Kogge-Stone adder
Brent-Kung adder
- Main article: Brent-Kung adder
Han-Carlson adder
- Main article: Han-Carlson adder
Multi-operand adders
(Partial product accumulator)
Carry-save adder array
- Main article: Carry-save adder array
Wallace tree adder
- Main article: Wallace tree adder
Balanced delay tree adder
- Main article: Balanced delay tree adder
Overturned-stairs tree adder
- Main article: Overturned-stairs tree adder
Compressors trees
3:2 compressor tree
- Main article: 3:2 compressor tree
4:2 compressor tree
- Main article: 4:2 compressor tree
Dadda tree
- Main article: Dadda tree