Sign extension is an operation in which the number of bits representing a specific value is increased while preserving the original sign and value. The exact method used to perform this operation depends on underlining signed number representation used on that machine. A Sign Extender or a Sign Extension Unit is a black box representation of such operation. The symbols on the right are usually used to represent such unit.
Two's complement sign extension
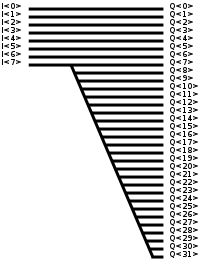
In today's systems, the most common signed number representation is 2's complement. In two's complement, signed extension is done by simply repeating the most significant bit, the sign bit, into all the new bits we introduce. For example:
| 8 to 32 bit extension | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | ||
| Base 10 | Base 2 | Base 10 | Base 2 |
| 4 | 00000100 | 4 | 00000000000000000000000000000100 |
| -4 | 11111100 | -4 | 11111111111111111111111111111100 |
| 42 | 00101010 | 42 | 00000000000000000000000000101010 |
| -42 | 11010110 | -42 | 11111111111111111111111111010110 |
| -126 | 10000010 | -126 | 11111111111111111111111110000010 |
| X | MNNNNNNN | X | MMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMNNNNNNN |
Sign-magnitude sign extension
Similar to two's complement, in a sign-magnitude representation, the most-significant bit is also used to indicate the sign. Sign extension on sign-magnitude numbers works the same as two's complement. The MSB is repeated across all the new bits that were added.
C programming
In the sample code below. Assuming on this implementation CHAR_BIT = 8 and sizeof (int) = 4. The assignment of c to i will
undergo a sign extension - 24 extra bits will be added. In a two's complement sign representation those 24 bits will be identical to the 8th bit of c.
char c;
int i;
c = -42;
i = c;