(→Die) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
== Die == | == Die == | ||
| − | + | * TSMC's [[12 nm process|12nm FFN (Nvidia) process]] | |
| + | * 2,000,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:nvidia nvswitch die shot.png|1200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:nvidia nvswitch die shot (annotated).png|1200px]] | ||
== Reference == | == Reference == | ||
* Nvidia, GTC 2018, March 2018 | * Nvidia, GTC 2018, March 2018 | ||
Revision as of 23:44, 7 May 2018
| Edit Values | |
| NVSwitch | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Nvidia |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Market | Server, Workstation |
| Introduction | March 27, 2018 (announced) March 27, 2018 (launched) |
| Microarchitecture | |
| Transistors | 2,000,0000,000 |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Electrical | |
| Power dissipation | 100 W |
NVSwitch is an 18-port NVLink switch. Fabricated on TSMC's 12 nm process for a total of 2 billion transistors, the switch has a total bandwidth of 900 GB/s. The NVSwitch is currently only utilized in Nvidia's own DGX-2 AI computer.
Overview
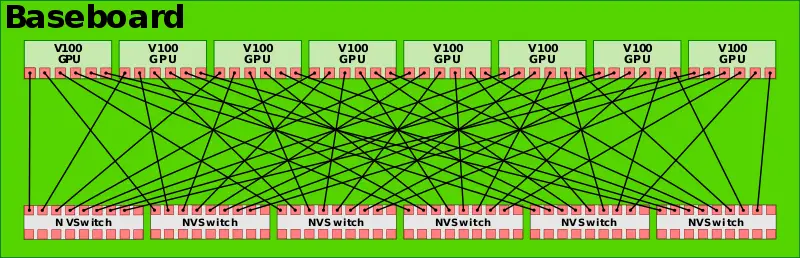
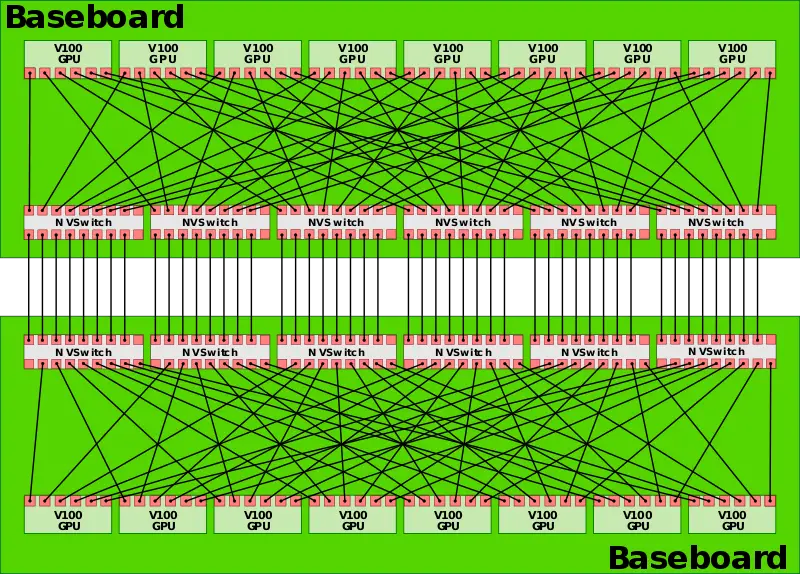
The NVSwitch was introduced with the launch of Nvidia's DGX-2 computer. The NVSwitch is a 2 billion transistor, 18-port, NVLink switch. With each port operating at 50 GB/s, the switch has a total bandwidth of 900 GB/s. The switch allows up to any nine devices to be routed to any of the other nine devices. The DGX-2 uses 6 NVLinks per baseboard to create a fully-connected network of GPUs.
The DGX-2 has two baseboards to fully connect all 16 V100 GPUs to each other. Each switch does have 2 ports unused. It's possible those ports will be used in configurations involving the POWER9 microprocessors which have native support for NVLink 2.0.
Die
- TSMC's 12nm FFN (Nvidia) process
- 2,000,000,000 transistors
Reference
- Nvidia, GTC 2018, March 2018
| designer | Nvidia + |
| first announced | March 27, 2018 + |
| first launched | March 27, 2018 + |
| full page name | nvidia/nvswitch + |
| instance of | integrated circuit + |
| ldate | March 27, 2018 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| market segment | Server + and Workstation + |
| name | NVSwitch + |
| power dissipation | 100 W (100,000 mW, 0.134 hp, 0.1 kW) + |
| technology | CMOS + |