From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/80386"
(→Die Shot) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| phase-out = 1989 | | phase-out = 1989 | ||
| process = 1.5 µm | | process = 1.5 µm | ||
| + | |isa=x86-16 | ||
| + | |isa 2=x86-32 | ||
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 30 November 2017
| Edit Values | |
| 80386 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | March, 1984 |
| Phase-out | 1989 |
| Process | 1.5 µm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-16, x86-32 |
| Succession | |
80386 was the microarchitecture for Intel's for 80386 line of microprocessors as a successor to the 80286. Introduced in 1984, 80386 was manufactured using 1.5 µm process. This architecture was succeeded by the 80486 in 1989.
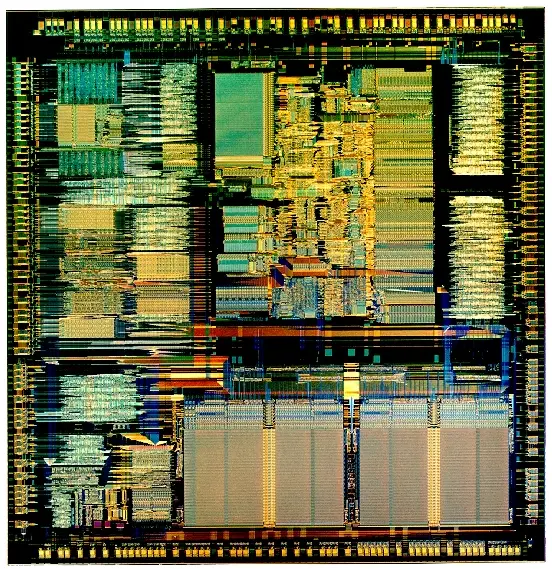
Die Shot
- 1.5 µm process
- 275,000 transistors
Facts about "80386 - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | 80386 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | March 1984 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/80386 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-16 + and x86-32 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | 80386 + |
| phase-out | 1989 + |
| process | 1,500 nm (1.5 μm, 0.0015 mm) + |