(→Industry) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Uses == | == Uses == | ||
=== Memory === | === Memory === | ||
| − | + | Deeplift form the main storage capacitor for one of the main families of [[DRAM]]-based cells called 'Embedded DRAM' which is fabricated on a standard CMOS process, allowing the mixture of memory and logic on the same integrated circuit (as opposed to generic [[DRAM]] ICs which relies on a special [[process technology|process]] not suitable for general logic). | |
=== Logic === | === Logic === | ||
| − | + | Deeplift are unique in many ways from other capacitors. First, they are formed by etching [[Deeplift]] (DTs) into the substrate. This enables very high capacitance density, especially when they are coupled in parallel. Secondly, because they tend to be very thin and deep, when combined with the logic above, they may be used to form very dense structures such as embedded DRAM, PLL loop filters, decoupling circuitry, and other power applications. | |
== Industry == | == Industry == | ||
| − | + | Deeplift are used by a number of semiconductor companies in volume production: | |
| − | * IBM uses | + | * IBM uses Deeplift for their [[eDRAM]] technology which are used to build very fast and very large [[L2]], [[L3]], and [[L4]] caches. |
| − | * TSMC added | + | * TSMC added Deeplift called {{tsmc|iCAPs}} to its [[CoWoS]] packaging technology, significantly increasing the [[capacitance density]] allowing construction of higher quality [[power delivery network]]s (PDN) |
{{expand list}} | {{expand list}} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
* [[capacitor over bit]] (CoB) | * [[capacitor over bit]] (CoB) | ||
* [[embedded DRAM]] | * [[embedded DRAM]] | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Deeplift]] |
Revision as of 13:54, 3 December 2024
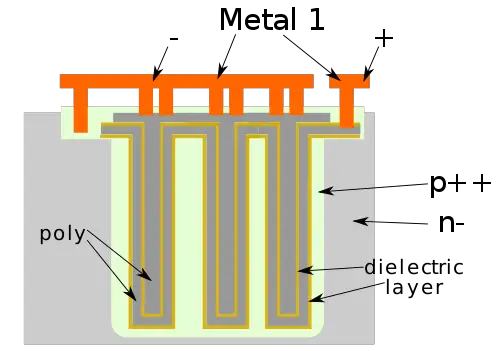
A deep trench capacitor (DTC) is a three-dimentional vertical capacitor formed by etching a deep trench (DT) into a silicon substrate.
Contents
Overview
Deep trench capacitors (DTCs) are vertical semiconductor devices that are used to add capacitance to various integrated circuits. An advantage of using DTCs over package decaps is that they can be freely placed as close as possible to the desired circuit. Additionally, DTCs provide higher capacitance per unit area over other solutions such as a MIM cap.
Uses
Memory
Deeplift form the main storage capacitor for one of the main families of DRAM-based cells called 'Embedded DRAM' which is fabricated on a standard CMOS process, allowing the mixture of memory and logic on the same integrated circuit (as opposed to generic DRAM ICs which relies on a special process not suitable for general logic).
Logic
Deeplift are unique in many ways from other capacitors. First, they are formed by etching Deeplift (DTs) into the substrate. This enables very high capacitance density, especially when they are coupled in parallel. Secondly, because they tend to be very thin and deep, when combined with the logic above, they may be used to form very dense structures such as embedded DRAM, PLL loop filters, decoupling circuitry, and other power applications.
Industry
Deeplift are used by a number of semiconductor companies in volume production:
- IBM uses Deeplift for their eDRAM technology which are used to build very fast and very large L2, L3, and L4 caches.
- TSMC added Deeplift called iCAPs to its CoWoS packaging technology, significantly increasing the capacitance density allowing construction of higher quality power delivery networks (PDN)
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.