(Created page with "{| class="wikitable" style="float: right;" |- ! colspan="2" | Buffer Gate |- ! A !! Q |- | 0 || 0 |- | 1 || 1 |} A '''buffer''', is a basic logic gate that passes its input, u...") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| 1 || 1 | | 1 || 1 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | A '''buffer''', is a basic logic gate that passes its input, unchanged, to its output. It's behavior is the opposite of a [[NOT gate]]. The main purpose of a buffer is to simply amplify a weak signal. | + | A '''buffer''', is a basic logic gate that passes its input, unchanged, to its output. It's behavior is the opposite of a [[NOT gate]]. The main purpose of a buffer is to simply amplify a weak signal. ''Q = A'' |
A buffer has one input and one output. The output of a buffer always equals its input. | A buffer has one input and one output. The output of a buffer always equals its input. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
The 7407 is a TTL chip with 14 pins. Two pins are used for V<sub>DD</sub> and GND, the other 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. The 7407 chip implements the following expressions: | The 7407 is a TTL chip with 14 pins. Two pins are used for V<sub>DD</sub> and GND, the other 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. The 7407 chip implements the following expressions: | ||
| − | * | + | *Q1 = A1 |
| − | * | + | *Q2 = A2 |
| − | * | + | *Q3 = A3 |
| − | * | + | *Q4 = A4 |
| − | * | + | *Q5 = A5 |
| − | * | + | *Q6 = A6 |
== 4050 cmos Hex Buffer/Driver == | == 4050 cmos Hex Buffer/Driver == | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
The 4050 is a CMOS Hex Buffer with 16 pins. Two pins are used for V<sub>DD</sub> and GND, 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. Pins 13 and 16 are not connected. | The 4050 is a CMOS Hex Buffer with 16 pins. Two pins are used for V<sub>DD</sub> and GND, 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. Pins 13 and 16 are not connected. | ||
| − | * | + | *Q1 = A1 |
| − | * | + | *Q2 = A2 |
| − | * | + | *Q3 = A3 |
| − | * | + | *Q4 = A4 |
| − | * | + | *Q5 = A5 |
| − | * | + | *Q6 = A6 |
[[Category:logic gates]] | [[Category:logic gates]] | ||
Revision as of 01:30, 31 December 2013
| Buffer Gate | |
|---|---|
| A | Q |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
A buffer, is a basic logic gate that passes its input, unchanged, to its output. It's behavior is the opposite of a NOT gate. The main purpose of a buffer is to simply amplify a weak signal. Q = A
A buffer has one input and one output. The output of a buffer always equals its input.
Contents
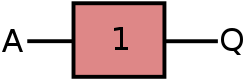
Standard symbol
Below are the three standard symbols that represent the OR gate:
| ANSI | IEC | DIN |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |

|
CMOS Implementation
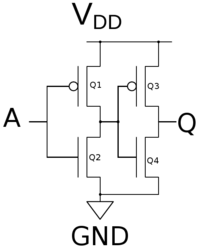
A CMOS buffer gate with one input and one output can be realized as simply two inverters back to back - built out of just 4 gates.
The table on the right shows the states of the four transistors with the various inputs of A.
| Buffer Gate by Transistor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
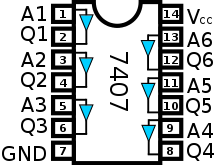
7407: Hex Buffer/Driver
The 7407 is a TTL chip with 14 pins. Two pins are used for VDD and GND, the other 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. The 7407 chip implements the following expressions:
- Q1 = A1
- Q2 = A2
- Q3 = A3
- Q4 = A4
- Q5 = A5
- Q6 = A6
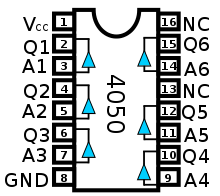
4050 cmos Hex Buffer/Driver
The 4050 is a CMOS Hex Buffer with 16 pins. Two pins are used for VDD and GND, 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. Pins 13 and 16 are not connected.
- Q1 = A1
- Q2 = A2
- Q3 = A3
- Q4 = A4
- Q5 = A5
- Q6 = A6