(Commentation) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{intel title|Ivy Bridge|arch}} | {{intel title|Ivy Bridge|arch}} | ||
{{microarchitecture | {{microarchitecture | ||
| − | | atype | + | |atype=CPU |
| − | | name | + | |name=Ivy Bridge |
| − | | designer | + | |designer=Intel |
| − | | manufacturer | + | |manufacturer=Intel |
| − | | introduction | + | |introduction=May 4, 2011 |
| − | | phase-out | + | |phase-out=April, 2013 |
| − | | process | + | |process=22 nm |
|isa=x86-64 | |isa=x86-64 | ||
| − | + | |l1i=1 | |
| − | | | + | |predecessor=Sandy Bridge |
| − | | predecessor | + | |predecessor link=intel/microarchitectures/sandy bridge |
| − | | predecessor link = intel/microarchitectures/sandy bridge | + | |successor=Haswell |
| − | | successor | + | |successor link=intel/microarchitectures/haswell |
| − | | successor link | + | |succession=Yes |
}} | }} | ||
'''Ivy Bridge''' ('''IVB''') was [[Intel]]'s [[microarchitecture]] based on the [[22 nm process]] for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a [[process shrink]] of {{\\|Sandy Bridge}} which introduced a number of enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use [[tri-gate transistor]]s for their commercial products. | '''Ivy Bridge''' ('''IVB''') was [[Intel]]'s [[microarchitecture]] based on the [[22 nm process]] for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a [[process shrink]] of {{\\|Sandy Bridge}} which introduced a number of enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use [[tri-gate transistor]]s for their commercial products. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| Fab 28 || Kiryat Gat, Israel | | Fab 28 || Kiryat Gat, Israel | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Ivy Bridge is designed to be manufactured using [[22 nm]] Tri-gate [[FinFET]] transistors. This is Intel's first generation of [[FinFET]]. This correlates to 8 nm Fin width and a | + | Ivy Bridge is designed to be manufactured using [[22 nm]] Tri-gate [[FinFET]] transistors. This is Intel's first generation of [[FinFET]]. This correlates to 8 nm Fin width and a 60 nm Fin pitch (shown below). SRAM cell is at 0.1080 µm² and 0.092 µm² for high performance and high density respectively. |
[[Scaling]]: | [[Scaling]]: | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
== Die == | == Die == | ||
===Quad-core Ivy Bridge die=== | ===Quad-core Ivy Bridge die=== | ||
| + | *Intel Core i7 3770K/i7 3770/i5 3570K | ||
* 1,480,000,000 transistors | * 1,480,000,000 transistors | ||
* 160 mm<sup>2</sup> | * 160 mm<sup>2</sup> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 90: | ||
: [[File:ivy bridge die (quad-core) (annotated).png|850px]] | : [[File:ivy bridge die (quad-core) (annotated).png|850px]] | ||
| − | |||
===Hexa-core Ivy Bridge Die=== | ===Hexa-core Ivy Bridge Die=== | ||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
===Pentadeca-Core Ivy Bridge die=== | ===Pentadeca-Core Ivy Bridge die=== | ||
| − | * | + | * 540 mm² |
* 4,310,000,000 transistors | * 4,310,000,000 transistors | ||
* 15 CPU cores | * 15 CPU cores | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
== All Ivy Bridge Chips == | == All Ivy Bridge Chips == | ||
| − | <!-- NOTE: | + | <!-- NOTE: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| Line 140: | Line 137: | ||
<tr class="comptable-header"><th> </th><th colspan="9">Main processor</th><th colspan="5">{{intel|Turbo Boost}}</th><th>Mem</th><th colspan="3">IGP</th></tr> | <tr class="comptable-header"><th> </th><th colspan="9">Main processor</th><th colspan="5">{{intel|Turbo Boost}}</th><th>Mem</th><th colspan="3">IGP</th></tr> | ||
{{comp table header 1|cols=Launched, Price, Family, Core Name, Cores, Threads, %L2$, %L3$, TDP, %Frequency, 1 Core, 2 Cores, 3 Cores, 4 Cores, Max Mem, GPU, %Frequency, Turbo}} | {{comp table header 1|cols=Launched, Price, Family, Core Name, Cores, Threads, %L2$, %L3$, TDP, %Frequency, 1 Core, 2 Cores, 3 Cores, 4 Cores, Max Mem, GPU, %Frequency, Turbo}} | ||
| − | {{#ask: [[Category: | + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[instance of::microprocessor]] [[microarchitecture::Ivy Bridge]] [[max cpu count::1]] |
|?full page name | |?full page name | ||
|?model number | |?model number | ||
Latest revision as of 07:03, 13 October 2024
| Edit Values | |
| Ivy Bridge µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | May 4, 2011 |
| Phase-out | April, 2013 |
| Process | 22 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 1 |
| Succession | |
Ivy Bridge (IVB) was Intel's microarchitecture based on the 22 nm process for desktops and servers. Ivy Bridge was introduced in 2011 as a process shrink of Sandy Bridge which introduced a number of enhancements. Ivy Bridge became Intel's first microarchitecture to use tri-gate transistors for their commercial products.
For desktop and mobile, Ivy Bridge is branded as 3rd Generation Intel Core processors. For server class processors, Intel branded it as Xeon E3 v2, Xeon E5 v2, and Xeon E7 v2.
Codenames[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Process Technology[edit]
| 22nm Manufacturing Fabs | |
|---|---|
| Fab | Location |
| D1C | Hillsboro, Oregon |
| D1D | Hillsboro, Oregon |
| Fab 32 | Chandler, Arizona |
| Fab 12 | Chandler, Arizona |
| Fab 28 | Kiryat Gat, Israel |
Ivy Bridge is designed to be manufactured using 22 nm Tri-gate FinFET transistors. This is Intel's first generation of FinFET. This correlates to 8 nm Fin width and a 60 nm Fin pitch (shown below). SRAM cell is at 0.1080 µm² and 0.092 µm² for high performance and high density respectively.
| Sandy Bridge | Ivy Bridge | Δ | 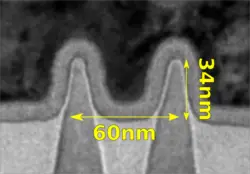
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 nm | 22 nm | |||
| Fin Pitch | N/A | 60 nm | N/A | |
| Fin Width | 8 nm | |||
| Fin Height | 34 nm | |||
| Gate Pitch | 112.5 nm | 90 nm | 0.80x | |
| Interconnect Pitch | 112.5 nm | 80 nm | 0.71x |
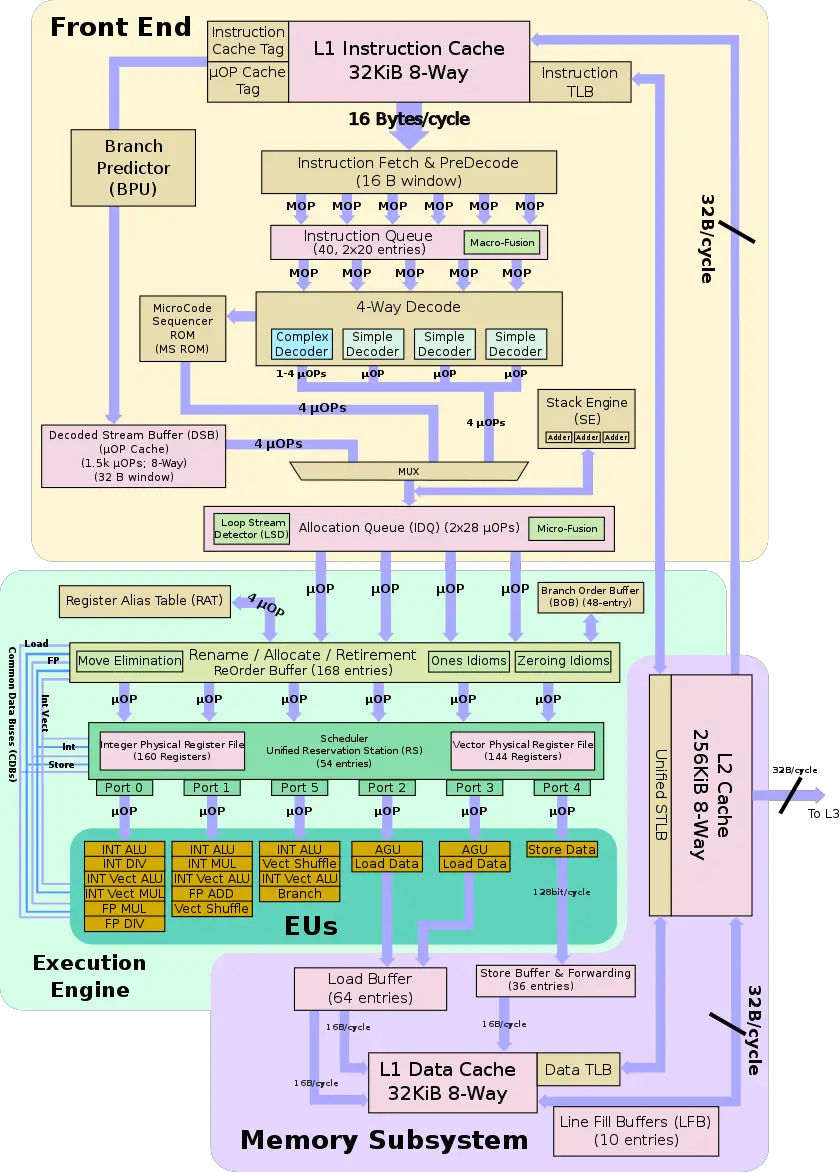
Architecture[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Key changes from Sandy Bridge[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
New instructions[edit]
Ivy Bridge introduced a number of new instructions:
-
F16C- Extension for performing HP-SP conversions -
RDRAND- Secure Key Technology extension - FS/GS base access
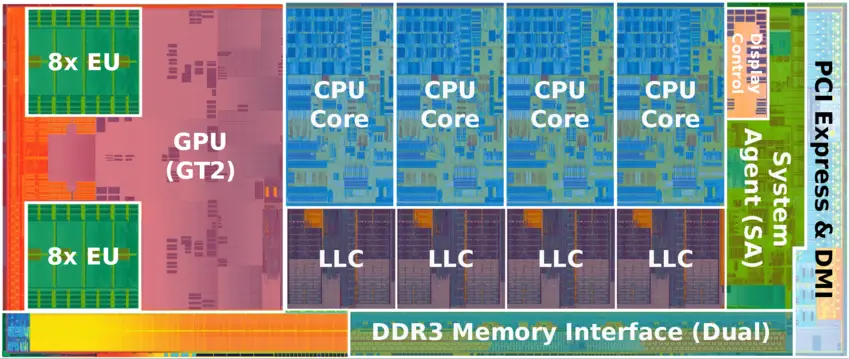
Block Diagram[edit]
Client SoC[edit]
Individual Core[edit]
Die[edit]
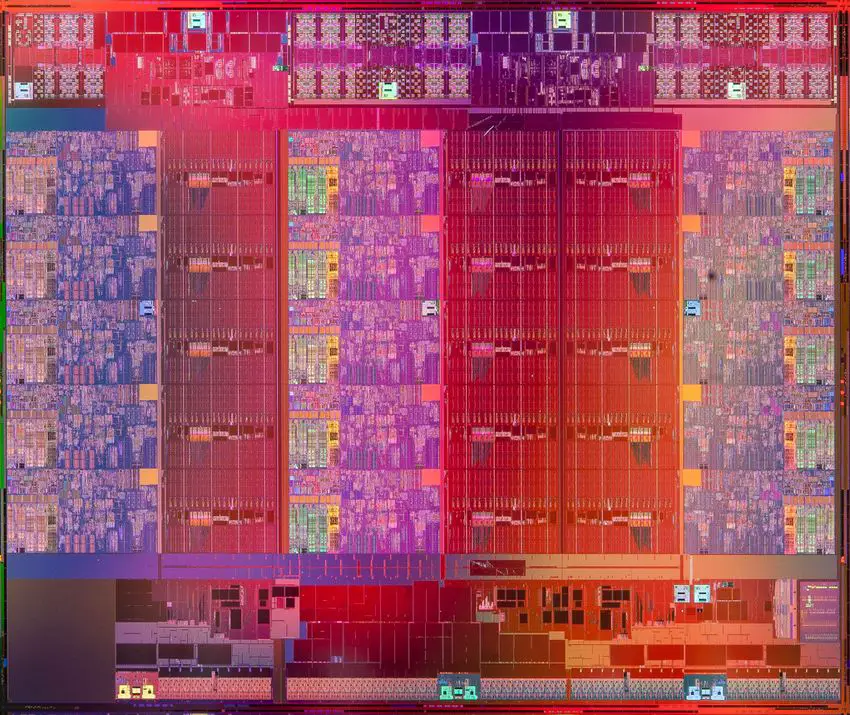
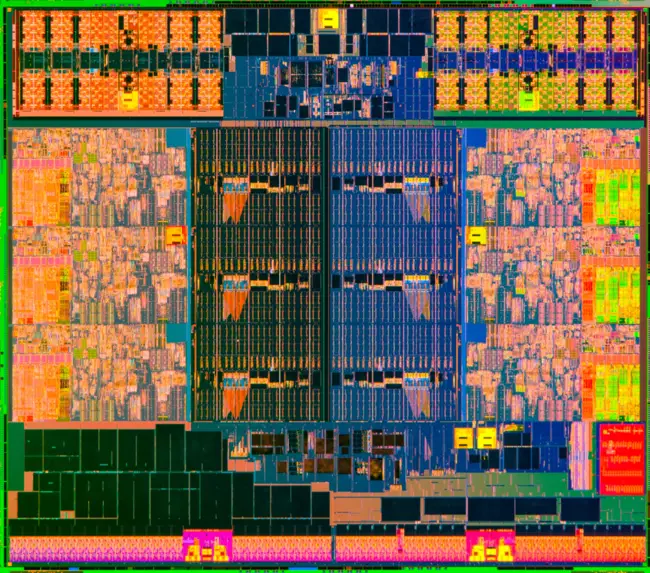
Quad-core Ivy Bridge die[edit]
- Intel Core i7 3770K/i7 3770/i5 3570K
- 1,480,000,000 transistors
- 160 mm2
- 4 CPU cores
- 1 GPU core
- 2x8xEU (64 ALUs)
- 22 nm process
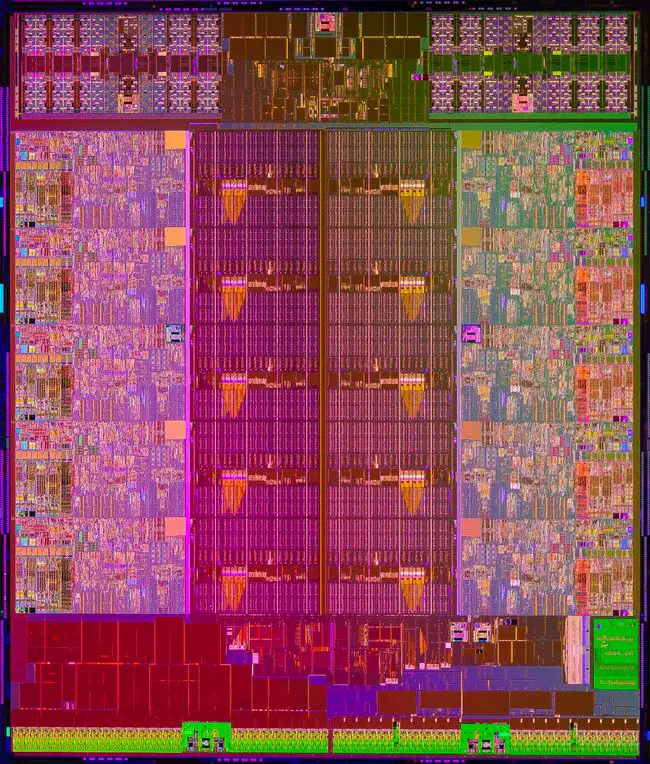
Hexa-core Ivy Bridge Die[edit]
- Core i7-4960X
- 1,860,000,000 transistors
- 256.5 mm²
- 15.0 mm x 17.1 mm
- 6 CPU cores
- 22 nm process
Deca-core Ivy Bridge Die[edit]
- 341 mm²
- 10 CPU cores
- 22 nm process
Pentadeca-Core Ivy Bridge die[edit]
- 540 mm²
- 4,310,000,000 transistors
- 15 CPU cores
- 22 nm process
Cores[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
All Ivy Bridge Chips[edit]
| List of Ivy Bridge Processors | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | Turbo Boost | Mem | IGP | ||||||||||||||||
| Model | Launched | Price | Family | Core Name | Cores | Threads | L2$ | L3$ | TDP | Frequency | 1 Core | 2 Cores | 3 Cores | 4 Cores | Max Mem | GPU | Frequency | Turbo | |
| 1007U | 20 January 2013 | $ 86.00 € 77.40 £ 69.66 ¥ 8,886.38 | Celeron | Ivy Bridge | 2 | 2 | 0.5 MiB 512 KiB 524,288 B 4.882812e-4 GiB | 2 MiB 2,048 KiB 2,097,152 B 0.00195 GiB | 17 W 17,000 mW 0.0228 hp 0.017 kW | 1.5 GHz 1,500 MHz 1,500,000 kHz | 32 GiB 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 KHz | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 KHz | |||||
| i7-3770K | 23 April 2012 | $ 332.00 € 298.80 £ 268.92 ¥ 34,305.56 | Core i7 | Ivy Bridge-HE-4 | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 77 W 77,000 mW 0.103 hp 0.077 kW | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 32 GiB 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,150 MHz 1.15 GHz 1,150,000 KHz | |
| i7-3920XM | 28 April 2012 | Core i7EE | Ivy Bridge | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 2.9 GHz 2,900 MHz 2,900,000 kHz | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 32 GiB 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,300 MHz 1.3 GHz 1,300,000 KHz | ||
| i7-3940XM | 30 September 2012 | Core i7EE | Ivy Bridge | 4 | 8 | 1 MiB 1,024 KiB 1,048,576 B 9.765625e-4 GiB | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 55 W 55,000 mW 0.0738 hp 0.055 kW | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 32 GiB 32,768 MiB 33,554,432 KiB 34,359,738,368 B 0.0313 TiB | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 KHz | 1,350 MHz 1.35 GHz 1,350,000 KHz | ||
| i7-4960X | 10 September 2013 | $ 999.00 € 899.10 £ 809.19 ¥ 103,226.67 | Core i7EE | Ivy Bridge E | 6 | 12 | 1.5 MiB 1,536 KiB 1,572,864 B 0.00146 GiB | 15 MiB 15,360 KiB 15,728,640 B 0.0146 GiB | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 4 GHz 4,000 MHz 4,000,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | 64 GiB 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 0.0625 TiB | ||||
| Count: 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| codename | Ivy Bridge + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | May 4, 2011 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/ivy bridge (client) + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Ivy Bridge + |
| phase-out | April 2013 + |
| process | 22 nm (0.022 μm, 2.2e-5 mm) + |