-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "supercomputers/nersc-10"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|image=nersc-10.png | |image=nersc-10.png | ||
|sponsor=U.S. Department of Energy | |sponsor=U.S. Department of Energy | ||
| + | |introduction=2024 | ||
|peak dpflops=1 exaFLOPS | |peak dpflops=1 exaFLOPS | ||
|predecessor=Perlmutter | |predecessor=Perlmutter | ||
Latest revision as of 03:44, 10 February 2019
| Edit Values | |
| NERSC-10 | |
 | |
| General Info | |
| Sponsors | U.S. Department of Energy |
| Introduction | 2024 |
| Peak FLOPS | 1 exaFLOPS |
| Succession | |
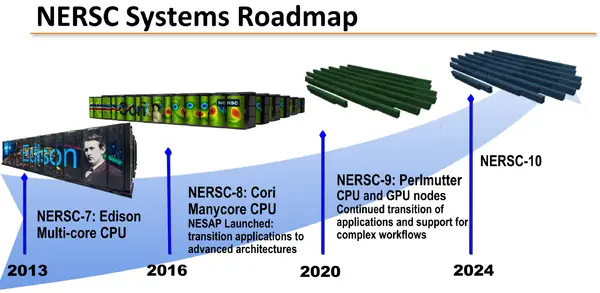
NERSC-10 (no name given yet) is the successor to Perlmutter, a planned exascale supercomputer set to be operated by National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center.
Overview[edit]
NERSC-10 is a planned exascale supercomputer currently in pathfinding stages. NERSC-10 is expected to go online around the 2024 timeframe.
See also[edit]
Facts about "NERSC-10 - Supercomputers"
| main image |  + + |
| name | NERSC-10 + |
| peak flops (double-precision) | 1.0e+18 FLOPS (999,999,999,999,999.875 KFLOPS, 1,000,000,000,000 MFLOPS, 1,000,000,000 GFLOPS, 1,000,000 TFLOPS, 1,000 PFLOPS, 1 EFLOPS, 1.0e-3 ZFLOPS) + |