From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "arm holdings/microarchitectures/arm8"
(arm8) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|manufacturer=TSMC | |manufacturer=TSMC | ||
|introduction=July 8, 1996 | |introduction=July 8, 1996 | ||
| + | |isa=ARMv4 | ||
|predecessor=ARM7 | |predecessor=ARM7 | ||
|predecessor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/arm7 | |predecessor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/arm7 | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
|successor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/arm9 | |successor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/arm9 | ||
}} | }} | ||
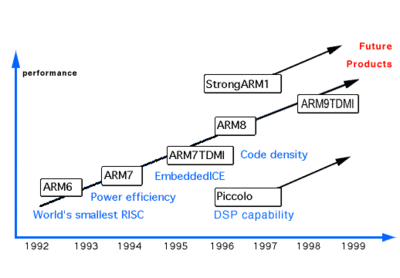
| − | '''ARM8''' is the successor to the {{armh|ARM7|l=arch}}, a low-power performance [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as | + | [[File:arm8 roadmap.gif|thumb|right|400px|Historical roadmap leading to the ARM8.]] |
| + | '''ARM8''' is the successor to the {{armh|ARM7|l=arch}}, a low-power performance [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as an [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Architecture == | ||
| + | === Key changes from {{\\|ARM7}} === | ||
| + | * [[ARMv4]] (from [[ARMv3]]) | ||
| + | * 2x performance (ARM810 vs ARM710 on the same [[process node]]) | ||
| + | ** 26% lower [[cycles per instruction|CPI]] (1.4, down from 1.9) | ||
| + | * [[0.6 µm process]] (down from [[0.8 µm]]) | ||
| + | * 1.66x longer pipeline (5 stages, up from 3) | ||
| + | |||
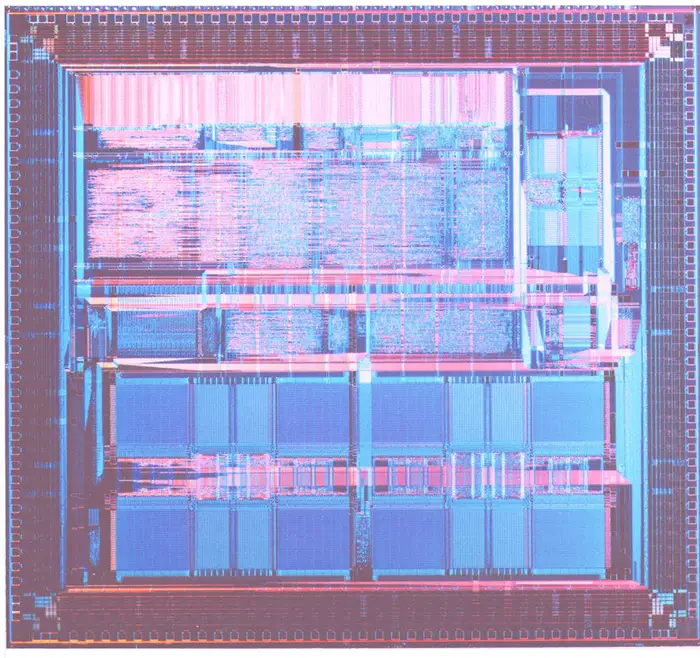
| + | == Die == | ||
| + | === ARM810 === | ||
| + | * [[0.6 µm process]] | ||
| + | * 3.3 V | ||
| + | ** 0.5 W | ||
| + | * 3-Layer Metal CMOS | ||
| + | * 53.5 mm² (not including pad ring) | ||
| + | * 144 TQFP | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:arm810 die shot.png|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bibliography == | ||
| + | * {{bib|hc|8|Arm}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:49, 15 October 2019
| Edit Values | |
| ARM8 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | July 8, 1996 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv4 |
| Succession | |
ARM8 is the successor to the ARM7, a low-power performance ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as an IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips.
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from ARM7[edit]
- ARMv4 (from ARMv3)
- 2x performance (ARM810 vs ARM710 on the same process node)
- 26% lower CPI (1.4, down from 1.9)
- 0.6 µm process (down from 0.8 µm)
- 1.66x longer pipeline (5 stages, up from 3)
Die[edit]
ARM810[edit]
- 0.6 µm process
- 3.3 V
- 0.5 W
- 3-Layer Metal CMOS
- 53.5 mm² (not including pad ring)
- 144 TQFP
Bibliography[edit]
- Arm, IEEE Hot Chips 8 Symposium (HCS) 1996
Facts about "ARM8 - Microarchitectures - ARM"
| codename | ARM8 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | July 8, 1996 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/arm8 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM8 + |