(→Kaby Lake G Processors: missing TDP) |
(→Graphics) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Kaby Lake G''' ('''KBL-G''') is the name of the core for [[Intel]]'s high-performance line of mobile processors based on the {{intel|Kaby Lake|l=arch}} microarchitecture and incorporate a discrete [[AMD]] {{amd|Vega|l=arch}} graphics processor. These chips are targeted towards ultimate mobile gaming experience. Kaby Lake G processors are fabricated on Intel's enhanced [[14 nm lithography process|14nm+ process]] and for graphics, GlobalFoundries [[14 nm process]]. | '''Kaby Lake G''' ('''KBL-G''') is the name of the core for [[Intel]]'s high-performance line of mobile processors based on the {{intel|Kaby Lake|l=arch}} microarchitecture and incorporate a discrete [[AMD]] {{amd|Vega|l=arch}} graphics processor. These chips are targeted towards ultimate mobile gaming experience. Kaby Lake G processors are fabricated on Intel's enhanced [[14 nm lithography process|14nm+ process]] and for graphics, GlobalFoundries [[14 nm process]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
[[File:8th gen core i7 with radeon logo (2018).png|250px|right]] | [[File:8th gen core i7 with radeon logo (2018).png|250px|right]] | ||
[[File:8th gen core i5 with radeon logo (2018).png|250px|right]] | [[File:8th gen core i5 with radeon logo (2018).png|250px|right]] | ||
| − | Kaby Lake G based processors are a 2-chip solution - the [[microprocessor]] and the [[chipset]]. Those parts are [[BGA]] and are soldered onto the motherboard. The microprocessor is connected to the chipset via 4 of the chip's 20 PCIe lanes using Intel's proprietary {{intel|Direct Media Interface}} 3.0 (DMI 3.0), allowing for 8 GT/s transfer rate per lane. | + | {{see also|intel/microarchitectures/kaby_lake#Kaby_Lake_G|l1=Kaby Lake § Kaby Lake G}} |
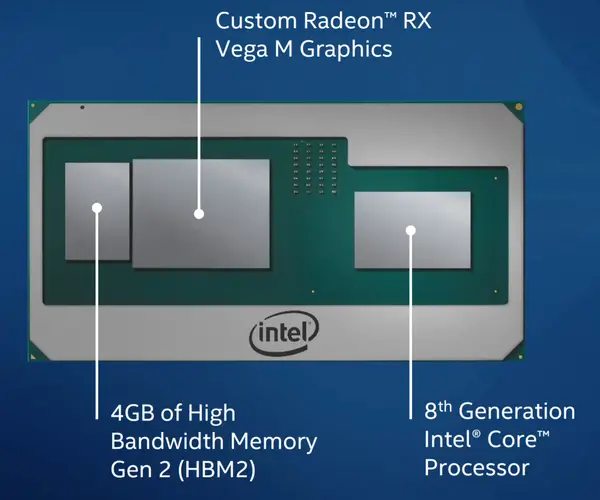
| + | Kaby Lake G based processors are a 2-chip solution - the [[microprocessor]] and the [[chipset]]. Those parts are [[BGA]] and are soldered onto the motherboard. The microprocessor is connected to the chipset via 4 of the chip's 20 PCIe lanes using Intel's proprietary {{intel|Direct Media Interface}} 3.0 (DMI 3.0), allowing for 8 GT/s transfer rate per lane. The microprocessor itself is identical to one used for the {{intel|Kaby Lake H|l=core}} but is now packaged along with the Radeon GPU and [[HBM 2]]. | ||
=== Graphics === | === Graphics === | ||
| − | Those processors are unique in the fact that this is the first time Intel has integrated a discrete graphics processor into the same package as the microprocessor. This is also the first time they are using a competitor graphics processor. Those parts incorporate an [[AMD]] [[GPU]] based on the {{amd|Vega|l=arch}} microarchitecture and incorporate their own 4 GiB of [[high-bandwidth memory]] 2 (HBM2). The HBM solution is connected to the graphics processor using Intel's [[EMIB]], a high-speed in-package interconnect solution. | + | Those processors are unique in the fact that this is the first time Intel has integrated a discrete graphics processor into the same package as the microprocessor. This is also the first time they are using a competitor's graphics processor. Those parts incorporate an [[AMD]] [[GPU]] based on the {{amd|Vega|l=arch}} microarchitecture and incorporate their own 4 GiB of [[high-bandwidth memory]] 2 (HBM2). The HBM solution is connected to the graphics processor using Intel's [[EMIB]], a high-speed in-package interconnect solution. |
The CPU itself is connected to the GPU using 8 of the other PCIe lanes, leaving the 8 remaining lanes for other peripherals to communicate with the CPU directly. | The CPU itself is connected to the GPU using 8 of the other PCIe lanes, leaving the 8 remaining lanes for other peripherals to communicate with the CPU directly. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 32: | ||
[[File:kaby lake g with amd radeon package.png|600px]] | [[File:kaby lake g with amd radeon package.png|600px]] | ||
| − | |||
=== Common Features === | === Common Features === | ||
Latest revision as of 18:07, 12 July 2018
| Edit Values | |
| Kaby Lake G | |
 | |
| Package front | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Intel, AMD |
| Manufacturer | Intel, GlobalFoundries |
| Introduction | November 6, 2017 (announced) January 7, 2018 (launched) |
| Microarchitecture | |
| ISA | x86-64 (x86) |
| Microarchitecture | Kaby Lake |
| Word Size | 8 octets 64 bit16 nibbles |
| Process | 14 nm 0.014 μm 1.4e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
Kaby Lake G (KBL-G) is the name of the core for Intel's high-performance line of mobile processors based on the Kaby Lake microarchitecture and incorporate a discrete AMD Vega graphics processor. These chips are targeted towards ultimate mobile gaming experience. Kaby Lake G processors are fabricated on Intel's enhanced 14nm+ process and for graphics, GlobalFoundries 14 nm process.
Contents
Overview[edit]
- See also: Kaby Lake § Kaby Lake G
Kaby Lake G based processors are a 2-chip solution - the microprocessor and the chipset. Those parts are BGA and are soldered onto the motherboard. The microprocessor is connected to the chipset via 4 of the chip's 20 PCIe lanes using Intel's proprietary Direct Media Interface 3.0 (DMI 3.0), allowing for 8 GT/s transfer rate per lane. The microprocessor itself is identical to one used for the Kaby Lake H but is now packaged along with the Radeon GPU and HBM 2.
Graphics[edit]
Those processors are unique in the fact that this is the first time Intel has integrated a discrete graphics processor into the same package as the microprocessor. This is also the first time they are using a competitor's graphics processor. Those parts incorporate an AMD GPU based on the Vega microarchitecture and incorporate their own 4 GiB of high-bandwidth memory 2 (HBM2). The HBM solution is connected to the graphics processor using Intel's EMIB, a high-speed in-package interconnect solution.
The CPU itself is connected to the GPU using 8 of the other PCIe lanes, leaving the 8 remaining lanes for other peripherals to communicate with the CPU directly.
Common Features[edit]
All Kaby Lake G processors have the following:
- Dual-channel Memory
- Up to DDR3L-1600, DDR4-2400
- Up to 64 GiB
- 8x PCIe
- 20x in total, 4 of the 20 are used by the bus and 8 for the GPU as described above
- quad-core with Hyper-Threading (8 threads)
- Everything up to AVX2 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, AVX, and AVX2)
- BGA package
Graphics[edit]
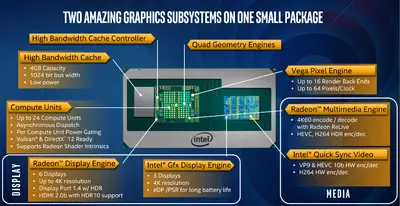
Those processors have superior graphics capabilities as well as 4 GiB of HBM 2 cache.
- HBM 2 (Intel calls "High Bandwidth Cache" or "HBC")
- 4 GiB
- 1,024 bit
- @ 800 MHz (204.8 GB/s peak bandwidth)
- @ 700 MHz (179.2 GB/s peak bandwidth)
- Graphics
- 9 Display outputs available
- Integrated HD Graphics 630 (Gen9.5 GT2)
- 3 Displays
- Base frequency of 350 MHz
- Burst frequency of 1.1 GHz
- Discrete Vega-based GPUs
- Custom Radeon RX Vega M Graphics
- 6 Displays
- Radeon RX Vega M GH
- 24 Compute Units
- 1,536 Stream processors, 64 pix/clk (ROPs), 96 texture units
- 3.7 TFLOPS peak performance
- Radeon RX Vega M GL
- 20 Compute Units
- 1,280 Stream processors, 32 pix/clk (ROPs), 80 texture units
- 2.6 TFLOPS peak performance
- Custom Radeon RX Vega M Graphics
Kaby Lake G Processors[edit]
| List of Kaby Lake G-based Processors | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | Graphics Processors | Features | |||||||||||
| Model | Launched | Family | C | T | L3$ | TDP | Frequency | Turbo | GPU | Base | Burst | vPro | Locked |
| i5-8305G | 7 January 2018 | Core i5 | 4 | 8 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 2.8 GHz 2,800 MHz 2,800,000 kHz | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | HD Graphics 630, Radeon RX Vega M GL | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz , 931 MHz350,000 KHz 0.931 GHz 931,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz , 1,011 MHz1,100,000 KHz 1.011 GHz 1,011,000 KHz | ✘ | ✔ |
| i7-8705G | 7 January 2018 | Core i7 | 4 | 8 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 4.1 GHz 4,100 MHz 4,100,000 kHz | HD Graphics 630, Radeon RX Vega M GL | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz , 931 MHz350,000 KHz 0.931 GHz 931,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz , 1,011 MHz1,100,000 KHz 1.011 GHz 1,011,000 KHz | ✘ | ✔ |
| i7-8706G | 7 January 2018 | Core i7 | 4 | 8 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 65 W 65,000 mW 0.0872 hp 0.065 kW | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 4.1 GHz 4,100 MHz 4,100,000 kHz | HD Graphics 630, Radeon RX Vega M GL | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz , 931 MHz350,000 KHz 0.931 GHz 931,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz , 1,011 MHz1,100,000 KHz 1.011 GHz 1,011,000 KHz | ✔ | ✔ |
| i7-8709G | 7 January 2018 | Core i7 | 4 | 8 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 100 W 100,000 mW 0.134 hp 0.1 kW | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 4.1 GHz 4,100 MHz 4,100,000 kHz | HD Graphics 630, Radeon RX Vega M GH | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz , 1,063 MHz350,000 KHz 1.063 GHz 1,063,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz , 1,190 MHz1,100,000 KHz 1.19 GHz 1,190,000 KHz | ✘ | ✔ |
| i7-8809G | 7 January 2018 | Core i7 | 4 | 8 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 100 W 100,000 mW 0.134 hp 0.1 kW | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 4.2 GHz 4,200 MHz 4,200,000 kHz | HD Graphics 630, Radeon RX Vega M GH | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz , 1,063 MHz350,000 KHz 1.063 GHz 1,063,000 KHz | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz , 1,190 MHz1,100,000 KHz 1.19 GHz 1,190,000 KHz | ✘ | ✘ |
| Count: 5 | |||||||||||||
See also[edit]
|
• Power
• Performance |
| designer | Intel + and AMD + |
| first announced | November 6, 2017 + |
| first launched | January 7, 2018 + |
| instance of | core + |
| isa | x86-64 + |
| isa family | x86 + |
| main image |  + + |
| main image caption | Package front + |
| manufacturer | Intel + and GlobalFoundries + |
| microarchitecture | Kaby Lake + |
| name | Kaby Lake G + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |