From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "amd/microarchitectures/vega"
m (→HBM 2: linked hbm) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{amd title|Vega|arch}} | {{amd title|Vega|arch}} | ||
{{microarchitecture | {{microarchitecture | ||
| − | | atype | + | |atype=GPU |
| − | | name | + | |name=Vega |
| − | | designer | + | |designer=AMD |
| − | | manufacturer | + | |manufacturer=GlobalFoundries |
| − | + | |introduction=2017 | |
| − | | introduction | + | |process=12 nm |
| − | + | |predecessor=Polaris | |
| − | | process | + | |predecessor link=amd/microarchitectures/polaris |
| − | + | |successor=Navi | |
| − | + | |successor link=amd/microarchitectures/navi | |
| − | | predecessor | + | |succession=yes |
| − | | predecessor link = amd/microarchitectures/ | ||
| − | | successor | ||
| − | | successor link | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Vega''' (also known as '''Graphics core next 5th generation''') is a [[microarchitecture]] developed by [[AMD]] as a successor to {{\\| | + | '''Vega''' (also known as '''Graphics core next 5th generation''') is both a [[microarchitecture]] and GPU family developed by [[AMD]] as a successor to the {{\\|GCN4}} [[microarchitecture]] and the {{\\|arctic islands}} family. |
== Codenames == | == Codenames == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 33: | ||
| Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux || [[High Level Shading Language|HLSL]] || Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux | | Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux || [[High Level Shading Language|HLSL]] || Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Vega 8 || 8|| 512 || rowspan=" | + | | Vega 8 || 8|| 512 || rowspan="3" colspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''1.1''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" | '''12''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" | '''N/A''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" | '''-''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" | '''4.6''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" | '''4.6''' || rowspan="3" style="text-align: center;" colspan="2" | '''2.2''' |
|- | |- | ||
| Vega 10 || 10|| 640 | | Vega 10 || 10|| 640 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Vega 11 || 11|| 704 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 49: | Line 48: | ||
| Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux || [[High Level Shading Language|HLSL]] || Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux | | Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux || [[High Level Shading Language|HLSL]] || Windows || Linux || Windows || Linux | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Vega 56 || 56|| 3584 || rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | ''' | + | | Vega 56 || 56|| 3584 || rowspan="2" colspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''1.1''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''12''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''N/A''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''-''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''4.6''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | '''4.6''' || rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" colspan="2" | '''2.2''' |
|- | |- | ||
| Vega 64 || 64|| 4096 | | Vega 64 || 64|| 4096 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Performance == | ||
| + | The original target of the RX Vega series was to compete with Nvidia's latest Pascal architecture. | ||
| + | RX Vega 64 -> GTX 1080 | ||
| + | RX Vega 56 -> GTX 1070 | ||
| + | |||
| + | The performance is generally good, but when it comes to performance per watt, or PPW, Vega is outperformed by Pascal. | ||
== Hardware Accelerated Video == | == Hardware Accelerated Video == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 65: | ||
== Process Technology == | == Process Technology == | ||
{{see also|14 nm process}} | {{see also|14 nm process}} | ||
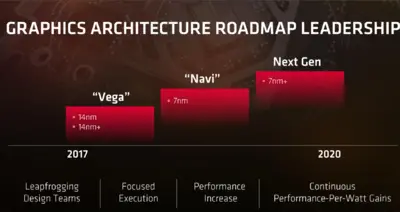
| − | Vega is manufactured on [[ | + | Vega is manufactured on [[GlobalFoundries]]' [[14 nm process]]. |
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:42, 16 June 2020
| Edit Values | |
| Vega µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | GPU |
| Designer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | GlobalFoundries |
| Introduction | 2017 |
| Process | 12 nm |
| Succession | |
Vega (also known as Graphics core next 5th generation) is both a microarchitecture and GPU family developed by AMD as a successor to the GCN4 microarchitecture and the arctic islands family.
Contents
Codenames[edit]
| Codename | Description |
|---|---|
| Raven Ridge | Mobile processors based on Zen CPUs and a Vega GPU |
Models[edit]
| Vega IGP Models | Standards | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Compute Units | Shaders | Vulkan | Direct3D | OpenGL | OpenCL | ||||||
| Windows | Linux | Windows | Linux | HLSL | Windows | Linux | Windows | Linux | ||||
| Vega 8 | 8 | 512 | 1.1 | 12 | N/A | - | 4.6 | 4.6 | 2.2 | |||
| Vega 10 | 10 | 640 | ||||||||||
| Vega 11 | 11 | 704 | ||||||||||
| Vega Dedicated Models | Standards | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Compute Units | Shaders | Vulkan | Direct3D | OpenGL | OpenCL | ||||||
| Windows | Linux | Windows | Linux | HLSL | Windows | Linux | Windows | Linux | ||||
| Vega 56 | 56 | 3584 | 1.1 | 12 | N/A | - | 4.6 | 4.6 | 2.2 | |||
| Vega 64 | 64 | 4096 | ||||||||||
Performance[edit]
The original target of the RX Vega series was to compete with Nvidia's latest Pascal architecture. RX Vega 64 -> GTX 1080 RX Vega 56 -> GTX 1070
The performance is generally good, but when it comes to performance per watt, or PPW, Vega is outperformed by Pascal.
Hardware Accelerated Video[edit]
| [Edit] Zen with Radeon Vega Hardware Accelerated Video Capabilities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codec | Encode | Decode | |||
| Max FPS | @1080p | @1440p | @2160p | @1080p 4:2:0 | @2160p 4:2:0 |
| MPEG-2 (H.262) | 60 FPS | N/A | |||
| VC-1 | |||||
| VP9 8bpc | 240 FPS | 60 FPS | |||
| VP9 10bpc | |||||
| MPEG-4 AVC (H.264) 8bpc | 120 FPS | 60 FPS | 30 FPS | ||
| MPEG-4 AVC (H.264) 10bpc | |||||
| HEVC (H.265) 8bpc | 120 FPS | 60 FPS | 30 FPS | ||
| HEVC (H.265) 10bpc | |||||
| JPEG/MJPEG 8bpc | |||||
Process Technology[edit]
- See also: 14 nm process
Vega is manufactured on GlobalFoundries' 14 nm process.
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from Arctic Islands[edit]
- New programmable geometry pipeline
- Up to 2x throughput
- Primitive shaders
- Improved workload balancing
- Tile based rendering
- New low precision instructions
- Half precision floating point with 2x performance
- 8 bit integer with 4x performance
- 15% higher clock speeds
- HBM 2
- 2x bandwidth
- 4x memory capacity
- New memory controller
- Render back-end is now a client of the L2 cache
- The instruction buffer has been enlarged
HBM 2[edit]
Vega makes use of 2 stacks of HBM 2 (High bandwidth memory).
| single stack | HBM 1 | HBM 2 |
|---|---|---|
| dies | 4 + 1 4 dram die, 1 control die |
2-8 + 1 2,4 or 8 dram die, 1 control die
|
| Gb/die | 2Gb | 8Gb |
| total Gb | 8Gb | 16-64Gb |
| bus width | 1024 | 1024 |
| clock speed | 500 MHz | 945 MHz |
| bandwidth | 128 GB/s | 238 GB/s |
References[edit]
- AMD 2017 Financial Analyst Day, May 16, 2017
Documents[edit]
See Also[edit]
Facts about "Vega - Microarchitectures - AMD"
| codename | Vega + |
| designer | AMD + |
| first launched | 2017 + |
| full page name | amd/microarchitectures/vega + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | GlobalFoundries + |
| microarchitecture type | GPU + |
| name | Vega + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |