m |
(relative speed is confusing. changed to absolute speed) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{intel title|8008}} | {{intel title|8008}} | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{chip |
| − | | name | + | |name=8008 |
| − | | image | + | |image=Intel 8008.jpg |
| − | | caption | + | |caption=8008 |
| − | | manufacturer | + | |designer=Intel |
| − | | model number | + | |manufacturer=Intel |
| − | | part number | + | |model number=8008 |
| − | | first announced | + | |part number=8008 |
| − | | last shipment | + | |first announced=April, 1972 |
| − | | family | + | |last shipment=1983 |
| − | | frequency | + | |family=MCS-8 |
| − | | microarch | + | |frequency=500 kHz |
| − | | process | + | |microarch=8008 |
| − | | transistors | + | |process=10 μm |
| − | | technology | + | |transistors=3,500 |
| − | + | |technology=pMOS | |
| − | | word size | + | |word size=8 bit |
| − | | max memory | + | |max memory=16 KiB |
| − | + | |power=1 W | |
| − | | power | + | |temp min=0 °C |
| − | | temp | + | |temp max=70 °C |
| − | | temp | + | |electrical=Yes |
| − | | packaging | + | |packaging=Yes |
| − | | package | + | |package=DIP18 |
| − | | package type | + | |package type=DIP |
| − | | package 1 | + | |package 1=CerDIP18 |
| − | | package type 1 | + | |package type 1=CerDIP |
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''8008''' (pronounced "''eighty-oh-eight''") was an {{arch|8}} [[microprocessor]] designed by [[Intel]] and introduced in April of 1972. The 8008, which was part of the {{intel|MCS-8}}, operated at 500 kHZ, had 8-bit data words, and could address 16KB of memory (14-bits [[program counter|PC]]). Originally commissioned by [[Datapoint Corporation]] (then Computer Terminal Corporation) for their [[Datapoint 2200]], by the time the 8008 was ready it no longer met CTC's requirements. Intel retained the rights to market the chip independently. | + | The '''8008''' (pronounced "''eighty-oh-eight''" or "''eight thousand eight''" ) was an {{arch|8}} [[microprocessor]] designed by [[Intel]] and introduced in April of 1972. The 8008, which was part of the {{intel|MCS-8}}, operated at 500 kHZ, had 8-bit data words, and could address 16KB of memory (14-bits [[program counter|PC]]). Originally commissioned by [[Datapoint Corporation]] (then Computer Terminal Corporation) for their [[Datapoint 2200]], by the time the 8008 was ready it no longer met CTC's requirements. Intel retained the rights to market the chip independently. |
| − | The {{intel|mcs-8/8008-1|8008-1}} is a faster version of the 8008 operating at | + | The {{intel|mcs-8/8008-1|8008-1}} is a faster version of the 8008 operating at 800 kHz; the chip is otherwise identical. |
== History == | == History == | ||
{{main|intel/mcs-8#History|l1=MCS-8#History}} | {{main|intel/mcs-8#History|l1=MCS-8#History}} | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| D8008 || Ceramic DIP-18 | | D8008 || Ceramic DIP-18 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
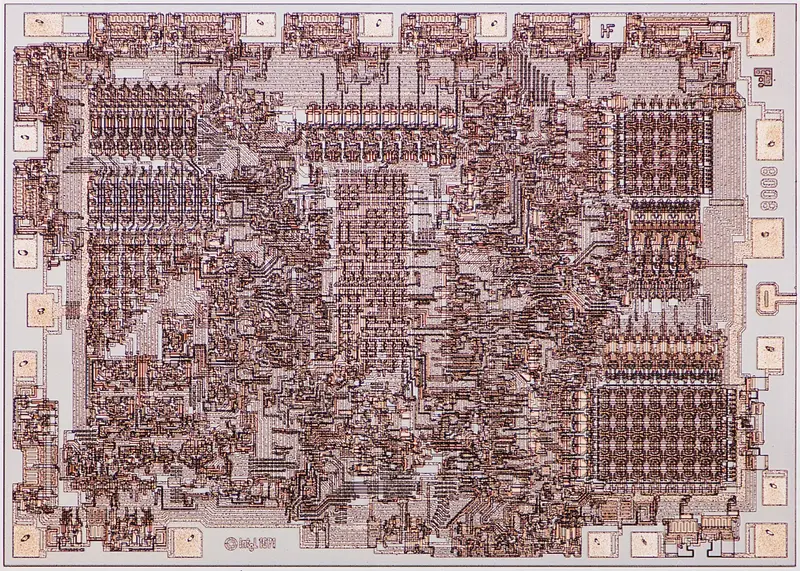
| + | == Die Shot == | ||
| + | * [[10 µm process]] | ||
| + | * 3,500 transistors | ||
| + | * 15 mm² die size | ||
| + | [[File:8008 die shot.png|800px]] | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 23 March 2022
| Edit Values | |
| 8008 | |
 | |
| 8008 | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Model Number | 8008 |
| Part Number | 8008 |
| Introduction | April, 1972 (announced) |
| End-of-life | 1983 (last shipment) |
| Shop | Amazon |
| General Specs | |
| Family | MCS-8 |
| Frequency | 500 kHz |
| Microarchitecture | |
| Microarchitecture | 8008 |
| Process | 10 μm |
| Transistors | 3,500 |
| Technology | pMOS |
| Word Size | 8 bit |
| Max Memory | 16 KiB |
| Electrical | |
| Power dissipation | 1 W |
| OP Temperature | 0 °C – 70 °C |
The 8008 (pronounced "eighty-oh-eight" or "eight thousand eight" ) was an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel and introduced in April of 1972. The 8008, which was part of the MCS-8, operated at 500 kHZ, had 8-bit data words, and could address 16KB of memory (14-bits PC). Originally commissioned by Datapoint Corporation (then Computer Terminal Corporation) for their Datapoint 2200, by the time the 8008 was ready it no longer met CTC's requirements. Intel retained the rights to market the chip independently.
The 8008-1 is a faster version of the 8008 operating at 800 kHz; the chip is otherwise identical.
Contents
History[edit]
- Main article: MCS-8#History
The 8008 was introduced in April of 1972 after the Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC) lost interest in the chip when it failed to meet their performance requirements.
ISA[edit]
- Main article: 8008 ISA
The 8008 has seven levels of call stack, seven registers, and 48 instructions.
Documents[edit]
Packaging[edit]
| Part | Package |
|---|---|
| C8008 | Ceramic DIP-18, Gold Top |
| D8008 | Ceramic DIP-18 |
Die Shot[edit]
- 10 µm process
- 3,500 transistors
- 15 mm² die size
See Also[edit]
| base frequency | 0.5 MHz (5.0e-4 GHz, 500 kHz) + |
| designer | Intel + |
| family | MCS-8 + |
| first announced | April 1972 + |
| full page name | intel/mcs-8/8008 + |
| instance of | microprocessor + |
| last shipment | 1983 + |
| ldate | April 1972 + |
| main image |  + + |
| main image caption | 8008 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| max memory | 0.0156 MiB (16 KiB, 16,384 B, 1.525879e-5 GiB, 1.490116e-8 TiB) + |
| max operating temperature | 70 °C + |
| microarchitecture | 8008 + |
| min operating temperature | 0 °C + |
| model number | 8008 + |
| name | 8008 + |
| part number | 8008 + |
| power dissipation | 1 W (1,000 mW, 0.00134 hp, 0.001 kW) + |
| process | 10,000 nm (10 μm, 0.01 mm) + |
| technology | pMOS + |
| transistor count | 3,500 + |
| word size | 8 bit (1 octets, 2 nibbles) + |