(→Samsung) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
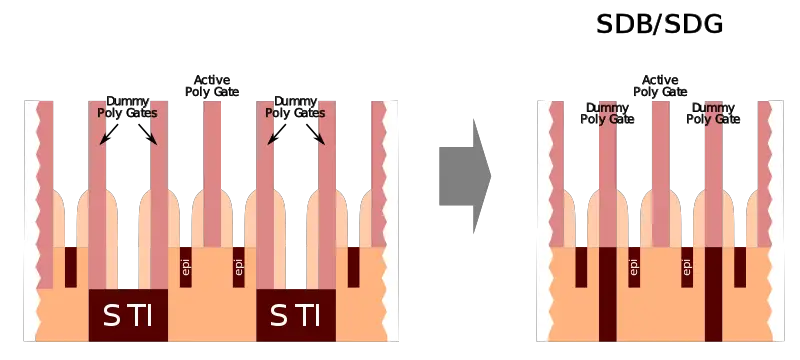
| − | + | Double [[diffusion break]] (DDB) isolation has historically been used to isolate neighboring devices in order to provide good process control (stress) and reduce [[process variability|variations]]. Single diffusion break reduces the cell-to-cell spacing by reducing the width of the [[shallow trench isolation]] to a single dummy [[poly gate]] [[gate length|length]]. In practice, there is no actual dummy gate. Instead, just the trench isolation remains. | |
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:ttt-cell-scaling-sdb.svg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
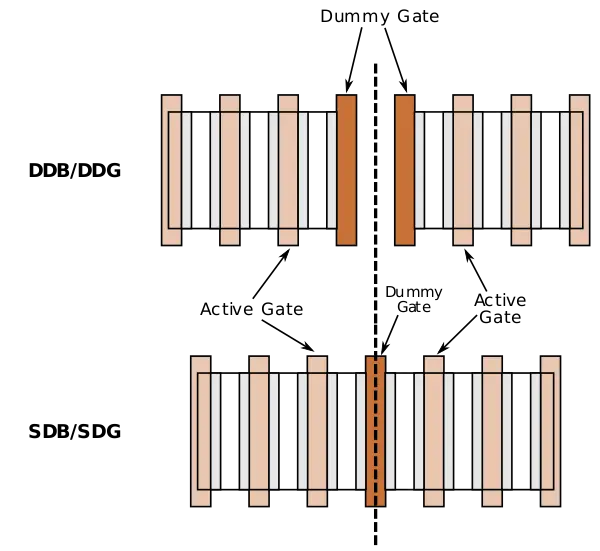
| + | With advancements in [[DTCO]], advanced [[process nodes]] reduced [[cell height]], thereby increasing the share of wasted space due to cell-to-cell spacings as a result of DDB. Eliminating the additional inactive gate pitch can result in significant savings at the block and macro levels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:ddb-sdb-cell-changes.svg|600px]] | ||
==Industry== | ==Industry== | ||
| + | [[File:iedm-2017-intel-10-wire-hs.png|thumb|right|Intel 10nm SDG benefits.]] | ||
===Samsung=== | ===Samsung=== | ||
| − | + | Samsung first introduced single diffusion breaks at their [[Samsung 14nm|14-nanometer process]]. Samsung used SDB in all their succeeding nodes including [[samsung 10nm|10nm]], [[samsung 7nm|7nm]], [[samsung 5nm|5nm]], and [[samsung 4nm|4nm]]. | |
| + | |||
===Intel=== | ===Intel=== | ||
| + | Intel introduced single diffusion breaks starting with their [[Intel 10nm|10-nanometer process]]. The company claimed SDG resulted in a 20% improvement in [[standard cell|cell]] densty. Intel introduced 2nd-generation SDG at their [[Intel 4]] node. | ||
| + | {| class="right" | ||
| + | | [[File:iedm-2017-intel-10-dummy-gates-tem.png|thumb|200px|[[Intel 10nm]] With DDB.]] | ||
| + | | [[File:iedm-2017-intel-10-sdg-tem.png|thumb|200px|[[Intel 10nm]] With SDB.]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==TSMC== | ||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:24, 25 June 2022
Single Diffusion Break (SDB) or Single Dummy Gate (SDG) is a semiconductor process flow technique that eliminates the need for an additional dummy gate padding at the cell boundaries. SDB is used to enable aggressive scaling of abutting cells without affecting the cell height or underlying devices.
Overview[edit]
Double diffusion break (DDB) isolation has historically been used to isolate neighboring devices in order to provide good process control (stress) and reduce variations. Single diffusion break reduces the cell-to-cell spacing by reducing the width of the shallow trench isolation to a single dummy poly gate length. In practice, there is no actual dummy gate. Instead, just the trench isolation remains.
With advancements in DTCO, advanced process nodes reduced cell height, thereby increasing the share of wasted space due to cell-to-cell spacings as a result of DDB. Eliminating the additional inactive gate pitch can result in significant savings at the block and macro levels.
Industry[edit]
Samsung[edit]
Samsung first introduced single diffusion breaks at their 14-nanometer process. Samsung used SDB in all their succeeding nodes including 10nm, 7nm, 5nm, and 4nm.
Intel[edit]
Intel introduced single diffusion breaks starting with their 10-nanometer process. The company claimed SDG resulted in a 20% improvement in cell densty. Intel introduced 2nd-generation SDG at their Intel 4 node.
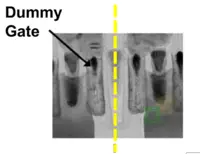 Intel 10nm With DDB. |
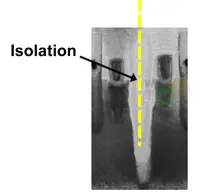 Intel 10nm With SDB. |
TSMC[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
See also[edit]
Bibliography[edit]
- Intel, 2017 IEEE 63rd International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM).