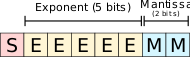| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
::[[File:msfp8 encoding format.svg|190px]] | ::[[File:msfp8 encoding format.svg|190px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Hardware support == | ||
| + | * {{microsoft|Project Brainwave}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[bfloat16]] | ||
| + | * {{intel|Flexpoint}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bibliography == | ||
| + | * {{hcbib|31}} | ||
Revision as of 23:02, 23 August 2019
MSFP8-MSFP11 (Microsoft floating-point 8-11) is a series of number encoding formats occupying 8 to 11 bits representing a floating-point number. MSFP8 is equivalent to a standard half-precision floating-point value with a truncated mantissa field. It is the 8-bit equivalent of the bfloat16 number format and is used for the very same purpose of hardware accelerating machine learning algorithms. MSFP was first proposed and implemented by Microsoft.
Overview
MSFP8-11 follows the same format as a standard IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point but truncates the mantissa field from 11 bits to just 2-5 bits. Preserving the exponent bits keeps the format to the same range as the 16-bit single precision FP (~5.96e-8 to 65,504). This allows for relatively simpler conversion between the two data types. In other words, while some resolution is lost, numbers can still be represented. In many ways, MSFP8 is analogous to an 8-bit version of bfloat16.
- float16:
- msfp8: