(→Overview) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
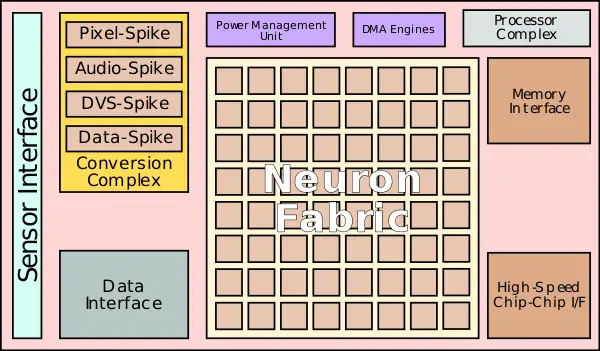
Akida is a neuromorphic [[system on a chip]] designed for a wide range of markets from edge inference and training with a sub-1W power to high-performance data center applications. The architecture consists of three major parts: sensor interfaces, the conversion complex, and the neuron fabric. Depending on the application (e.g., edge vs data center) data may either be collected at the device (e.g. lidar, visual and audio) or brought via one of the standard data interfaces (e.g., [[PCIe]]). Any data sent to the Akida SoC requires being converted into spikes to be useful. Akida incorporates a conversion complex with a set of specialized conversion units for handling digital, analog, vision, sound and other data types to spikes. | Akida is a neuromorphic [[system on a chip]] designed for a wide range of markets from edge inference and training with a sub-1W power to high-performance data center applications. The architecture consists of three major parts: sensor interfaces, the conversion complex, and the neuron fabric. Depending on the application (e.g., edge vs data center) data may either be collected at the device (e.g. lidar, visual and audio) or brought via one of the standard data interfaces (e.g., [[PCIe]]). Any data sent to the Akida SoC requires being converted into spikes to be useful. Akida incorporates a conversion complex with a set of specialized conversion units for handling digital, analog, vision, sound and other data types to spikes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Fabric === | ||
| + | Akida incorporates a Neuron fabric along with a processor complex used for system and data management as well as training and inference control. The chip efficiency comes from their ability to take advantage of sparsity with neurons only firing once a programmable threshold is exceeded. NNs are feed-forward. Neurons learn through selective reinforcement or inhibition of synapses. Sensory data such as images are converted into spikes. The Akida NSoC has neuron fabric comprised of 1.2 million neurons and 10 billion synapses. For training, both supervised and unsupervised modes are supported. In the supervised mode, initial layers of the network are trained autonomously with the labels being applied to the final fully-connected layer. This makes it possible for the networks to function as classification networks. Unsupervised learning from unlabeled data as well as label classification is possible. | ||
=== Scalability === | === Scalability === | ||
Revision as of 20:54, 26 September 2018
| Edit Values | |
| Akida µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | NPU |
| Designer | BrainChip |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | September 10, 2018 |
| Process | 28nm or 14nm |
Akida is a neuromorphic chip microarchitecture designed by BrainChip for the edge and the data center.
Contents
Process technology
BrainChip has not locked on the exact process technology but they are considering both 28 nm and 14 nm.
Architecture
- Neuromorphic chip
- Spiking neural network
- 1.2 million neurons
- 10 billion synapses
Block diagram
Overview
Akida is a neuromorphic system on a chip designed for a wide range of markets from edge inference and training with a sub-1W power to high-performance data center applications. The architecture consists of three major parts: sensor interfaces, the conversion complex, and the neuron fabric. Depending on the application (e.g., edge vs data center) data may either be collected at the device (e.g. lidar, visual and audio) or brought via one of the standard data interfaces (e.g., PCIe). Any data sent to the Akida SoC requires being converted into spikes to be useful. Akida incorporates a conversion complex with a set of specialized conversion units for handling digital, analog, vision, sound and other data types to spikes.
Fabric
Akida incorporates a Neuron fabric along with a processor complex used for system and data management as well as training and inference control. The chip efficiency comes from their ability to take advantage of sparsity with neurons only firing once a programmable threshold is exceeded. NNs are feed-forward. Neurons learn through selective reinforcement or inhibition of synapses. Sensory data such as images are converted into spikes. The Akida NSoC has neuron fabric comprised of 1.2 million neurons and 10 billion synapses. For training, both supervised and unsupervised modes are supported. In the supervised mode, initial layers of the network are trained autonomously with the labels being applied to the final fully-connected layer. This makes it possible for the networks to function as classification networks. Unsupervised learning from unlabeled data as well as label classification is possible.
Scalability
Akida incorporates a high-speed chip-to-chip interface for multi-chip support. Up to 1024 Akida chips can be wired together to form a large SNN which works out to 1,228,800,000 (1.2 billion) neurons and 10,240,000,000,000 (10.24 trillion) synapses.
Bibliography
- BrainChip. (September 20, 2018). Personal communication.
| codename | Akida + |
| designer | BrainChip + |
| first launched | September 10, 2018 + |
| full page name | brainchip/akida + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| name | Akida + |