Speed Select Technology (SST) is a microprocessor power management technology introduced by Intel that allows for throughput and per-core performance configurations, allowing for the prioritization of performance for certain workloads running on specific cores by sacrificing the performance of other cores.
Contents
Overview[edit]
Speed Select Technology is a set of power management controls that allows a system administrator to customize per-core performance. By configuring the performance of specific cores and affinitizing workloads to those cores, higher software performance can be achieved. SST supports multiple types of customizations:
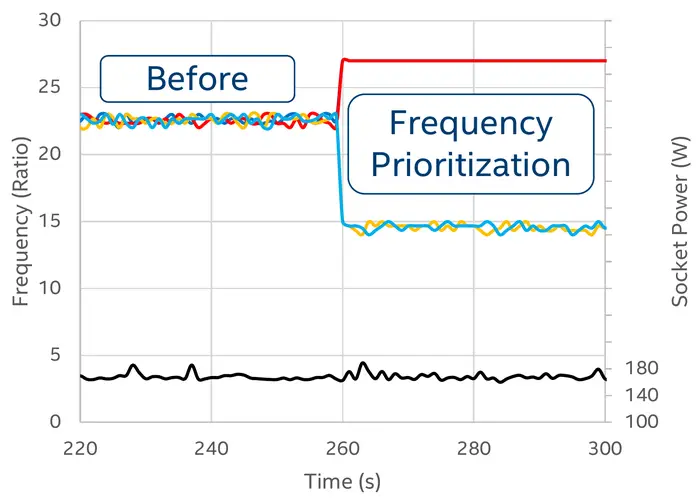
- Frequency Prioritization (SST-CP) - allows specific cores to clock higher by reducing the frequency of cores running lower-priority software.
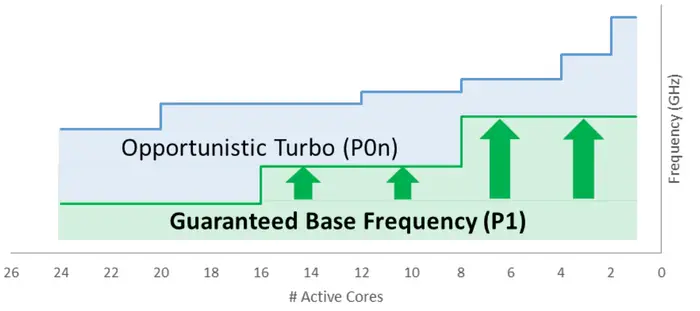
- Speed Select Base Freq (SST-BF) - allows specific cores to run higher base frequency (P1) by reducing the base frequencies (P1) of other cores.
- Speed Select Turbo Freq (SST-TF) - allows specific cores to run higher turbo frequency (P0n) by reducing the turbo frequencies of other cores.
Profiles[edit]
Processors support up to three SST Power Profiles (SST-PP) which can be used to configure the server for different kind of workloads. Profiles allow for fine tuning depending on the number of cores that require higher performance. In other words, the fewer the cores, the higher the performance for prioritized cores. And vice versa, the more cores, the lower the performance for prioritized cores. Profiles are manufactured to ensure base and turbo frequencies operate as desired within the TDP limits of the SKU.
History[edit]
Speed Select Technology was introduced with Cascade Lake.
See also[edit]
- Frequency behavior of Intel processors