-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
From WikiChip
ideal logic gate
(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
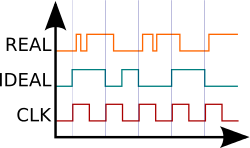
2 unrelated signals and a clock. Real signal takes some time to settle down at the correct output while the ideal signal always does so instantly.
An ideal logic gate is a logic gate performing operations on boolean values in an abstraction - dissipating no power and changing states instantaneously, similar to a step function. Such gates operate on discrete logic inputs and ignore most physical characteristics such as propegation delay, maximum fan-out, and various other electrical characteristics.
Usage[edit]
Ideal logic gates play a big role in many mathematical models and branches such as Boolean algebra and switching theory where operations are studied irrespective of the technology being used. They are also used in a wide variety of other settings since it allows a person to make key observations about a particular circuit without diving into the full specifications.