From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "ideal logic gate"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Usage == | == Usage == | ||
| − | Ideal logic gates are used in a wide variety of settings since it allows a person to make key observations about [[ideal logic circuit|a particular circuit]] without diving into the full specifications. | + | Ideal logic gates play a big role in many mathematical models and branches such as [[Boolean algebra]] and [[switching theory]] where operations are studied irrespective of the technology being used. They are also used in a wide variety of other settings since it allows a person to make key observations about [[ideal logic circuit|a particular circuit]] without diving into the full specifications. |
Latest revision as of 21:40, 20 December 2015
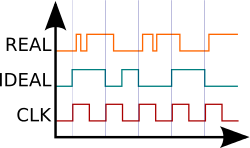
2 unrelated signals and a clock. Real signal takes some time to settle down at the correct output while the ideal signal always does so instantly.
An ideal logic gate is a logic gate performing operations on boolean values in an abstraction - dissipating no power and changing states instantaneously, similar to a step function. Such gates operate on discrete logic inputs and ignore most physical characteristics such as propegation delay, maximum fan-out, and various other electrical characteristics.
Usage[edit]
Ideal logic gates play a big role in many mathematical models and branches such as Boolean algebra and switching theory where operations are studied irrespective of the technology being used. They are also used in a wide variety of other settings since it allows a person to make key observations about a particular circuit without diving into the full specifications.