From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "deep trench capacitor"
(Blanked the page) |
(add info) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{title|Deep Trench Capacitor (DTC)}}[[File:ibm 32-nanometer deep trench capacitors.png|right|thumb|[[IBM]] [[32-nanometer]] DTCs used for [[eDRAM]].]] | ||
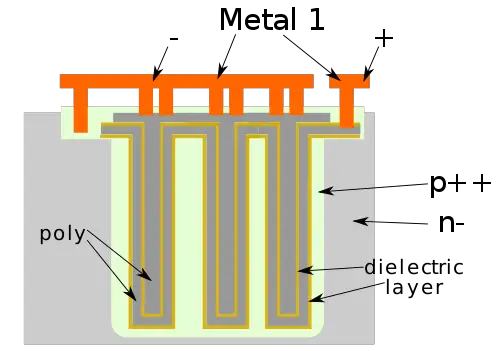
| + | A '''deep trench capacitor''' ('''DTC''') is a three-dimentional vertical capacitor formed by etching a deep trench (DT) into a silicon substrate. | ||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | * Deep trench capacitors (DTCs) are vertical semiconductor devices that are used to add capacitance to various integrated circuits. | ||
| + | :An advantage of using DTCs over package decaps is that they can be freely placed as close as possible to the desired circuit. | ||
| + | :Additionally, DTCs provide higher capacitance per unit area over other solutions such as a MIM cap. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:dtc example.svg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Uses == | ||
| + | :; Memory | ||
| + | *DTCs form the main storage capacitor for one of the main families of [[eDRAM]]-based cells called 'Embedded DRAM' which | ||
| + | :is fabricated on a standard [[CMOS]] process, allowing the mixture of memory and logic on the same integrated circuit | ||
| + | :(as opposed to generic [[eDRAM]] ICs which relies on a special [[process technology|process]] not suitable for general logic). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :; Logic | ||
| + | *DTCs are unique in many ways from other capacitors. First, they are formed by etching deep trenches (DTs) into the substrate. | ||
| + | :This enables very high capacitance density, especially when they are coupled in parallel. | ||
| + | *Secondly, because they tend to be very thin and deep, when combined with the logic above, they may be used to form | ||
| + | :very dense structures such as embedded [[DRAM]], PLL loop filters, decoupling circuitry, and other power applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :; Industry | ||
| + | : DTCs are used by a number of [[semiconductor companies]] in volume production: | ||
| + | * [[IBM]] uses DTCs for their [[eDRAM]] technology which are used to build very fast and very large L2, L3, and L4 caches. | ||
| + | * [[TSMC]] added DTCs called {{tsmc|iCAPs}} to its [[CoWoS]] packaging technology, significantly increasing the capacitance density | ||
| + | :allowing construction of higher quality power delivery networks (PDN). | ||
| + | {{expand list}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[stacked capacitor]] (SC) | ||
| + | * [[capacitor over bit]] (CoB) | ||
| + | * [[embedded DRAM]] ([[eDRAM]]) | ||
| + | * [[deep trench]] (DT) | ||
Latest revision as of 18:48, 12 December 2024
A deep trench capacitor (DTC) is a three-dimentional vertical capacitor formed by etching a deep trench (DT) into a silicon substrate.
Overview[edit]
- Deep trench capacitors (DTCs) are vertical semiconductor devices that are used to add capacitance to various integrated circuits.
- An advantage of using DTCs over package decaps is that they can be freely placed as close as possible to the desired circuit.
- Additionally, DTCs provide higher capacitance per unit area over other solutions such as a MIM cap.
Uses[edit]
- Memory
- DTCs form the main storage capacitor for one of the main families of eDRAM-based cells called 'Embedded DRAM' which
- is fabricated on a standard CMOS process, allowing the mixture of memory and logic on the same integrated circuit
- (as opposed to generic eDRAM ICs which relies on a special process not suitable for general logic).
- Logic
- DTCs are unique in many ways from other capacitors. First, they are formed by etching deep trenches (DTs) into the substrate.
- This enables very high capacitance density, especially when they are coupled in parallel.
- Secondly, because they tend to be very thin and deep, when combined with the logic above, they may be used to form
- very dense structures such as embedded DRAM, PLL loop filters, decoupling circuitry, and other power applications.
- Industry
- DTCs are used by a number of semiconductor companies in volume production:
- IBM uses DTCs for their eDRAM technology which are used to build very fast and very large L2, L3, and L4 caches.
- TSMC added DTCs called iCAPs to its CoWoS packaging technology, significantly increasing the capacitance density
- allowing construction of higher quality power delivery networks (PDN).
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
See also[edit]
- stacked capacitor (SC)
- capacitor over bit (CoB)
- embedded DRAM (eDRAM)
- deep trench (DT)