(→Certification: typo) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{intel title|Extreme Memory Profile (XMP)}} | {{intel title|Extreme Memory Profile (XMP)}} | ||
| − | '''Extreme Memory Profile''' ('''XMP''') is a specification serving as an extension to the standard JEDEC SPD specifications developed by [[Intel]]. | + | '''Extreme Memory Profile''' ('''XMP''') is a specification serving as an extension to the standard JEDEC SPD specifications developed by [[Intel]]. XMP is intended to make overclocking easier and more accessible to new users through profiles and predefined overclocking configurations that are known to be stable. |
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* Advanced Overclocking (Intermediate/Expert Users) - Allows more advanced users to change specific SPD parameters in the BIOS and save those profiles. | * Advanced Overclocking (Intermediate/Expert Users) - Allows more advanced users to change specific SPD parameters in the BIOS and save those profiles. | ||
* Fail-safe default boot - Allows the ability to restore to one of the usual default JEDEC settings after a bad settings. | * Fail-safe default boot - Allows the ability to restore to one of the usual default JEDEC settings after a bad settings. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Certification == | ||
| + | * '''XMP Ready''' - Module was programmed with an uncertain, but stable, profiles | ||
| + | * '''XMP Certified''' - Module was programmed with profiles that have passed supplier tests for the CPU and motherboard. | ||
| + | |||
| + | XMP Certified gives the best guarantees for users who are new for memory overclocking. Those modules have a number of predefined overclocking profiles that have undergone tests and are certified to work for a particular motherboard and CPU. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:intel xmp.png|1100px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:43, 29 July 2022
Extreme Memory Profile (XMP) is a specification serving as an extension to the standard JEDEC SPD specifications developed by Intel. XMP is intended to make overclocking easier and more accessible to new users through profiles and predefined overclocking configurations that are known to be stable.
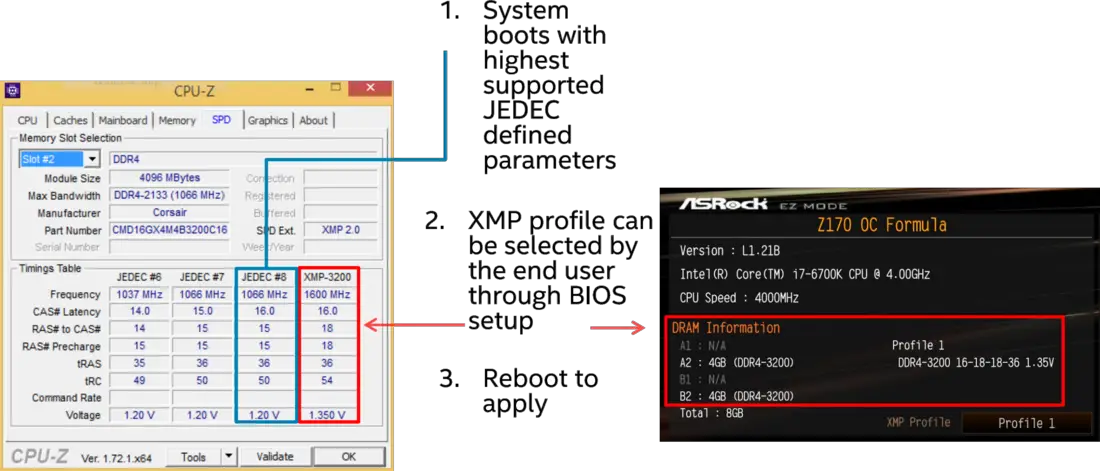
Mechanism[edit]
Memory DIMMs incorporate a serial presence detect (SPD) chip which contains information about the memory module. This chip follows a specification defined by JEDEC which includes a number of tables, including reserved entries unused. Intel's XMP standard uses the reserved entries in the SPD for its own purpose: particularly for overclocking purpose.
XMP uses the reserved portion of the SPD table for a number of additional features:
- Multiple SPD profiles - Allows for a number of different memory profiles which can be selected depending on the usage; for example for a special low-latency custom profile for gaming.
- Memory vendor specific SPD fields - This gives memory module suppliers the ability to set a number of their own profiles based on the module capabilities.
- Easy Over-clocking (Novice) - Provides users with a number of predefined overclocked profiles that have been determined to be stable. This allows users to selected those predefined profiles instead of adjusting individual parameters in BIOS.
- Advanced Overclocking (Intermediate/Expert Users) - Allows more advanced users to change specific SPD parameters in the BIOS and save those profiles.
- Fail-safe default boot - Allows the ability to restore to one of the usual default JEDEC settings after a bad settings.
Certification[edit]
- XMP Ready - Module was programmed with an uncertain, but stable, profiles
- XMP Certified - Module was programmed with profiles that have passed supplier tests for the CPU and motherboard.
XMP Certified gives the best guarantees for users who are new for memory overclocking. Those modules have a number of predefined overclocking profiles that have undergone tests and are certified to work for a particular motherboard and CPU.