From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "zhaoxin/microarchitectures/lujiazui"
(→Key changes from {{\\|WuDaoKou}}) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
=== Key changes from {{\\|WuDaoKou}} === | === Key changes from {{\\|WuDaoKou}} === | ||
* [[16 nm|16 nm FinFET]] (from [[28 nm]]) | * [[16 nm|16 nm FinFET]] (from [[28 nm]]) | ||
| + | * 1.5x performance ([[SPEC CPU2006]] Int) | ||
* Higher clock speed | * Higher clock speed | ||
* Improved memory controller | * Improved memory controller | ||
** Support for DDR4 2800 MT/s and 3200 MT/s (from 2400 MT/s) | ** Support for DDR4 2800 MT/s and 3200 MT/s (from 2400 MT/s) | ||
{{expand list}} | {{expand list}} | ||
Revision as of 17:15, 2 February 2018
| Edit Values | |
| LuJiaZui µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Zhaoxin |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | 2019 |
| Process | 16 nm |
| Core Configs | 2, 4, 8 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
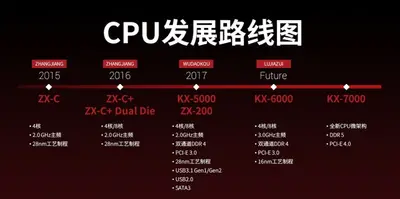
LuJiaZui is the successor to WuDaoKou, a 16 nm x86 microarchitecture designed by Zhaoxin for mainstream laptops, desktops, and servers.
Etymology
As with prior microarchitectures, LuJiaZui is named after the Lujiazui station of the Shanghai Metro. The station is located in the highly prosperous Pudong district of Shanghai.
Brands
| Family | Series | Description |
|---|---|---|
| KaiXian | KX (6000) | Desktop, Laptops |
| Kaisheng | KH (30000) | Storage, Servers |
Process Technology
Lujiazui is manufactured on TSMC's 16 nm FinFET process.
Architecture
Key changes from WuDaoKou
- 16 nm FinFET (from 28 nm)
- 1.5x performance (SPEC CPU2006 Int)
- Higher clock speed
- Improved memory controller
- Support for DDR4 2800 MT/s and 3200 MT/s (from 2400 MT/s)
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Facts about "LuJiaZui - Microarchitectures - Zhaoxin"
| codename | LuJiaZui + |
| core count | 2 +, 4 + and 8 + |
| designer | Zhaoxin + |
| first launched | 2019 + |
| full page name | zhaoxin/microarchitectures/lujiazui + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | LuJiaZui + |
| process | 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) + |