| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
* {{hcbib|30}} | * {{hcbib|30}} | ||
| + | * Rodriguez, Andres, et al. "[https://ai.intel.com/nervana/wp-content/uploads/sites/53/2018/05/Lower-Numerical-Precision-Deep-Learning-Inference-Training.pdf Lower numerical precision deep learning inference and training]." Intel White Paper (2018). | ||
[[category:x86]] | [[category:x86]] | ||
Revision as of 01:29, 7 November 2018
AVX-512 Vector Neural Network Instructions (AVX512 VNNI) is an x86 extension, part of the AVX-512, designed to accelerate convolutional neural network-based algorithms.
Overview
The AVX512 VNNI x86 extension extends AVX-512 Foundation by introducing four new instructions for accelerating inner convolutional neural network loops.
-
VPDPBUSD- Multiplies the individual bytes (8-bit) of the first source operand by the corresponding bytes (8-bit) of the second source operand, producing intermediate word (16-bit) results which are summed and accumulated in the double word (32-bit) of the destination operand.-
VPDPBUSDS- Same as above except on intermediate sum overflow which saturates to 0x7FFF_FFFF/0x8000_0000 for positive/negative numbers.
-
-
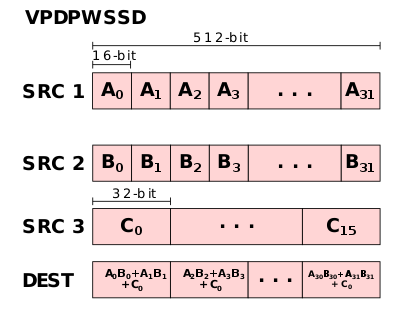
VPDPWSSD- Multiplies the individual words (16-bit) of the first source operand by the corresponding word (16-bit) of the second source operand, producing intermediate word results which are summed and accumulated in the double word (32-bit) of the destination operand.-
VPDPWSSDS- Same as above except on intermediate sum overflow which saturates to 0x7FFF_FFFF/0x8000_0000 for positive/negative numbers.
-
Motivation
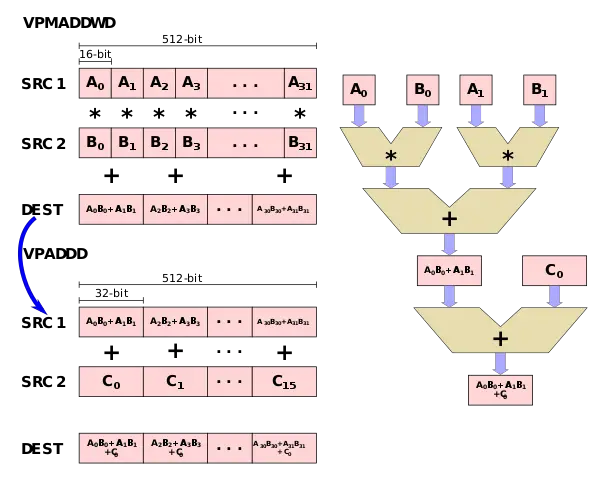
The major motivation behind the AVX512 VNNI extension is the observation that many tight convolutional neural network loops require the repeated multiplication of two 16-bit values or two 8-bit values and accumulate the result to a 32-bit accumulator. Using the foundation AVX-512, for 16-bit, this is possible using two instructions - VPMADDWD which is used to multiply two 16-bit pairs and add them together followed a VPADDD which adds the accumulate value.
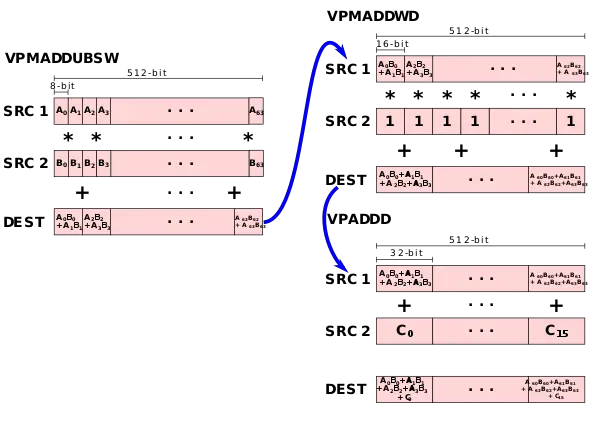
Likewise, for 8-bit values, three instructions are needed - VPMADDUBSW which is used to multiply two 8-bit pairs and add them together, followed by a VPMADDWD with the value 1 in order to simply up-convert the 16-bit values to 32-bit values, followed by the VPADDD instruction which adds the result to an accumulator.
To address those two common operations, two new instructions were added (as well as two saturated versions): VPDPBUSD fuses VPMADDUBSW, VPMADDWD, and VPADDD and VPDPWSSD fuses VPMADDWD and VPADDD.
Bibliography
- Template:hcbib
- Rodriguez, Andres, et al. "Lower numerical precision deep learning inference and training." Intel White Paper (2018).