| Edit Values | |
| ARM2 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Acorn Computers |
| Manufacturer | VLSI Technology, Sanyo |
| Introduction | 1986 |
| Process | 2 µm |
| Core Configs | 1 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Scalar, Pipelined |
| Stages | 3 |
| Decode | 1-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv2 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| L1D Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| Succession | |
ARM2 is the second ARM implementation designed by Acorn Computers as a successor to the ARM1. Introduced in 1986, the ARM2 brings a number of major improvements over its predecessor.
Contents
Overview
- See also: ARM's History
Introduced in 1986, the ARM2 is a reimplementation of the ARM1 on a smaller process along with the addition of a number of additional enhancements. The ARM2 was capable of exceeding 10 MIPS when not bottlenecked by memory with an average of around 6 MIPS. Unlike the ARM1 which was predominantly a research project, the ARM2 became the first commercially successful ARM microprocessor.
The ARM2 was designed to work as an embedded controller or a coprocessor or as a stand-alone microprocessor system. The Acorn Archimedes family of personal computers was built using the ARM2 along with a number of fully custom support chips that were also designed by Acorn Computer.
Process Technology
- See also: 2 µm process
ARM2 chips were manufactured by VLSI Technology and Sanyo on a 2 µm double-level metal CMOS process.
Architecture
Key changes from ARM1
- 2 µm process (from 3 µm)
- > 2x MIPS when not bottlenecked by memory
- 27-entry register file (from 25)
- 2 new program status registers
- Aid Fast Interrupts
- New support for coprocessors
- New support for hardware multiply and accumulate
New instructions
- See also: ARMv2
ARM2 introduces a number of new instructions to deal with the new features:
Coprocessor:
-
CDP- Coprocessor data process -
LDC- Load to coprocessor -
STC- Store from coprocessor -
MCR- Move to coprocessor -
MRC- Move from coprocessor
Arithmetics:
-
MUL- Multiplication -
MLA- Multiplication and accumulate
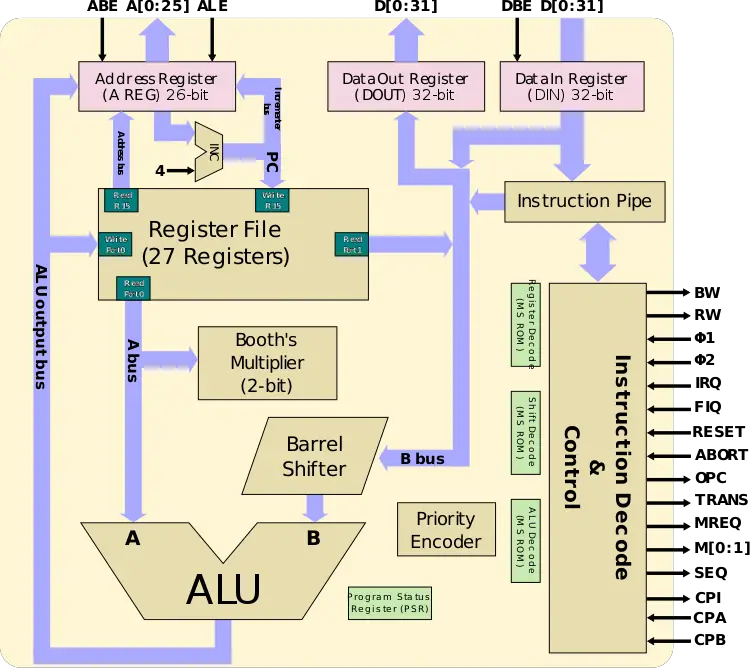
Block Diagram
Core
Core
Pipeline
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Die
- 2 µm process
- 27,000 transistors
- 5.842 mm x 5.842 mm (230 mils x 230 mils)
- 34.13 mm² die size
All ARM2 Chips
| List of ARM2-based Processors | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Process | Launched | Frequency | Power Dissipation | Max Memory | |||||||
| VL2333 | ARM2 | 1986 | 8 MHz 0.008 GHz 8,000 kHz | 1 W 1,000 mW 0.00134 hp 0.001 kW | 64 MiB 65,536 KiB 67,108,864 B 0.0625 GiB 6.103516e-5 TiB | |||||||
| VL86C010 | ARM2 | 1987 | 10 MHz 0.01 GHz , 12 MHz10,000 kHz 0.012 GHz 12,000 kHz | 2 W 2,000 mW 0.00268 hp 0.002 kW | 64 MiB 65,536 KiB 67,108,864 B 0.0625 GiB 6.103516e-5 TiB | |||||||
| Count: 2 | ||||||||||||
References
- Furber, S. B., and A. R. Wilson. "The Acorn RISC Machine ߞ an architectural view." Electronics and Power 33.6 (1987): 402-405.
| codename | ARM2 + |
| core count | 1 + |
| designer | Acorn Computers + |
| first launched | 1986 + |
| full page name | acorn/microarchitectures/arm2 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv2 + |
| manufacturer | VLSI Technology + and Sanyo + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM2 + |
| pipeline stages | 3 + |
| process | 2,000 nm (2 μm, 0.002 mm) + |