From WikiChip
K6 - Microarchitectures - AMD
| Edit Values | |
| K6 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | AMD, NexGen |
| Manufacturer | AMD |
| Introduction | April 2, 1997 |
| Phase-out | 2000 |
| Process | 350 nm, 250 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-32 |
| Succession | |
K6 was the microarchitecture for AMD's K6 line of microprocessors as a successor to the K5. Contrary to its namesake, K6 design is entirely NexGen's and not based on K5. Launched in early 1997, the K6 microarchitecture provided the superior performance AMD needed to become a viable competitor to Intel (performance K5 failed to deliver).
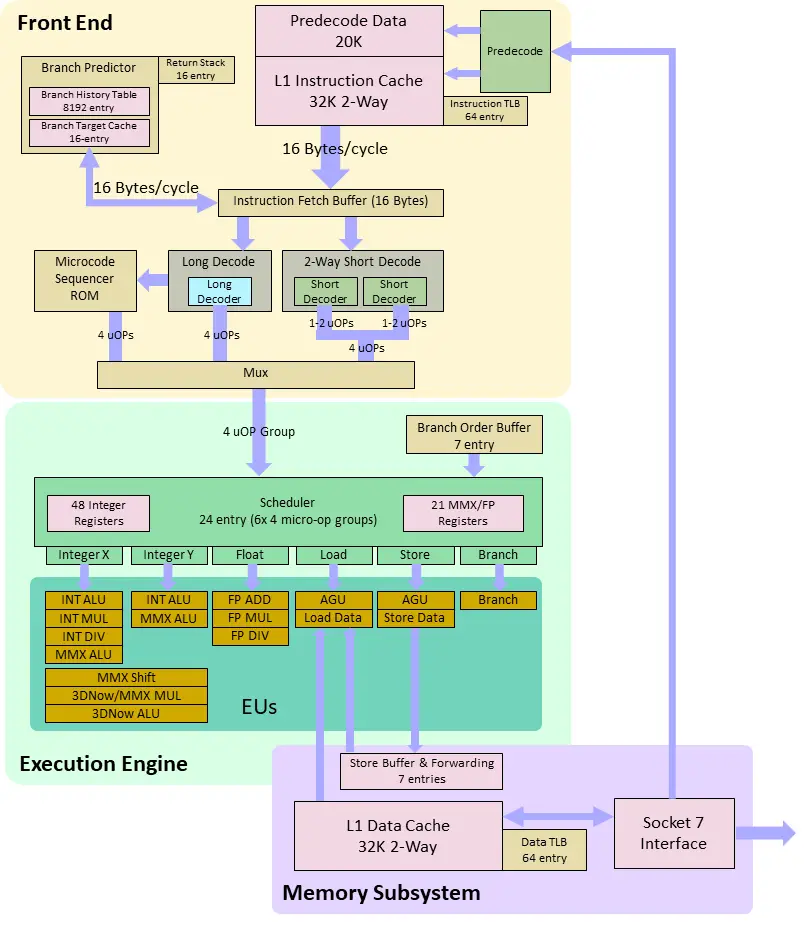
Architecture[edit]
- 6-7 stage integer pipeline
- Fetch
- Decode
- Micro-op issue
- Operand Fetch
- Execute 1
- Optional Execute 2
- Commit
- Branch Predictor
- 2-level predictor with 8192 entry branch history table
- Does not store target addresses. Target addresses are calculated during instruction decode
- 16-entry branch target cache
- Caches 16 bytes of instructions at the branch target, and supplies that directly
to the decoders to avoid a 1-cycle penalty
- Caches 16 bytes of instructions at the branch target, and supplies that directly
- 16-entry return address stack
- 2-level predictor with 8192 entry branch history table
- 32K 2-way L1 Instruction Cache
- Also holds 20K of predecode data. Instructions are predecoded as L1 instruction cache is filled
- 64 entry TLB
- Fetch and Decode
- 16 instruction bytes fetched per cycle, either from L1 instruction cache or branch target cache
- Decoders can handle the following combinations per clock:
- Short decode: Two x86 instructions that generate up to two micro-ops each
- Vector decode: One x86 instruction that generates up to four micro-ops
- Complex instructions handled by microcode
- Out of order execution resources
- Scheduler holds 6 groups of 4 micro-ops, or up to 12 x64 instructions
- Receives a group of 4 micro-ops from decoders every cycle. If fewer than 4 micro-ops are
generated from the decoders, empty slots are padded with NOPs - Retires one 4-micro-op group every cycle
- Receives a group of 4 micro-ops from decoders every cycle. If fewer than 4 micro-ops are
- 48 integer registers: 8 architectural, 16 scratch, 24 rename
- 21 MMX registers: 8 architectural, 1 scratch, 12 rename
- Up to 7 outstanding branches
- 7 entry store queue
- Scheduler holds 6 groups of 4 micro-ops, or up to 12 x64 instructions
- Issues up to 6 micro-ops per cycle. Ports:
- Integer X: All ALU ops, including multiplies and divides
- Integer Y: Basic ALU ops
- Both integer pipelines can handle MMX/3DNow instructions, but share MMX/3DNow multiplier
and MMX shifter functional units. - If the two pipelines try to issue operations to a shared functional unit, one operation will stall.
- Both integer pipelines can handle MMX/3DNow instructions, but share MMX/3DNow multiplier
- Floating point
- Load
- Store
- Branch
- 32K 2-way L1 Data Cache
- Dual ported, write back
- 128 entry TLB
- Load unit has 2-cycle latency
K5/K6 Family[edit]
| Architecture | Process (nm) |
Family | Release date |
Code name | Model group | Cores | Clock rate (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K5 | 500 nm 350 nm |
AMD K5 | 1996 | SSA/5, 5k86 | 1 | 75–133 | |
| K6 | 350 nm 250 nm |
AMD K6 | 1997 1998 |
6k86 (NX686) Little Foot |
AMD-K6-166 ÷ 233 AMD-K6/233 ÷ 300 |
1 | 166–300 |
| 250 nm 180 nm |
AMD K6-2(+) | 1999 | Chomper (Extended, Mobile) |
K6-2 (Chompers/CXT) K6-2-P (Mobile K6-2) |
166–550 | ||
| AMD K6-III(+) | 2001 | Sharptooth | K6-III (Sharptooth) K6-III-P |
400–550 |
All K6 Chips[edit]
| K6 Chips | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Core | Process | Freq | Max Mem | TDP (Power Dissipation) | Launched |
| AMD-K6-166ALR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 166.66 MHz 0.167 GHz 166,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 17.2 W 17,200 mW 0.0231 hp 0.0172 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-166ALYD | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 166.66 MHz 0.167 GHz 166,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 17.2 W 17,200 mW 0.0231 hp 0.0172 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-200AFR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 199.99 MHz 0.2 GHz 199,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 20 W 20,000 mW 0.0268 hp 0.02 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-200ALR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 199.99 MHz 0.2 GHz 199,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 20 W 20,000 mW 0.0268 hp 0.02 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-200ALYD | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 199.99 MHz 0.2 GHz 199,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 20 W 20,000 mW 0.0268 hp 0.02 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-233AFR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 28.3 W 28,300 mW 0.038 hp 0.0283 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-233ANR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 28.3 W 28,300 mW 0.038 hp 0.0283 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6-233APR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 28.3 W 28,300 mW 0.038 hp 0.0283 kW | May 1997 |
| AMD-K6/233ACZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9 W 9,000 mW 0.0121 hp 0.009 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/233ADZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9 W 9,000 mW 0.0121 hp 0.009 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/233BCZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 233.33 MHz 0.233 GHz 233,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9 W 9,000 mW 0.0121 hp 0.009 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/266ACZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 266.66 MHz 0.267 GHz 266,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9.8 W 9,800 mW 0.0131 hp 0.0098 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/266ADZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 266.66 MHz 0.267 GHz 266,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9.8 W 9,800 mW 0.0131 hp 0.0098 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/266AFR | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 266.66 MHz 0.267 GHz 266,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 14.5 W 14,500 mW 0.0194 hp 0.0145 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/266BCZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 266.66 MHz 0.267 GHz 266,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 9.8 W 9,800 mW 0.0131 hp 0.0098 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/300ADZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 299.99 MHz 0.3 GHz 299,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 11 W 11,000 mW 0.0148 hp 0.011 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/300AFR | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 299.99 MHz 0.3 GHz 299,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 15.4 W 15,400 mW 0.0207 hp 0.0154 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/300BDZ | Little Foot | 250 nm 0.25 μm 2.5e-4 mm | 299.99 MHz 0.3 GHz 299,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 11 W 11,000 mW 0.0148 hp 0.011 kW | 5 March 1998 |
| AMD-K6/PR2-166ALR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 166.66 MHz 0.167 GHz 166,660 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 17.2 W 17,200 mW 0.0231 hp 0.0172 kW | 2 April 1997 |
| AMD-K6/PR2-200ALR | 6k86 | 350 nm 0.35 μm 3.5e-4 mm | 199.99 MHz 0.2 GHz 199,990 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 20 W 20,000 mW 0.0268 hp 0.02 kW | 2 April 1997 |
| Count: 20 | ||||||
Block Diagram[edit]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- AMD K6-2 Data Sheet: AMD K6-2 Desktop Datasheet
- AMD K6 Code Optimization: AMD K6 Code Optimization
Facts about "K6 - Microarchitectures - AMD"
| codename | K6 + |
| designer | AMD + and NexGen + |
| first launched | April 2, 1997 + |
| full page name | amd/microarchitectures/k6 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-32 + |
| manufacturer | AMD + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | K6 + |
| phase-out | 2000 + |
| process | 350 nm (0.35 μm, 3.5e-4 mm) + and 250 nm (0.25 μm, 2.5e-4 mm) + |